Directed Reading A
... c. magma zone. b. tectonic boundary. d. tectonic ridge. ______ 3. Which of the following is NOT a type of tectonic plate boundary? a. convergent boundary c. divergent boundary b. fault-block boundary d. transform boundary ______ 4. The three ways that tectonic plates can move relative to each other ...
... c. magma zone. b. tectonic boundary. d. tectonic ridge. ______ 3. Which of the following is NOT a type of tectonic plate boundary? a. convergent boundary c. divergent boundary b. fault-block boundary d. transform boundary ______ 4. The three ways that tectonic plates can move relative to each other ...
1 MAY 2011 Oceanogra phy Ch 2 Plate Tectonics and the Ocean
... Earthquakes associated with Convergence. Largest and deepest, up to 670 km deep. Transform Boundary Features. The offset on Mid-Ocean ridges result from Transform faults. Oceanic – Continental crust transform faults. P.59. Earthquakes associated with transform boundaries. These are shallow but often ...
... Earthquakes associated with Convergence. Largest and deepest, up to 670 km deep. Transform Boundary Features. The offset on Mid-Ocean ridges result from Transform faults. Oceanic – Continental crust transform faults. P.59. Earthquakes associated with transform boundaries. These are shallow but often ...
Earth Science Chapter 9 Section 4 Review
... a. iron-rich rocks show the location of the magnetic poles at the time of their formation b. all rocks, regardless of when they are formed, have the same polarity c. all rocks have a reversed polarity d. rocks do not possess magnetic properties ...
... a. iron-rich rocks show the location of the magnetic poles at the time of their formation b. all rocks, regardless of when they are formed, have the same polarity c. all rocks have a reversed polarity d. rocks do not possess magnetic properties ...
Earth Science – Quiz 2
... B) divergent C) convergent D) all plate boundaries 15. Linear, magnetic patterns associated with mid-ocean ridges are configured as ________. A) concentric circles about a rising plume of hot mantle rocks and magma B) reversed magnetizations along the rift valleys and normal magnetizations along the ...
... B) divergent C) convergent D) all plate boundaries 15. Linear, magnetic patterns associated with mid-ocean ridges are configured as ________. A) concentric circles about a rising plume of hot mantle rocks and magma B) reversed magnetizations along the rift valleys and normal magnetizations along the ...
GLG101online_05A_IgneousProcesses_MCC_Leighty
... you won’t be responsible for knowing everything contained in them. As a distance learning student, you need to explore and understand the content more independently than in a traditional class. As always, I will help guide you through this learning adventure. Remember, email Dr. Bob if you have any ...
... you won’t be responsible for knowing everything contained in them. As a distance learning student, you need to explore and understand the content more independently than in a traditional class. As always, I will help guide you through this learning adventure. Remember, email Dr. Bob if you have any ...
Table of Contents - Mr. Tobin`s Earth Science Class
... Oceanic Rocks only 180 million years old. Continental Rocks can be up to 3.8 billion years old. Layer of sediment on oceanic crust is only a few hundred meters thick. Layer of sediment on continental crust is 20 kilometers thick. ...
... Oceanic Rocks only 180 million years old. Continental Rocks can be up to 3.8 billion years old. Layer of sediment on oceanic crust is only a few hundred meters thick. Layer of sediment on continental crust is 20 kilometers thick. ...
Seafloor Spreading - Paramus Public Schools
... fills gap in ridge 2. When hardens adds new ocean floor 3. As spreading occurs, more magma is forced upward and the crust moves away from ridge 4. Crust is destroyed by subduction at trenches ...
... fills gap in ridge 2. When hardens adds new ocean floor 3. As spreading occurs, more magma is forced upward and the crust moves away from ridge 4. Crust is destroyed by subduction at trenches ...
plates
... moving away from each other Transform ► ____________boundary between tectonic plates that are sliding past each other horizontally ...
... moving away from each other Transform ► ____________boundary between tectonic plates that are sliding past each other horizontally ...
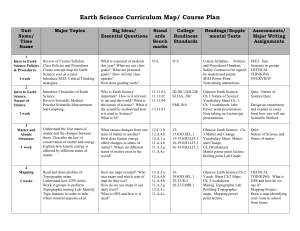
Earth Science Curriculum Map 11-12
... Locate the Ring of Fire and which plate it is situated around. Distinguish the three types of faults and how stress and strain apply to these fault types. ...
... Locate the Ring of Fire and which plate it is situated around. Distinguish the three types of faults and how stress and strain apply to these fault types. ...
Chapter 2 PPT
... –Tension – pulls on the crust, stretching rock so that it becomes thinner in the middle like warm bubble gum ...
... –Tension – pulls on the crust, stretching rock so that it becomes thinner in the middle like warm bubble gum ...
Document
... This type of boundary occurs when two plates slide past each other, this is occurring in California with the Juan de Fuca plate and the North American plate. a) transform b) convergent c) subduction d) divergent ...
... This type of boundary occurs when two plates slide past each other, this is occurring in California with the Juan de Fuca plate and the North American plate. a) transform b) convergent c) subduction d) divergent ...
geologic highlights of southeastern arizona and vicinity
... crust. Thick deposits of limestone, mudstone (shale) and sandstone form in these marine and tidal/beach environments. Paleozoic marine sedimentary rocks from this time are now exposed throughout Arizona, notably in the Grand Canyon and Whetstone Mountains. The first abundant fossils of marine life w ...
... crust. Thick deposits of limestone, mudstone (shale) and sandstone form in these marine and tidal/beach environments. Paleozoic marine sedimentary rocks from this time are now exposed throughout Arizona, notably in the Grand Canyon and Whetstone Mountains. The first abundant fossils of marine life w ...
Weathering and Erosion
... deposited at the mouth, and new land is formed. The new, soil-rich land is known as a Delta ...
... deposited at the mouth, and new land is formed. The new, soil-rich land is known as a Delta ...
Chapter Three: The Dynamic Earth
... Plates: a block of the lithosphere that consists of the crust and the rigid, outermost part of the mantle Continents move on these plates Plate Boundaries is where mountain building occurs ...
... Plates: a block of the lithosphere that consists of the crust and the rigid, outermost part of the mantle Continents move on these plates Plate Boundaries is where mountain building occurs ...
Earthquakes - NewPath Learning
... Earthquakes are measured by machines called seismographs. The different seismic waves are measured and recorded on a paper or drum (or as a computerized image) called a seismogram. The first up tick on a seismogram records the arrival of the P-waves. The next significant up tick is the arrival of th ...
... Earthquakes are measured by machines called seismographs. The different seismic waves are measured and recorded on a paper or drum (or as a computerized image) called a seismogram. The first up tick on a seismogram records the arrival of the P-waves. The next significant up tick is the arrival of th ...
Plate Tectonics Section 1 Wegener`s Hypothesis continental drift
... 1. The sediment that covers the sea floor is thinner closer to a ridge than it is farther from the ridge 2. The ocean floor is very young. While rocks on land are as much as 4 billion years old, none of the oceanic rocks are more than 200 million years old. ...
... 1. The sediment that covers the sea floor is thinner closer to a ridge than it is farther from the ridge 2. The ocean floor is very young. While rocks on land are as much as 4 billion years old, none of the oceanic rocks are more than 200 million years old. ...
GLS100 LAB: PLATE TECTONICS Discovering Plate Boundaries
... You will each have a blank map of the Earth with the names of the major plates labeled. However, the plates themselves are not outlined. With a pencil lightly dash the boundaries on the map. Then as a group discuss your hypotheses and create a group map with boundaries clearly drawn in pencil. Corre ...
... You will each have a blank map of the Earth with the names of the major plates labeled. However, the plates themselves are not outlined. With a pencil lightly dash the boundaries on the map. Then as a group discuss your hypotheses and create a group map with boundaries clearly drawn in pencil. Corre ...
The Biogeochemical Carbon Cycle
... The Residence time of a molecule is the average amount of time it is expected to remain in a given reservoir. ...
... The Residence time of a molecule is the average amount of time it is expected to remain in a given reservoir. ...
The Earth`s Layers Foldable
... 3. Now you may cut out the layers! Also cut out the four squares and the 12 labels. Remember to cut out The Earth's Layers title. 4. Set one piece of blue paper in front of you. Closely trim the title. Paste The Earth's Layers title in the top left corner of the paper. 5. Paste the Crust right below ...
... 3. Now you may cut out the layers! Also cut out the four squares and the 12 labels. Remember to cut out The Earth's Layers title. 4. Set one piece of blue paper in front of you. Closely trim the title. Paste The Earth's Layers title in the top left corner of the paper. 5. Paste the Crust right below ...
Plate Tectonics - Johnston County Schools
... convergent boundary consist of continental (buoyant) material. Modern example: Himalayas ...
... convergent boundary consist of continental (buoyant) material. Modern example: Himalayas ...
Answer Key - Learn Earth Science
... the continents were once a supercontintent called Pangea, the continents are plowing through the ocean crust---most people didn’t believe ...
... the continents were once a supercontintent called Pangea, the continents are plowing through the ocean crust---most people didn’t believe ...
Plate Tectonics - Coventry Local Schools
... c. magma zone. b. tectonic boundary. d. tectonic ridge. ______ 3. Which of the following is NOT a type of tectonic plate boundary? a. convergent boundary c. divergent boundary b. fault-block boundary d. transform boundary ______ 4. The three ways that tectonic plates can move relative to each other ...
... c. magma zone. b. tectonic boundary. d. tectonic ridge. ______ 3. Which of the following is NOT a type of tectonic plate boundary? a. convergent boundary c. divergent boundary b. fault-block boundary d. transform boundary ______ 4. The three ways that tectonic plates can move relative to each other ...
Size Matters, The Royal Institution Christmas Lectures 2010
... 4. Glue your continents below to show how the modern continents might have been arranged many millions of years ago. ...
... 4. Glue your continents below to show how the modern continents might have been arranged many millions of years ago. ...
landforms created and changed?
... the continents and the ocean floors. As you can see in Figure 1.10, where the plates of the lithosphere pull apart from each other, magma erupts through the Earth’s surface as lava (Figure 1.9), creating volcanic mountains. Where the plates collide or rub together, they create mountains and sometime ...
... the continents and the ocean floors. As you can see in Figure 1.10, where the plates of the lithosphere pull apart from each other, magma erupts through the Earth’s surface as lava (Figure 1.9), creating volcanic mountains. Where the plates collide or rub together, they create mountains and sometime ...
Geology

Geology (from the Greek γῆ, gē, i.e. ""earth"" and -λoγία, -logia, i.e. ""study of, discourse"") is an earth science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change. Geology can also refer generally to the study of the solid features of any celestial body (such as the geology of the Moon or Mars).Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates. Geology is important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation, evaluating water resources, understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline.