No Slide Title
... The Earth is composed of about a dozen rigid plates that are moving with several smaller plates. The plates contain areas of light continental rock (felsic) as well as dense oceanic bottoms(mafic) ...
... The Earth is composed of about a dozen rigid plates that are moving with several smaller plates. The plates contain areas of light continental rock (felsic) as well as dense oceanic bottoms(mafic) ...
Section 1: Earth`s Interior (pages 16 – 24)
... 1. Crust – layer of rock that forms Earths OUTER surface. - It includes both dry land and the ocean floor. - The crust beneath the ocean is called oceanic crust. - The oceanic crust consists mostly of dense rock called basalt. - The continental crust (crust that forms the continents) consists mainly ...
... 1. Crust – layer of rock that forms Earths OUTER surface. - It includes both dry land and the ocean floor. - The crust beneath the ocean is called oceanic crust. - The oceanic crust consists mostly of dense rock called basalt. - The continental crust (crust that forms the continents) consists mainly ...
Chapter One: Plate Tectonics
... Journey to the Center of Earth If you could travel to the center of Earth… • What would happen to the temperature as you traveled? – the temperature would rise as you descend ...
... Journey to the Center of Earth If you could travel to the center of Earth… • What would happen to the temperature as you traveled? – the temperature would rise as you descend ...
The Sea Floor
... Dust particles collided with each other – those larger particles collided with one another – then those larger particles collided with one another, and so on… ...
... Dust particles collided with each other – those larger particles collided with one another – then those larger particles collided with one another, and so on… ...
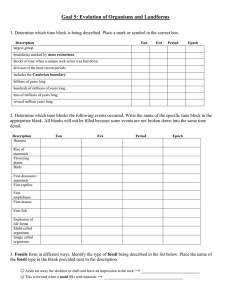
Goal 5: Evolution of Organisms and Landforms
... 17. If you found fossils of seashells in a rock layer near the top of a mountain, what would the fossils tell you about the history of that area? ...
... 17. If you found fossils of seashells in a rock layer near the top of a mountain, what would the fossils tell you about the history of that area? ...
Plate Tectonics Test
... 4_______________ approximately 15 large masses of rock 5_______________ long area of frequent plate activity 6_______________ innermost part of the earth 7_______________ outermost layer of the earth 8_______________ weathering due to wind, water, sand movement 9_______________ theory of large super ...
... 4_______________ approximately 15 large masses of rock 5_______________ long area of frequent plate activity 6_______________ innermost part of the earth 7_______________ outermost layer of the earth 8_______________ weathering due to wind, water, sand movement 9_______________ theory of large super ...
Name: #: Date: Section: HR: Inside Earth WebQuest: Worksheet Part
... Inside Earth WebQuest: Worksheet Part 1: Earth's Interior Site 1 How is Earth’s interior like an apple? ...
... Inside Earth WebQuest: Worksheet Part 1: Earth's Interior Site 1 How is Earth’s interior like an apple? ...
Powerpoint for today
... - Dust storms sometimes envelop most of Mars, can last months. A "Reverse Runaway Greenhouse Effect" may have happened: during volcanic phase (first two billion years), thicker atmosphere, warmer surface, possibly oceans. But gradually most CO2 dissolved into surface water and combined with rocks, t ...
... - Dust storms sometimes envelop most of Mars, can last months. A "Reverse Runaway Greenhouse Effect" may have happened: during volcanic phase (first two billion years), thicker atmosphere, warmer surface, possibly oceans. But gradually most CO2 dissolved into surface water and combined with rocks, t ...
Lesson 1 - Humanities.Com
... These are all images of tectonic hazards. Tectonic hazards are created when the surface of Earth breaks open or moves! To find out why the Earth moves we need to look at its structure. ...
... These are all images of tectonic hazards. Tectonic hazards are created when the surface of Earth breaks open or moves! To find out why the Earth moves we need to look at its structure. ...
Earth interior
... the earth is now known to be truly pear-shaped, in that, added to facts of earth’s equatorial bulge and polar flattening, the south pole is ~40 m closer to the earth’s center than the north pole. ...
... the earth is now known to be truly pear-shaped, in that, added to facts of earth’s equatorial bulge and polar flattening, the south pole is ~40 m closer to the earth’s center than the north pole. ...
earth space science review problem sheet
... ___ 8. What plate boundary involves plates moving together and is associated with the formation of mountain ranges? a. subduction zone b. divergent boundary c. convergent boundary d. transform boundary ___ 9. One major agent of erosion that has shaped Earth’s land surface is a. mass movement. b. mov ...
... ___ 8. What plate boundary involves plates moving together and is associated with the formation of mountain ranges? a. subduction zone b. divergent boundary c. convergent boundary d. transform boundary ___ 9. One major agent of erosion that has shaped Earth’s land surface is a. mass movement. b. mov ...
Earth`s Interior Section 1
... to the center of Earth. Seismic waves are produced by earthquakes. 2. A Journey to the Center of the Earth. The temperature increases, at first quickly and then more slowly. Pressure increases as you go from the surface to the center of Earth. ...
... to the center of Earth. Seismic waves are produced by earthquakes. 2. A Journey to the Center of the Earth. The temperature increases, at first quickly and then more slowly. Pressure increases as you go from the surface to the center of Earth. ...
AP Chapter 5 Study Guide - Bennatti
... nitrogen oxides, and hydrocarbons. Some of the pollutants in photochemical smog include peroxyacetyl nitrates (PANs), ozone, and aldehydes. Acid deposition- sulfur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide emissions that react with water vapor in the atmosphere to form acids that return to the surface as either ...
... nitrogen oxides, and hydrocarbons. Some of the pollutants in photochemical smog include peroxyacetyl nitrates (PANs), ozone, and aldehydes. Acid deposition- sulfur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide emissions that react with water vapor in the atmosphere to form acids that return to the surface as either ...
A fault is a CRACK in the Earth. 1. A tsunami is a giant wave formed
... 1. A tsunami is a giant wave formed from an EARTHQUAKE on the ocean floor. 2. How far a place is above sea level is its ALTITUDE. 3. Volcanoes and earthquakes both happen at the edges of TECTONI ...
... 1. A tsunami is a giant wave formed from an EARTHQUAKE on the ocean floor. 2. How far a place is above sea level is its ALTITUDE. 3. Volcanoes and earthquakes both happen at the edges of TECTONI ...
Worksheet
... 21. _________This is the name of the super-continent 250 million years ago. 22. _________Molten rock under the surface of the Earth is called. 23. _________The deepest area of the oceans. 24. _________Along crack in the crust is called a 25. _________The idea that the Earth's plates are moving acros ...
... 21. _________This is the name of the super-continent 250 million years ago. 22. _________Molten rock under the surface of the Earth is called. 23. _________The deepest area of the oceans. 24. _________Along crack in the crust is called a 25. _________The idea that the Earth's plates are moving acros ...
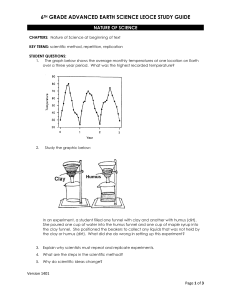
6TH GRADE ADVANCED EARTH SCIENCE LEOCE STUDY GUIDE
... KEY TERMS: climate, ocean currents (surface/deep – density), greenhouse gases, infrared radiation, global winds, evaporation, water cycle, weather, ozone layer, condensation, transpiration, precipitation, salinity, radiation, conduction, and convection, land breeze, sea breeze STUDENT QUESTIONS: 6. ...
... KEY TERMS: climate, ocean currents (surface/deep – density), greenhouse gases, infrared radiation, global winds, evaporation, water cycle, weather, ozone layer, condensation, transpiration, precipitation, salinity, radiation, conduction, and convection, land breeze, sea breeze STUDENT QUESTIONS: 6. ...
Earth - World Book Encyclopedia
... The Neptunists thought the entire earth had been covered by oceans at one time and had since evaporated, leaving dry land in some places. In 2005, scientists of the American Geophysical Union reported that the earth’s north magnetic pole had been moving rapidly towards Siberia. Scientists believe ...
... The Neptunists thought the entire earth had been covered by oceans at one time and had since evaporated, leaving dry land in some places. In 2005, scientists of the American Geophysical Union reported that the earth’s north magnetic pole had been moving rapidly towards Siberia. Scientists believe ...
Earthlike planets
... b.the interior of the moon is too hot to produce a magnetic field. c.the crust of the moon is so thick that the magnetic field can not get out of the interior d. the moon's core contains little if any molten iron. e. the moon is moving further from Earth. 15. The geology of Venus appears to be domin ...
... b.the interior of the moon is too hot to produce a magnetic field. c.the crust of the moon is so thick that the magnetic field can not get out of the interior d. the moon's core contains little if any molten iron. e. the moon is moving further from Earth. 15. The geology of Venus appears to be domin ...
Student Notes
... - Glaciers move materials towards the oceans. Origins of Ocean Water: How was the water in the ocean formed? - Oceans formed 3 billion years ago. - Outside of Earth cooled but the inside remained hot. - Water trapped in volcanic materials was released as vapour. - It cooled, condensed and fell back ...
... - Glaciers move materials towards the oceans. Origins of Ocean Water: How was the water in the ocean formed? - Oceans formed 3 billion years ago. - Outside of Earth cooled but the inside remained hot. - Water trapped in volcanic materials was released as vapour. - It cooled, condensed and fell back ...
Quiz Bowl Earth Terms
... Ozone – A form of oxygen. It can occur at ground level, but is found mostly in a layer in the stratosphere, where it filters some of the Sun’s harmful ultraviolet light. Photosynthesis – The process in which organisms use sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into oxygen and sugars. Planet – ...
... Ozone – A form of oxygen. It can occur at ground level, but is found mostly in a layer in the stratosphere, where it filters some of the Sun’s harmful ultraviolet light. Photosynthesis – The process in which organisms use sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into oxygen and sugars. Planet – ...
Earth`s Interior Worksheet A Journey to the Center of the Earth (p. 9
... 10. Right below the lithosphere is a layer of mantle that is made of softer rock called the _________________________. 11. How deep is the mantle? Core (p. 11) 12. The earth’s core is made of two parts… what are they? 13. Which two metals make up both parts of the core (the reason why the core is co ...
... 10. Right below the lithosphere is a layer of mantle that is made of softer rock called the _________________________. 11. How deep is the mantle? Core (p. 11) 12. The earth’s core is made of two parts… what are they? 13. Which two metals make up both parts of the core (the reason why the core is co ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Introduction to Earthquakes EASA
... ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______ ...
... ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______ ...
Just how integrated is the Earth System
... both Earth’s surface and the various layers of the Earth's interior. Atmosphere: gaseous envelope that surrounds the Earth and constitutes the transition between its surface and the vacuum of space Hydrosphere: includes all water on Earth (including surface water and groundwater) Biosphere: the life ...
... both Earth’s surface and the various layers of the Earth's interior. Atmosphere: gaseous envelope that surrounds the Earth and constitutes the transition between its surface and the vacuum of space Hydrosphere: includes all water on Earth (including surface water and groundwater) Biosphere: the life ...
Nature

Nature, in the broadest sense, is the natural, physical, or material world or universe. ""Nature"" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena.The word nature is derived from the Latin word natura, or ""essential qualities, innate disposition"", and in ancient times, literally meant ""birth"". Natura is a Latin translation of the Greek word physis (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics that plants, animals, and other features of the world develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre-Socratic philosophers, and has steadily gained currency ever since. This usage continued during the advent of modern scientific method in the last several centuries.Within the various uses of the word today, ""nature"" often refers to geology and wildlife. Nature can refer to the general realm of living plants and animals, and in some cases to the processes associated with inanimate objects – the way that particular types of things exist and change of their own accord, such as the weather and geology of the Earth. It is often taken to mean the ""natural environment"" or wilderness–wild animals, rocks, forest, and in general those things that have not been substantially altered by human intervention, or which persist despite human intervention. For example, manufactured objects and human interaction generally are not considered part of nature, unless qualified as, for example, ""human nature"" or ""the whole of nature"". This more traditional concept of natural things which can still be found today implies a distinction between the natural and the artificial, with the artificial being understood as that which has been brought into being by a human consciousness or a human mind. Depending on the particular context, the term ""natural"" might also be distinguished from the unnatural or the supernatural.