How Do Earthquakes Tell Us About the Earth`s Interior?
... • Plates with continental edges override ocean edges because they are less dense – Again, the ocean crust melts as it subducts, giving water to the asthenosphere which also melts – Coastal trench, huge earthquakes/volcanoes on land – Melting along continent edges richer in silica (Si) which makes th ...
... • Plates with continental edges override ocean edges because they are less dense – Again, the ocean crust melts as it subducts, giving water to the asthenosphere which also melts – Coastal trench, huge earthquakes/volcanoes on land – Melting along continent edges richer in silica (Si) which makes th ...
Basin Analysis - Louisiana State University
... classification scheme should not just create "order from the chaos", but highlight patterns that are useful for predicting stratigraphy, and faulting. Dickinson's (1974) classification scheme is based on tectonic history: (a) lithospheric substratum: oceanic versus continental (b) proximity of the b ...
... classification scheme should not just create "order from the chaos", but highlight patterns that are useful for predicting stratigraphy, and faulting. Dickinson's (1974) classification scheme is based on tectonic history: (a) lithospheric substratum: oceanic versus continental (b) proximity of the b ...
VOLCANOES AND OTHER IGNEOUS FEATURES
... • Plutonic-Intrusive igneous rocks can cool and solidify into large rock bodies: “plutons” – Plutons form in all sizes – several square meters to thousands of square meters – Smaller plutons are called stocks – The largest plutons are called batholiths ...
... • Plutonic-Intrusive igneous rocks can cool and solidify into large rock bodies: “plutons” – Plutons form in all sizes – several square meters to thousands of square meters – Smaller plutons are called stocks – The largest plutons are called batholiths ...
the Exciting World of Earthquakes Part I
... Where Earthquakes Occur The Earth is formed of several layers that have very different physical and chemical properties. The outer layer, which averages about 70 kilometers in thickness, consists of about a dozen large, irregularly shaped plates that slide over, under and past each other on top of t ...
... Where Earthquakes Occur The Earth is formed of several layers that have very different physical and chemical properties. The outer layer, which averages about 70 kilometers in thickness, consists of about a dozen large, irregularly shaped plates that slide over, under and past each other on top of t ...
Tectonics review
... that makes this proposal exciting. I do not know the two field areas proposed from personal experience. However, my knowledge of other exposures of (upper) mantle suggests that whilst some lithologies are indeed relatively simple, others are much more complex. For example, similar metre-scale, and l ...
... that makes this proposal exciting. I do not know the two field areas proposed from personal experience. However, my knowledge of other exposures of (upper) mantle suggests that whilst some lithologies are indeed relatively simple, others are much more complex. For example, similar metre-scale, and l ...
Earth as a System Section 1 Earth`s Interior, continued
... • The three compositional zones of Earth’s interior are divided into five structural zones. • lithosphere the solid, outer layer of Earth that consists of the crust and the rigid upper part of the mantle ...
... • The three compositional zones of Earth’s interior are divided into five structural zones. • lithosphere the solid, outer layer of Earth that consists of the crust and the rigid upper part of the mantle ...
4. Where Volcanoes are Found PPT
... 3b - Students know the principal structures that form at the three different kinds of plate boundaries. 3c - Students know the explanation for the location and properties of volcanoes that are due to hot spots and the explanation for those that are due to subduction. ...
... 3b - Students know the principal structures that form at the three different kinds of plate boundaries. 3c - Students know the explanation for the location and properties of volcanoes that are due to hot spots and the explanation for those that are due to subduction. ...
Where are Volcanoes Found?
... 3b - Students know the principal structures that form at the three different kinds of plate boundaries. 3c - Students know the explanation for the location and properties of volcanoes that are due to hot spots and the explanation for those that are due to subduction. ...
... 3b - Students know the principal structures that form at the three different kinds of plate boundaries. 3c - Students know the explanation for the location and properties of volcanoes that are due to hot spots and the explanation for those that are due to subduction. ...
Geography and Society – First Discussions
... o Explain how data collected on the magnetism, depth, and the age of oceanic crust support the Theory of Plate Tectonics. o Explain how the distribution of earthquakes, volcanoes, and the Hawaiian Island chain relate to plate tectonics. o Identify at least 2 characteristics that allow us to differen ...
... o Explain how data collected on the magnetism, depth, and the age of oceanic crust support the Theory of Plate Tectonics. o Explain how the distribution of earthquakes, volcanoes, and the Hawaiian Island chain relate to plate tectonics. o Identify at least 2 characteristics that allow us to differen ...
WELIM Solar Energy
... and have cooled since formation at a midocean ridge. Further, the sediments they carry contain minerals that have low melting points, having been formed at the Earth’s surface at cool temperatures. Subducting slabs are also accompanied by water, which further depresses melting points for the mineral ...
... and have cooled since formation at a midocean ridge. Further, the sediments they carry contain minerals that have low melting points, having been formed at the Earth’s surface at cool temperatures. Subducting slabs are also accompanied by water, which further depresses melting points for the mineral ...
HS Earth Science Crosswalk
... floor features. external processes a. Explain the external processes (i.e., weathering, erosion, deposition of sediment) that result in the formation and modification of landforms b. Describe the factors that affect rates of weathering and erosion of landforms (e.g., soil/rock type, amount and force ...
... floor features. external processes a. Explain the external processes (i.e., weathering, erosion, deposition of sediment) that result in the formation and modification of landforms b. Describe the factors that affect rates of weathering and erosion of landforms (e.g., soil/rock type, amount and force ...
Earthquakes Fill
... 1. Used to determine overall movement along a plate boundary. 2. Pen motion represents the reaction of the P-Wave to rocks being pulled apart or compressed. 3. From the pen drawing on a seismogram first motion as a push or pull is determined. a. Push i First arrival waves cause the pen drawing to be ...
... 1. Used to determine overall movement along a plate boundary. 2. Pen motion represents the reaction of the P-Wave to rocks being pulled apart or compressed. 3. From the pen drawing on a seismogram first motion as a push or pull is determined. a. Push i First arrival waves cause the pen drawing to be ...
Earthquakes
... the Earth. Slowest moving waves collectively referred to as L or Long waves. • Love waves - transverse side-to-side wave motion in a horizontal plane parallel to Earth’s surface. • Rayleigh waves - backward rotating, circular motion similar to water molecule in ocean waves. ...
... the Earth. Slowest moving waves collectively referred to as L or Long waves. • Love waves - transverse side-to-side wave motion in a horizontal plane parallel to Earth’s surface. • Rayleigh waves - backward rotating, circular motion similar to water molecule in ocean waves. ...
FAMILY EARTHQUAKE DRILLS (contd.)
... • The earth’s different layers are in constant motion, their movement is due to many different aspects like underground volcanic activity or oceanic movements etc. • Due this constant motion, small intensity earthquakes occur continuously on all faults around the world. • Science has yet to discover ...
... • The earth’s different layers are in constant motion, their movement is due to many different aspects like underground volcanic activity or oceanic movements etc. • Due this constant motion, small intensity earthquakes occur continuously on all faults around the world. • Science has yet to discover ...
ch03_sec1 copy
... tectonic plate boundaries because of the enormous stresses that are generated when tectonic plates separate, collide or slip past each other. • Over the past 15 million to 20 million years, large numbers of earthquakes have occurred along the San Andreas fault in California, where parts of the North ...
... tectonic plate boundaries because of the enormous stresses that are generated when tectonic plates separate, collide or slip past each other. • Over the past 15 million to 20 million years, large numbers of earthquakes have occurred along the San Andreas fault in California, where parts of the North ...
Section 1: The Geosphere
... tectonic plate boundaries because of the enormous stresses that are generated when tectonic plates separate, collide or slip past each other. • Over the past 15 million to 20 million years, large numbers of earthquakes have occurred along the San Andreas fault in California, where parts of the North ...
... tectonic plate boundaries because of the enormous stresses that are generated when tectonic plates separate, collide or slip past each other. • Over the past 15 million to 20 million years, large numbers of earthquakes have occurred along the San Andreas fault in California, where parts of the North ...
A Q A G E O G R A P H Y
... changing because these highly folded and faulted regions do not become seismically quiet after 1st impact. At this extreme altitude wreathing and erosion reduce mountain height, but isostatic lift in some areas produced by continuing plate motion means that Everest is increasing by 2.5cm a year. The ...
... changing because these highly folded and faulted regions do not become seismically quiet after 1st impact. At this extreme altitude wreathing and erosion reduce mountain height, but isostatic lift in some areas produced by continuing plate motion means that Everest is increasing by 2.5cm a year. The ...
File
... plates (plate tectonics). Earthquakes can happen along any type of plate boundary. Earthquakes are caused when the tension is released from inside the crust. This happens because plates do not move smoothly - sometimes they get stuck. When this happens a great deal of pressure builds up. When this p ...
... plates (plate tectonics). Earthquakes can happen along any type of plate boundary. Earthquakes are caused when the tension is released from inside the crust. This happens because plates do not move smoothly - sometimes they get stuck. When this happens a great deal of pressure builds up. When this p ...
8 The dynamic Earth
... has been provided by the location of volcanoes and earthquakes, growing mountain ranges, spreading ocean ridges and the movement of the continents. However there is further evidence: • Two-hundred-million-year-old fossils of the same land animals have been found in all of the southern continents. A ...
... has been provided by the location of volcanoes and earthquakes, growing mountain ranges, spreading ocean ridges and the movement of the continents. However there is further evidence: • Two-hundred-million-year-old fossils of the same land animals have been found in all of the southern continents. A ...
Vocabulary #3
... 4. Plate: large section of Earth’s crust layer and upper mantle layer that moves around on the asthenosphere 5. Plate tectonics: theory that Earth’s crust and upper mantle are broken into plates that move around on a plastic-like layer of the mantle. ...
... 4. Plate: large section of Earth’s crust layer and upper mantle layer that moves around on the asthenosphere 5. Plate tectonics: theory that Earth’s crust and upper mantle are broken into plates that move around on a plastic-like layer of the mantle. ...
Instructions
... tonic plates pulling apart; the Pacific Ring of Fire has examples of volcanoes caused by cor-rvergent tectonic plates corning together which, curiously enough, is the focus the exercise today. This was the data that originally caused Wegener to develop his idea of continental driff which was the gra ...
... tonic plates pulling apart; the Pacific Ring of Fire has examples of volcanoes caused by cor-rvergent tectonic plates corning together which, curiously enough, is the focus the exercise today. This was the data that originally caused Wegener to develop his idea of continental driff which was the gra ...
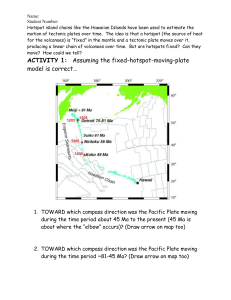
HotspotActivity_forSERC.v2
... Hotspot island chains like the Hawaiian Islands have been used to estimate the motion of tectonic plates over time. The idea is that a hotspot (the source of heat for the volcanoes) is “fixed” in the mantle and a tectonic plate moves over it, producing a linear chain of volcanoes over time. But are ...
... Hotspot island chains like the Hawaiian Islands have been used to estimate the motion of tectonic plates over time. The idea is that a hotspot (the source of heat for the volcanoes) is “fixed” in the mantle and a tectonic plate moves over it, producing a linear chain of volcanoes over time. But are ...
EARTHQUAKES !!!
... 2) Caused MAINLY by the breaking of rock due to moving tectonic plates. 3) EQ occur Mainly on plate boundaries & volcanoes 3) EQ CAN occur anywhere at any time. 4) EQ occur at least 1 per minute somewhere in the world. Approximately 20 Earthquakes have occurred while you have written this. • http:// ...
... 2) Caused MAINLY by the breaking of rock due to moving tectonic plates. 3) EQ occur Mainly on plate boundaries & volcanoes 3) EQ CAN occur anywhere at any time. 4) EQ occur at least 1 per minute somewhere in the world. Approximately 20 Earthquakes have occurred while you have written this. • http:// ...
Geology

Geology (from the Greek γῆ, gē, i.e. ""earth"" and -λoγία, -logia, i.e. ""study of, discourse"") is an earth science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change. Geology can also refer generally to the study of the solid features of any celestial body (such as the geology of the Moon or Mars).Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates. Geology is important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation, evaluating water resources, understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline.