The Precambrian - Ms. Alderson`s Earth and Space Science course
... formation (from which there are no surviving terrestrial rocks) and presenting a simple division of Archean and Proterozoic Eons into eras, and the other (based on Harland et al) having a larger number of Precambrian eras and periods. We follow the ICS system, but recognize a separate Hadean eon. Di ...
... formation (from which there are no surviving terrestrial rocks) and presenting a simple division of Archean and Proterozoic Eons into eras, and the other (based on Harland et al) having a larger number of Precambrian eras and periods. We follow the ICS system, but recognize a separate Hadean eon. Di ...
Mountain Formation
... collide with a continental plate and become stuck or embedded into the continent Terrane – any crustal fragment that has a geologic history distinct from the adjoining terranes Terranes can contain anything from sediment off the ocean floor to volcanic island arcs The newly added material incr ...
... collide with a continental plate and become stuck or embedded into the continent Terrane – any crustal fragment that has a geologic history distinct from the adjoining terranes Terranes can contain anything from sediment off the ocean floor to volcanic island arcs The newly added material incr ...
Nonrenewable Mineral Resources
... asthenosphere, crust, and lithosphere. Define mineral, mineral resource, and rock. Define and distinguish among sedimentary rock, igneous rock, and metamorphic rock and give an example of each. Define and describe the nature and importance of the rock cycle. Define ore and distinguish between a high ...
... asthenosphere, crust, and lithosphere. Define mineral, mineral resource, and rock. Define and distinguish among sedimentary rock, igneous rock, and metamorphic rock and give an example of each. Define and describe the nature and importance of the rock cycle. Define ore and distinguish between a high ...
Convergent Plate Boundaries
... continental plate and an oceanic plate. The subducting oceanic plate becomes more dense as it descends, its downward slide propelled by gravity. At a depth of about 80 kilometers (50 miles), heat drives water and other volatile components from the subducted sediments into the overlying mantle, lower ...
... continental plate and an oceanic plate. The subducting oceanic plate becomes more dense as it descends, its downward slide propelled by gravity. At a depth of about 80 kilometers (50 miles), heat drives water and other volatile components from the subducted sediments into the overlying mantle, lower ...
FREE Sample Here
... Full file at http://testbank360.eu/solution-manual-earth-9th-edition-tarbuck ...
... Full file at http://testbank360.eu/solution-manual-earth-9th-edition-tarbuck ...
Chapter 8 Earthquakes and Earth’s Interior
... amount of displacement that occurs along a fault More precise method used by scientists Only scale that estimates the energy released by earthquakes Provide a measure of how much energy rock can store before it suddenly slips and releases this energy as a quake ...
... amount of displacement that occurs along a fault More precise method used by scientists Only scale that estimates the energy released by earthquakes Provide a measure of how much energy rock can store before it suddenly slips and releases this energy as a quake ...
Divergent Boundaries
... submerged mountain range, which extends from the Arctic Ocean to beyond the southern tip of Africa, is but one segment of the global mid-ocean ridge system that encircles the Earth. The rate of spreading along the Mid-Atlantic Ridge averages about 2.5 centimeters per year (cm/yr), or 25 km in a mill ...
... submerged mountain range, which extends from the Arctic Ocean to beyond the southern tip of Africa, is but one segment of the global mid-ocean ridge system that encircles the Earth. The rate of spreading along the Mid-Atlantic Ridge averages about 2.5 centimeters per year (cm/yr), or 25 km in a mill ...
Plate Boundaries
... the Earth’s plates are moving because of convection currents in the asthenosphere. This is the reason for the break up of Pangaea. ...
... the Earth’s plates are moving because of convection currents in the asthenosphere. This is the reason for the break up of Pangaea. ...
Discovering how mountains grow
... There are additional questions about the Puna Plateau that Schoenbohm hopes to answer. The steep mountain ranges along the sides of plateaus have long been thought to protect the flatness of the plateau interior. This works because as moist air tries to flow over the plateau, it cools and forms rain ...
... There are additional questions about the Puna Plateau that Schoenbohm hopes to answer. The steep mountain ranges along the sides of plateaus have long been thought to protect the flatness of the plateau interior. This works because as moist air tries to flow over the plateau, it cools and forms rain ...
earthquakes - pjmbilingualsite
... 5. a place where two tectonic plates are moving apart 6. The “fault” labels should be located at the places where the blocks slide past each other. Star should be somewhere along one of the faults. 7. A lot of pressure builds up before the rock breaks. 8. Arrows should be perpendicular to the plate ...
... 5. a place where two tectonic plates are moving apart 6. The “fault” labels should be located at the places where the blocks slide past each other. Star should be somewhere along one of the faults. 7. A lot of pressure builds up before the rock breaks. 8. Arrows should be perpendicular to the plate ...
Plates on the Move
... • Seafloor Spreading provided insight to the mechanism for how the continents moved. • The magma which pushes up at the mid-ocean ridge provides the new land pushing the plates, and the subduction zones gobble up the land on the the other side of the plates. The mechanism was convection currents! ...
... • Seafloor Spreading provided insight to the mechanism for how the continents moved. • The magma which pushes up at the mid-ocean ridge provides the new land pushing the plates, and the subduction zones gobble up the land on the the other side of the plates. The mechanism was convection currents! ...
Plate Tectonics
... Plate tectonics causes movement in the plates and crust, resulting in cracks being formed. These cracks allows the pressure underneath the crust to push the magma, or sometimes water and steam, up the crust. ...
... Plate tectonics causes movement in the plates and crust, resulting in cracks being formed. These cracks allows the pressure underneath the crust to push the magma, or sometimes water and steam, up the crust. ...
Desktop PIA for Kwagga North project, Optimum Colliery, Arnot
... Whitehill Formation in the main basin might be correlated with the mid-Vryheid Formation. If this assumption proves correct, there is a possibility that Mesosaurus could be found in the Vryheid Formation. The late Carboniferous to early Jurassic Karoo Supergroup of South Africa includes economically ...
... Whitehill Formation in the main basin might be correlated with the mid-Vryheid Formation. If this assumption proves correct, there is a possibility that Mesosaurus could be found in the Vryheid Formation. The late Carboniferous to early Jurassic Karoo Supergroup of South Africa includes economically ...
earthquakes I
... • Earthquakes occur where there are breaks in the crust of the earth. Usually there are large plates of crust that move against each other. When the plates move side by side the rubbing together makes vibrations and these are earthquakes. The sliding plates grind off pieces of rock as they move. If ...
... • Earthquakes occur where there are breaks in the crust of the earth. Usually there are large plates of crust that move against each other. When the plates move side by side the rubbing together makes vibrations and these are earthquakes. The sliding plates grind off pieces of rock as they move. If ...
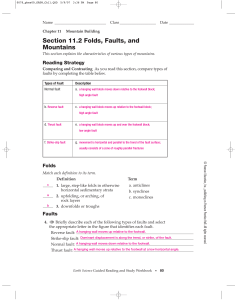
Section 11.2 Folds, Faults, and Mountains
... Briefly describe each of the following types of faults and select the appropriate letter in the figure that identifies each fault. Reverse fault: A hanging wall moves up relative to the footwall. Strike-slip fault: Dominant displacement is along the trend, or strike, of the fault. Normal fault: A ha ...
... Briefly describe each of the following types of faults and select the appropriate letter in the figure that identifies each fault. Reverse fault: A hanging wall moves up relative to the footwall. Strike-slip fault: Dominant displacement is along the trend, or strike, of the fault. Normal fault: A ha ...
earthquakes - SCHOOLinSITES
... What is seismology? It is the study of earthquakes Where do most earthquakes occur? Near the edges of tectonic plates. What are tectonic plates? Giant pieces of Earth’s thin, outermost layer Tectonic plates move in different directions and at different speeds Two plates can push toward or pull away ...
... What is seismology? It is the study of earthquakes Where do most earthquakes occur? Near the edges of tectonic plates. What are tectonic plates? Giant pieces of Earth’s thin, outermost layer Tectonic plates move in different directions and at different speeds Two plates can push toward or pull away ...
PTYS/ASTR 206 – Section 2 – Fall 2004 Activity #1: 8/25/04
... The purpose of this activity is to go over material covered both in class and in the textbook. This is an ACTIVITY, so feel free to discuss these with one or two of your neighbors. You must turn in your own work. You decide how much the question is worth! You can choose each number (4, 3, 2, 1) only ...
... The purpose of this activity is to go over material covered both in class and in the textbook. This is an ACTIVITY, so feel free to discuss these with one or two of your neighbors. You must turn in your own work. You decide how much the question is worth! You can choose each number (4, 3, 2, 1) only ...
Objectives
... The crustal portion of the subducting slab contains a significant amount of surface water, as well as water contained in hydrated minerals within the seafloor basalt. As the subducting slab descends to greater and greater depths, it progressively encounters greater temperatures and greater pressures ...
... The crustal portion of the subducting slab contains a significant amount of surface water, as well as water contained in hydrated minerals within the seafloor basalt. As the subducting slab descends to greater and greater depths, it progressively encounters greater temperatures and greater pressures ...
Empirical data support seafloor spreading and catastrophic plate
... themselves and not the perceived age of the rocks. These subduction zones.19 These are not merely faults as some have proposed,20 but 100-km-thick slabs of brittle, dense data indicate similar source rocks were deposited at rock descending into the mantle.19 The cooler temperatures different locatio ...
... themselves and not the perceived age of the rocks. These subduction zones.19 These are not merely faults as some have proposed,20 but 100-km-thick slabs of brittle, dense data indicate similar source rocks were deposited at rock descending into the mantle.19 The cooler temperatures different locatio ...
Notes on Plates: Sliding, Colliding, and Separating (text pgs. 174-175)
... Plates are cold, broken pieces of the lithosphere, that move on top of the hot, taffy-like asthenosphere.) ...
... Plates are cold, broken pieces of the lithosphere, that move on top of the hot, taffy-like asthenosphere.) ...
Structure of the Earth - South Kingstown High School Home Page
... There are 2 types of plates (oceanic, continental) There are 3 types of plate boundaries Volcanoes and Earthquakes are closely linked to the margins of the tectonic plates ...
... There are 2 types of plates (oceanic, continental) There are 3 types of plate boundaries Volcanoes and Earthquakes are closely linked to the margins of the tectonic plates ...
10.3 Plate Tectonics and Igneous Activity
... magma. The result may be a small volcanic region a few hundred kilometers across called a hot spot. More than 40 hot spots have been identified, and most have lasted for millions of years. By measuring the heat flow at hot spots, geologists found that the mantle beneath some hot spots may be 100–150°C ...
... magma. The result may be a small volcanic region a few hundred kilometers across called a hot spot. More than 40 hot spots have been identified, and most have lasted for millions of years. By measuring the heat flow at hot spots, geologists found that the mantle beneath some hot spots may be 100–150°C ...
W Geo Chapter 1 - Russell County Moodle
... the globe using the grid of longitude and latitude lines. Relative location describes the location of a place compared to other places. The character of a place consists of the place’s physical and human characteristics. A region is a group of places with at least one common physical or human charac ...
... the globe using the grid of longitude and latitude lines. Relative location describes the location of a place compared to other places. The character of a place consists of the place’s physical and human characteristics. A region is a group of places with at least one common physical or human charac ...
UNIT 10 Plate Tectonics Study Guide
... “movement” of various continents over the surface of the Earth. - We no longer use the term continental drift because all continents are attached to lithospheric plates which in turn are composed of both of oceanic crust and continental crust. - Lithospheric plates of all sizes on the surface of the ...
... “movement” of various continents over the surface of the Earth. - We no longer use the term continental drift because all continents are attached to lithospheric plates which in turn are composed of both of oceanic crust and continental crust. - Lithospheric plates of all sizes on the surface of the ...
Geology

Geology (from the Greek γῆ, gē, i.e. ""earth"" and -λoγία, -logia, i.e. ""study of, discourse"") is an earth science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change. Geology can also refer generally to the study of the solid features of any celestial body (such as the geology of the Moon or Mars).Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates. Geology is important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation, evaluating water resources, understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline.