Earth Science
... Large animals- moles Small Animals - termites Large plants-tree roots Small plants-mosses or other small plants that change rock into loose soil ...
... Large animals- moles Small Animals - termites Large plants-tree roots Small plants-mosses or other small plants that change rock into loose soil ...
Constructive and Destructive Landforms
... Interactions between hydrosphere, atmosphere and lithosphere. Weathering and erosion. ...
... Interactions between hydrosphere, atmosphere and lithosphere. Weathering and erosion. ...
Components of the Spheres
... Changes in the Geosphere are based on physical evidence such as rocks, fossils, and land forms Core- makes up 16% of the volume of the earth and 31% of mass. It is divided into 2 regions : Solid inner core and liquid outer core. Mantle- largest layer in the earth 82% of volume and 68% of mass dom ...
... Changes in the Geosphere are based on physical evidence such as rocks, fossils, and land forms Core- makes up 16% of the volume of the earth and 31% of mass. It is divided into 2 regions : Solid inner core and liquid outer core. Mantle- largest layer in the earth 82% of volume and 68% of mass dom ...
Abyssal Plain:
... mountain range found along the ocean floor (Only the peaks, if any, of the mid-ocean ridge are visible above the ocean's surface.) an underwater sea mountain ...
... mountain range found along the ocean floor (Only the peaks, if any, of the mid-ocean ridge are visible above the ocean's surface.) an underwater sea mountain ...
Earth Systems and Cycles Study Guide
... b. Mantle is hot middle section where convection occurs. c. Core is dense and solid inner most section that creates magnetic field. 2. Know that Earth can be divided into 4 spheres (or 4 separate systems). a. Geosphere – consists of the crust, mantle, and core. i. Where tectonic plates converge, div ...
... b. Mantle is hot middle section where convection occurs. c. Core is dense and solid inner most section that creates magnetic field. 2. Know that Earth can be divided into 4 spheres (or 4 separate systems). a. Geosphere – consists of the crust, mantle, and core. i. Where tectonic plates converge, div ...
Quiz (with answers)
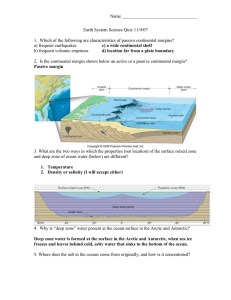
... 3. What are the two ways in which the properties (not location) of the surface mixed zone and deep zone of ocean water (below) are different? 1. Temperature 2. Density or salinity (I will accept either) ...
... 3. What are the two ways in which the properties (not location) of the surface mixed zone and deep zone of ocean water (below) are different? 1. Temperature 2. Density or salinity (I will accept either) ...
Ch 1 2 A View of Earth
... spheres: the hydrosphere, atmosphere, geosphere, and biosphere Hydrosphere – the water portion of Earth Atmosphere – the gaseous portion of a planet; the planet’s envelope of air Geosphere – layer of Earth under both the atmosphere and the oceans Because the geosphere is not uniform, it is divided i ...
... spheres: the hydrosphere, atmosphere, geosphere, and biosphere Hydrosphere – the water portion of Earth Atmosphere – the gaseous portion of a planet; the planet’s envelope of air Geosphere – layer of Earth under both the atmosphere and the oceans Because the geosphere is not uniform, it is divided i ...
Science Chapter 4 Notes- Our Dynamic Earth
... 2. Trenches, rift valleys, and abyssal plains are all features of the ocean floor. 3. You need to know the layers of the Earth: inner core, lower mantle, upper mantle, crust, atmosphere, hydrosphere 4. The atmosphere consists of gases around and above Earth. Lesson 2: Plate Tectonics 1. A geologist ...
... 2. Trenches, rift valleys, and abyssal plains are all features of the ocean floor. 3. You need to know the layers of the Earth: inner core, lower mantle, upper mantle, crust, atmosphere, hydrosphere 4. The atmosphere consists of gases around and above Earth. Lesson 2: Plate Tectonics 1. A geologist ...
Climate Change – Chapter 7
... _________ is the movement of air from areas of ________ pressure to areas of _________ pressure. This movement of air affects global ____________________ and ____________________ patterns. The _______________________ is the collective mass of water found on, under, and over the surface of Earth in t ...
... _________ is the movement of air from areas of ________ pressure to areas of _________ pressure. This movement of air affects global ____________________ and ____________________ patterns. The _______________________ is the collective mass of water found on, under, and over the surface of Earth in t ...
4-1 Role of Climate
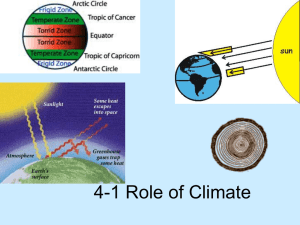
... A. CO2, methane, water vapor, and other gases trap heat energy and maintain Earth’s temperature range. B. A natural insulating blanket of gases that trap sun light from escaping into space. C. Solar energy penetrates the atmosphere and is converted to heat energy and then some radiates back to space ...
... A. CO2, methane, water vapor, and other gases trap heat energy and maintain Earth’s temperature range. B. A natural insulating blanket of gases that trap sun light from escaping into space. C. Solar energy penetrates the atmosphere and is converted to heat energy and then some radiates back to space ...
BAY - WeberTube
... Plants that can conserve water and withstand heat dot the DESERT landscape. Examples include cacti, shrubs, or sagebrush. ...
... Plants that can conserve water and withstand heat dot the DESERT landscape. Examples include cacti, shrubs, or sagebrush. ...
200 300 400 500 100 200 300 400 500 100 200 300 400 500 100
... It is the theory that Earth’s surface cracked into plates millions of years ago and these plates have been moving and shifting ever since. ...
... It is the theory that Earth’s surface cracked into plates millions of years ago and these plates have been moving and shifting ever since. ...
Ecosystems: What Are They and How Do They Work?
... Organism: Any form of life. Single cell, plant or animal Cells: Basic unit of life Species: Groups of organisms that share characteristics. ...
... Organism: Any form of life. Single cell, plant or animal Cells: Basic unit of life Species: Groups of organisms that share characteristics. ...
Earth`s Systems Study Guide 1. Name the four parts of Earth`s
... 28.____________________ is a measure of the amount of dissolved salts in a given amount of liquid. 29 Name the three temperature zones of the ocean. ...
... 28.____________________ is a measure of the amount of dissolved salts in a given amount of liquid. 29 Name the three temperature zones of the ocean. ...
Chapter 5 Test - Bloomsburg Area School District
... 1. What is the rock that makes up the Earth’s outer layer? ...
... 1. What is the rock that makes up the Earth’s outer layer? ...
EnvSci Chapter 3 Review Answers
... Magma - _Molten rock found underground_ Tectonic Plate - _The large sections of lithosphere that float around on the mantle_ Earthquake - _Vibrations along faults as the plates slip past each other_ Volcano - _A mountain made from magma as it erupts through the surface of the Earth_ Mudflow - _When ...
... Magma - _Molten rock found underground_ Tectonic Plate - _The large sections of lithosphere that float around on the mantle_ Earthquake - _Vibrations along faults as the plates slip past each other_ Volcano - _A mountain made from magma as it erupts through the surface of the Earth_ Mudflow - _When ...
Elaborating on a Preexisting Concept
... 28. New rock is added to plates only from the top when volcanoes spew out molten rock that solidifies into new rock on the surface of the plate. ...
... 28. New rock is added to plates only from the top when volcanoes spew out molten rock that solidifies into new rock on the surface of the plate. ...
Impact on Climate - Effingham County Schools
... Scientists theorize that global warming would cause higher ocean levels and global freezing would cause lower ocean levels. ...
... Scientists theorize that global warming would cause higher ocean levels and global freezing would cause lower ocean levels. ...
The Earth Layers
... Lithosphere( Land)- The solid part of the earth (rocks & minerals). Hydrosphere ( Water)- The liquid part of the earth ( ocean, river). Atmosphere( Air)-Gas part of the earth. ...
... Lithosphere( Land)- The solid part of the earth (rocks & minerals). Hydrosphere ( Water)- The liquid part of the earth ( ocean, river). Atmosphere( Air)-Gas part of the earth. ...
Nacho-Tonics
... through solids (metal pan for cooking) very even Convection- transfer of heat energy in a liquid very unequal (hot spots and cold areas develop that’s why you stir soups) ...
... through solids (metal pan for cooking) very even Convection- transfer of heat energy in a liquid very unequal (hot spots and cold areas develop that’s why you stir soups) ...
Nature

Nature, in the broadest sense, is the natural, physical, or material world or universe. ""Nature"" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena.The word nature is derived from the Latin word natura, or ""essential qualities, innate disposition"", and in ancient times, literally meant ""birth"". Natura is a Latin translation of the Greek word physis (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics that plants, animals, and other features of the world develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre-Socratic philosophers, and has steadily gained currency ever since. This usage continued during the advent of modern scientific method in the last several centuries.Within the various uses of the word today, ""nature"" often refers to geology and wildlife. Nature can refer to the general realm of living plants and animals, and in some cases to the processes associated with inanimate objects – the way that particular types of things exist and change of their own accord, such as the weather and geology of the Earth. It is often taken to mean the ""natural environment"" or wilderness–wild animals, rocks, forest, and in general those things that have not been substantially altered by human intervention, or which persist despite human intervention. For example, manufactured objects and human interaction generally are not considered part of nature, unless qualified as, for example, ""human nature"" or ""the whole of nature"". This more traditional concept of natural things which can still be found today implies a distinction between the natural and the artificial, with the artificial being understood as that which has been brought into being by a human consciousness or a human mind. Depending on the particular context, the term ""natural"" might also be distinguished from the unnatural or the supernatural.