Sixth Grade Science
... Know: The water cycle, How clouds are formed, Forms of precipitation. Understand: 1. Changes in movement of water in the atmosphere determines local weather patterns. 2. Sunlight and gravity propel global movements of water. 3. The oceans influence weather and climate. 4. Sunlight, the ocean, the at ...
... Know: The water cycle, How clouds are formed, Forms of precipitation. Understand: 1. Changes in movement of water in the atmosphere determines local weather patterns. 2. Sunlight and gravity propel global movements of water. 3. The oceans influence weather and climate. 4. Sunlight, the ocean, the at ...
Earth`s Surface
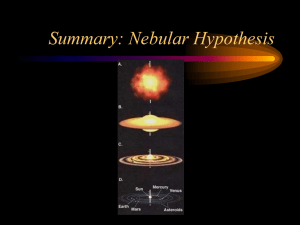
... single point, occurred about 13.7 billion years ago. From that explosion, dust particles began to collide and clump together. These clumps collided with other clumps until eventually, the Earth and other planets were formed. The early Earth was likely extremely hot and the rock was molten in nature. ...
... single point, occurred about 13.7 billion years ago. From that explosion, dust particles began to collide and clump together. These clumps collided with other clumps until eventually, the Earth and other planets were formed. The early Earth was likely extremely hot and the rock was molten in nature. ...
2013-2014_PACING_GUIDE_EARTH_SCIENCE
... The Earth Science standards connect the study of the Earth’s composition, structure, processes, and history; its atmosphere, fresh water, and oceans; and its environment in space. The standards emphasize historical contributions in the development of scientific thought about the Earth and space. The ...
... The Earth Science standards connect the study of the Earth’s composition, structure, processes, and history; its atmosphere, fresh water, and oceans; and its environment in space. The standards emphasize historical contributions in the development of scientific thought about the Earth and space. The ...
Purpose, Standards and Prelesson
... with this trip is to review basic earth science concepts that answer the questions: How has the Earth evolved?* What major geologic processes occur within the earth and on its surface? o Why are there ocean basins, continents, and mountains?* What are rocks and minerals, and how are they recyc ...
... with this trip is to review basic earth science concepts that answer the questions: How has the Earth evolved?* What major geologic processes occur within the earth and on its surface? o Why are there ocean basins, continents, and mountains?* What are rocks and minerals, and how are they recyc ...
Earth PowerPoint
... absorbed by Earth’s surface, warming it • Surface re-radiates as infrared thermal radiation • Atmosphere absorbs some infrared, causing further heating ...
... absorbed by Earth’s surface, warming it • Surface re-radiates as infrared thermal radiation • Atmosphere absorbs some infrared, causing further heating ...
Lesson 1 - Earth`s Interior
... layers vary greatly in size, composition, temperature and pressure. ...
... layers vary greatly in size, composition, temperature and pressure. ...
OUTDOOR SCIENCE SCHOOL VOC (#1 – Test)
... In 250 million years = a new Pangaea will be formed 14. (Pg 8) ACCUMULATION – a water cycle term referring to the “collection of water into larger bodies of water such as rivers, streams, lakes, oceans and ground water (a) forms the hydrosphere – all the waters that cover or infiltrate the crust acc ...
... In 250 million years = a new Pangaea will be formed 14. (Pg 8) ACCUMULATION – a water cycle term referring to the “collection of water into larger bodies of water such as rivers, streams, lakes, oceans and ground water (a) forms the hydrosphere – all the waters that cover or infiltrate the crust acc ...
Golf
... A. It has been sorted by particle size and density B. It is made from rock and other particles C. It was placed in layers by humans D. The layers have always been there ...
... A. It has been sorted by particle size and density B. It is made from rock and other particles C. It was placed in layers by humans D. The layers have always been there ...
Quiz # 6
... c. the rubbing of the continental plates warms up the Earth's surface d. we have no explanation for this higher temperature and that has scientists worried e. the heat given off by living things makes our planet warmer ____ 9. If no one has ever visited the core of the Earth, how do we know that it ...
... c. the rubbing of the continental plates warms up the Earth's surface d. we have no explanation for this higher temperature and that has scientists worried e. the heat given off by living things makes our planet warmer ____ 9. If no one has ever visited the core of the Earth, how do we know that it ...
Golf
... A. It has been sorted by particle size and density B. It is made from rock and other particles C. It was placed in layers by humans D. The layers have always been there ...
... A. It has been sorted by particle size and density B. It is made from rock and other particles C. It was placed in layers by humans D. The layers have always been there ...
Mars
... primordial Noachian atmosphere may have been 15 to 70 times more dense 10-50% pressure of Earth’s atmosphere, including extensive water vapour component. Primordial Martian atmosphere likely included significant greenhouse gases plus extensive cloud formation surface temperatures could have been ...
... primordial Noachian atmosphere may have been 15 to 70 times more dense 10-50% pressure of Earth’s atmosphere, including extensive water vapour component. Primordial Martian atmosphere likely included significant greenhouse gases plus extensive cloud formation surface temperatures could have been ...
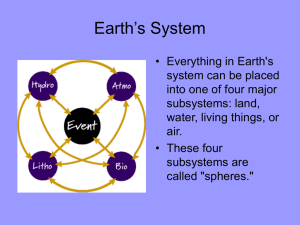
SPHERES
... Asthenosphere is the nonrigid layer below the lithosphere, convection currents within move the tectonic plates Geosphere is the densest parts of Earth, which consist mostly of rock and a heterogenous mixture. The dense geosphere is also subdivided into the crust, mantle, and core. Pedosphere is the ...
... Asthenosphere is the nonrigid layer below the lithosphere, convection currents within move the tectonic plates Geosphere is the densest parts of Earth, which consist mostly of rock and a heterogenous mixture. The dense geosphere is also subdivided into the crust, mantle, and core. Pedosphere is the ...
01 - 6th Grade Science with Mrs. Harlow
... Exploring the Oceans and Movement of Ocean Water 1. Name all the world’s ocean and include their size. Pacific – largest Atlantic – 2nd largest Indian – 3rd largest Southern - Extends from coast of Antartica to 60 degrees south latitude 2. What is evaporation? When a liquid changes into a vapor or g ...
... Exploring the Oceans and Movement of Ocean Water 1. Name all the world’s ocean and include their size. Pacific – largest Atlantic – 2nd largest Indian – 3rd largest Southern - Extends from coast of Antartica to 60 degrees south latitude 2. What is evaporation? When a liquid changes into a vapor or g ...
Grade 8 Science
... Salinity – The amount of salt dissolved in a specific amount of water. Drainage System – the area of land from which water drains into a certain body of water. Volcanic action – when heat and dust is coming from volcano Erosion - weathering away of rocks Plate Tectonics – huge rock plates that slip ...
... Salinity – The amount of salt dissolved in a specific amount of water. Drainage System – the area of land from which water drains into a certain body of water. Volcanic action – when heat and dust is coming from volcano Erosion - weathering away of rocks Plate Tectonics – huge rock plates that slip ...
File
... 2) ____________ mountains: When plates collide, rocks can fold if they are hot enough to act like bendable plastic. 3) ______________________ mountains: Sometimes the rocks in Earth’s crust are too brittle to fold, and they instead break, forming a fault. Fault blocks can tilt or slide down. 4) Moun ...
... 2) ____________ mountains: When plates collide, rocks can fold if they are hot enough to act like bendable plastic. 3) ______________________ mountains: Sometimes the rocks in Earth’s crust are too brittle to fold, and they instead break, forming a fault. Fault blocks can tilt or slide down. 4) Moun ...
Earth Science Notes
... _______________: _____ of Earth’s volume, _____ of Earth’s mass o 2 regions Solid _______________ core – iron, nickel, high density Liquid _______________ core – iron, nickel, sulfur, oxygen _______________: _____ of Earth’s volume; _____ of Earth’s mass o Magnesium and iron-rich minerals o ...
... _______________: _____ of Earth’s volume, _____ of Earth’s mass o 2 regions Solid _______________ core – iron, nickel, high density Liquid _______________ core – iron, nickel, sulfur, oxygen _______________: _____ of Earth’s volume; _____ of Earth’s mass o Magnesium and iron-rich minerals o ...
Earth`s Interior
... Was it always this way? Accretion of the protoplanet Homogeneous structure Density differentiation ...
... Was it always this way? Accretion of the protoplanet Homogeneous structure Density differentiation ...
plate - PAMS-Doyle
... Earth’s Spreading Ocean Floor Midocean ridges form the single largest mountain range in the world 80,000 km long and 3 km high Lava erupts to form new sea floor and spread As it spreads it takes continents with it This explained the mechanism for continental drift! ...
... Earth’s Spreading Ocean Floor Midocean ridges form the single largest mountain range in the world 80,000 km long and 3 km high Lava erupts to form new sea floor and spread As it spreads it takes continents with it This explained the mechanism for continental drift! ...
Nature

Nature, in the broadest sense, is the natural, physical, or material world or universe. ""Nature"" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena.The word nature is derived from the Latin word natura, or ""essential qualities, innate disposition"", and in ancient times, literally meant ""birth"". Natura is a Latin translation of the Greek word physis (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics that plants, animals, and other features of the world develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre-Socratic philosophers, and has steadily gained currency ever since. This usage continued during the advent of modern scientific method in the last several centuries.Within the various uses of the word today, ""nature"" often refers to geology and wildlife. Nature can refer to the general realm of living plants and animals, and in some cases to the processes associated with inanimate objects – the way that particular types of things exist and change of their own accord, such as the weather and geology of the Earth. It is often taken to mean the ""natural environment"" or wilderness–wild animals, rocks, forest, and in general those things that have not been substantially altered by human intervention, or which persist despite human intervention. For example, manufactured objects and human interaction generally are not considered part of nature, unless qualified as, for example, ""human nature"" or ""the whole of nature"". This more traditional concept of natural things which can still be found today implies a distinction between the natural and the artificial, with the artificial being understood as that which has been brought into being by a human consciousness or a human mind. Depending on the particular context, the term ""natural"" might also be distinguished from the unnatural or the supernatural.