A.G.B.U. Manoogian-Demirdjian School—One Week Schedule
... changed Earth over changed Earth over its long history; and its long history; and describe evidence describe evidence from Earth today of from Earth today of moving plates and moving plates and sea floor spreading. sea floor spreading. ...
... changed Earth over changed Earth over its long history; and its long history; and describe evidence describe evidence from Earth today of from Earth today of moving plates and moving plates and sea floor spreading. sea floor spreading. ...
Caledonian Structures of the Southern Uplands
... and igneous activity took place at, or near, the margins of an ocean (the Iapetus) that separated the Laurentian and Gondwanaland plates, over a period from the Precambrian through the early Palaeozoic. From studies of fauna, sedimentary history, igneous activity, structural and metamorphic evolutio ...
... and igneous activity took place at, or near, the margins of an ocean (the Iapetus) that separated the Laurentian and Gondwanaland plates, over a period from the Precambrian through the early Palaeozoic. From studies of fauna, sedimentary history, igneous activity, structural and metamorphic evolutio ...
Plate Tectonics Activity on Dynamic Earth
... -Watch the video, look at “Plate Tectonics 101” for more information 1. When did the supercontinent begin to separate? 2. What is a tectonic plate? What percentage of Earth’s radius do they make up? 3. Why do plates move? (two part answer) 4. Do all plates move at the same speed? How fast and in whi ...
... -Watch the video, look at “Plate Tectonics 101” for more information 1. When did the supercontinent begin to separate? 2. What is a tectonic plate? What percentage of Earth’s radius do they make up? 3. Why do plates move? (two part answer) 4. Do all plates move at the same speed? How fast and in whi ...
Erupting volcano - Mrs. Feigenbaum`s Science Classes
... • Side vent – vent that runs outward from main vent • Magma Chamber -reservoir of magma in the earth's crust where the magma may reside temporarily on its way from the upper mantle to the earth's surface ...
... • Side vent – vent that runs outward from main vent • Magma Chamber -reservoir of magma in the earth's crust where the magma may reside temporarily on its way from the upper mantle to the earth's surface ...
Geology 101 chapter2 Plate tectonics
... deformed sedimentary rocks igneous intrusions metamorphic rocks fragments of oceanic crust ...
... deformed sedimentary rocks igneous intrusions metamorphic rocks fragments of oceanic crust ...
Plates
... coast of South America of the same plants and the same reptiles. Plant is called Glossopteris; Reptile is called Lystrosauris. He also found the same type of rock on the two coasts. ...
... coast of South America of the same plants and the same reptiles. Plant is called Glossopteris; Reptile is called Lystrosauris. He also found the same type of rock on the two coasts. ...
WGCh2Notetaking
... a. The ____________________________________ is an area of high volcanic and earthquake activity along the Pacific Rim. Volcanic Eruptions 1. Volcanoes are mountains formed by lava or by _________________________ that breaks through the Earth’s crust. a. Volcanoes often form plate boundaries where on ...
... a. The ____________________________________ is an area of high volcanic and earthquake activity along the Pacific Rim. Volcanic Eruptions 1. Volcanoes are mountains formed by lava or by _________________________ that breaks through the Earth’s crust. a. Volcanoes often form plate boundaries where on ...
Quiz 1
... Africa, Madagascar, Arabia, India, Antarctica and Australia was one of the major pieces of evidence for the theory of continental drift. 33. Describe the Plate Tectonic model. Plate tectonics model describes the large scale motions of Earth's lithosphere. The theory encompasses the concepts of conti ...
... Africa, Madagascar, Arabia, India, Antarctica and Australia was one of the major pieces of evidence for the theory of continental drift. 33. Describe the Plate Tectonic model. Plate tectonics model describes the large scale motions of Earth's lithosphere. The theory encompasses the concepts of conti ...
Chapter 12 Whole Notes
... When compression causes the hanging wall to move upward relative to the footwall, a reverse fault forms. A thrust fault is a special type of reverse fault in which the fault plane is at a low angle or is nearly horizontal. Reverse faults & thrust faults are common in convergent boundaries and respon ...
... When compression causes the hanging wall to move upward relative to the footwall, a reverse fault forms. A thrust fault is a special type of reverse fault in which the fault plane is at a low angle or is nearly horizontal. Reverse faults & thrust faults are common in convergent boundaries and respon ...
File
... Crust, mantle, and core differ from each other in chemical composition. It's understandable that scientists know the most about the crust, and less about deeper layers. Earth’s crust is a thin, brittle outer shell. The crust is made of rock. This layer is thinner under the oceans and much thicker in ...
... Crust, mantle, and core differ from each other in chemical composition. It's understandable that scientists know the most about the crust, and less about deeper layers. Earth’s crust is a thin, brittle outer shell. The crust is made of rock. This layer is thinner under the oceans and much thicker in ...
Year 10 exams: tectonics revision
... Do earthquakes and volcanoes appear all over the earth’s surface or only in certain places? Is there a recognisable pattern to where earthquakes seem to occur? Which areas of the earth seem to be at the highest risk from earthquakes? ...
... Do earthquakes and volcanoes appear all over the earth’s surface or only in certain places? Is there a recognisable pattern to where earthquakes seem to occur? Which areas of the earth seem to be at the highest risk from earthquakes? ...
Plate Tectonics, Volcano and Earthquake Webquest
... plates, and there is massive _________________on the fault lines. This intense pressure resulting from energy build up causes the fault lines give way, and plates move over, against or apart from each other. iv. There is an __________________ at this point. In the form of _____________________ (like ...
... plates, and there is massive _________________on the fault lines. This intense pressure resulting from energy build up causes the fault lines give way, and plates move over, against or apart from each other. iv. There is an __________________ at this point. In the form of _____________________ (like ...
The Layers of the Earth
... Basalt is much denser than the granite. Because of this the less dense continents ride on the denser oceanic plates. ...
... Basalt is much denser than the granite. Because of this the less dense continents ride on the denser oceanic plates. ...
Plate tectonics ws File
... However, he couldn’t suggest a plausible mechanism as to how the continents could move around, hence his theory was not accepted by many scientists. His theory was finally accepted in 1960! Only recently have plate tectonics and continental drift become accepted as geology’s ‘big idea’ that explains ...
... However, he couldn’t suggest a plausible mechanism as to how the continents could move around, hence his theory was not accepted by many scientists. His theory was finally accepted in 1960! Only recently have plate tectonics and continental drift become accepted as geology’s ‘big idea’ that explains ...
A Model of Three Faults
... is frequently associated with specific types of plate movement. Normal Faults are often associated with divergent boundaries. Thrust faults are often associated with convergent boundaries. Strike-slip faults are often associated with transform boundaries. Problem: How are fault types related t ...
... is frequently associated with specific types of plate movement. Normal Faults are often associated with divergent boundaries. Thrust faults are often associated with convergent boundaries. Strike-slip faults are often associated with transform boundaries. Problem: How are fault types related t ...
Izalco volcano, El Salvador
... connecting a magma chamber to the surface. • Form because of erosion of cinder cones. • A neck is what is left over. • Best known pipes are the diamond bearing pipes of S. Africa Diamonds are formed in the Earth's mantle, ...
... connecting a magma chamber to the surface. • Form because of erosion of cinder cones. • A neck is what is left over. • Best known pipes are the diamond bearing pipes of S. Africa Diamonds are formed in the Earth's mantle, ...
Xtra_credit_MC_chapt_5_2014.txt Xtra_credit_MC_chapt_5_2014.txt
... 3. Regions of subduction are characterized by: a) earthquakes b) volcanoes c) trenches d) all the above e) a) and b) 4. Which mountain range was formed due to the subduction of the Nazca Plate a) The Rocky Mountains b) the Himalayas c) The Appalachians d) the Andes ...
... 3. Regions of subduction are characterized by: a) earthquakes b) volcanoes c) trenches d) all the above e) a) and b) 4. Which mountain range was formed due to the subduction of the Nazca Plate a) The Rocky Mountains b) the Himalayas c) The Appalachians d) the Andes ...
Earthquakes - Boone County Schools
... earthquake killed over 3,000 people and caused $524 million in property loss. The damage in San Francisco alone was over $20 million. Due to broken pipelines, water was shut off to the entire city. Many fires soon broke out throughout the city and caused major devastation as there was no water to pu ...
... earthquake killed over 3,000 people and caused $524 million in property loss. The damage in San Francisco alone was over $20 million. Due to broken pipelines, water was shut off to the entire city. Many fires soon broke out throughout the city and caused major devastation as there was no water to pu ...
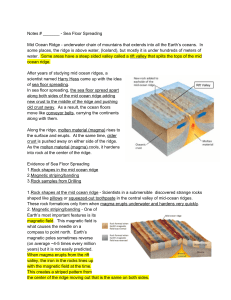
Notes # ______ Sea Floor Spreading Mid Ocean Ridge underwater
... in the central valley of midocean ridges. These rock formations only form when magma erupts underwater and hardens very quickly ...
... in the central valley of midocean ridges. These rock formations only form when magma erupts underwater and hardens very quickly ...
File
... a) ____-____: found on the seafloor where they form __________ ____________. It is in this rift where seafloor spreading begins. The formation of new ocean crust at most boundaries accounts for the high heat flow, __________________ and __________________ associated with these boundaries. Example: _ ...
... a) ____-____: found on the seafloor where they form __________ ____________. It is in this rift where seafloor spreading begins. The formation of new ocean crust at most boundaries accounts for the high heat flow, __________________ and __________________ associated with these boundaries. Example: _ ...
Plate Tectonics
... The continents are embedded in lithospheric plates. As these plates move, they carry the continents with them. The ocean basins are part of lithospheric plates as well. ...
... The continents are embedded in lithospheric plates. As these plates move, they carry the continents with them. The ocean basins are part of lithospheric plates as well. ...
magma
... Rocks partially melt at different levels within the Earth’s crust and mantle to form magma. Most magma never reaches the surface and cools at depth forming (1) intrusive or plutonic rocks, that are later uplifted and exposed by erosion. Magma that reaches the surface is erupted as lava, and ...
... Rocks partially melt at different levels within the Earth’s crust and mantle to form magma. Most magma never reaches the surface and cools at depth forming (1) intrusive or plutonic rocks, that are later uplifted and exposed by erosion. Magma that reaches the surface is erupted as lava, and ...
Geology

Geology (from the Greek γῆ, gē, i.e. ""earth"" and -λoγία, -logia, i.e. ""study of, discourse"") is an earth science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change. Geology can also refer generally to the study of the solid features of any celestial body (such as the geology of the Moon or Mars).Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates. Geology is important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation, evaluating water resources, understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline.