Classical Model of Selection at a Single Locus
... Genetic system: 1) diploid population 2) sexual reproduction 3) random mating Selection 1) identical selection in both sexes 2) viability selection 3) constant selection on each genotype Other factors 1) non-overlapping generations 2) infinite population size 3) no migration (gene flow) 4) no mutati ...
... Genetic system: 1) diploid population 2) sexual reproduction 3) random mating Selection 1) identical selection in both sexes 2) viability selection 3) constant selection on each genotype Other factors 1) non-overlapping generations 2) infinite population size 3) no migration (gene flow) 4) no mutati ...
natural selections
... contribution eyes have made to the survival of humans. But when it comes to the purpose of humans themselves, or of the mechanism of natural selection that made them, the theory says nothing. If Darwin is right, we have been sired by blind chance out of the laws of physics. We testify to nothing but ...
... contribution eyes have made to the survival of humans. But when it comes to the purpose of humans themselves, or of the mechanism of natural selection that made them, the theory says nothing. If Darwin is right, we have been sired by blind chance out of the laws of physics. We testify to nothing but ...
The origins of diversity in a simple model of evolution
... • Bacteria perhaps are more selected? • ~50% of genes are selected in bacteria (Charlesworth and Eyre-Walker, ...
... • Bacteria perhaps are more selected? • ~50% of genes are selected in bacteria (Charlesworth and Eyre-Walker, ...
Origlife_CERN
... • Ancient non-enzymatic pathway: • ABCD • Progressive depletion of D, then C, then B, then A • Selection pressure for enzyme appearance in this order • Homologous enzymes will have different mechanisms Jensen (1976) enzyme recruitment (patchwork) ...
... • Ancient non-enzymatic pathway: • ABCD • Progressive depletion of D, then C, then B, then A • Selection pressure for enzyme appearance in this order • Homologous enzymes will have different mechanisms Jensen (1976) enzyme recruitment (patchwork) ...
Lect 2 Evolution
... amongst individuals in a population which ultimately impact fitness • Organisms become ‘tailor made’ for their niche within an environment by processes of evolution • Characteristics of individuals making up current populations are a product of natural selection in ancestral populations ...
... amongst individuals in a population which ultimately impact fitness • Organisms become ‘tailor made’ for their niche within an environment by processes of evolution • Characteristics of individuals making up current populations are a product of natural selection in ancestral populations ...
分子演化 - 東華大學
... Fundamental aspects of cellular life are shared by different organisms and dependent on related genes ...
... Fundamental aspects of cellular life are shared by different organisms and dependent on related genes ...
Comparative Genomics of Plant Genes Responding to Fungi
... Itoh et al 2002 describe 3 proteins in gene family (AOS1, AOS2, HPL) in Arabidopsis. Numerous studies have cited AOS, but no phylogeny exists in plants. Research Goal: To determine the number of homologs of AOS in plants and understand the gene evolution, eventually designing primers to address ...
... Itoh et al 2002 describe 3 proteins in gene family (AOS1, AOS2, HPL) in Arabidopsis. Numerous studies have cited AOS, but no phylogeny exists in plants. Research Goal: To determine the number of homologs of AOS in plants and understand the gene evolution, eventually designing primers to address ...
EvolutionStudyGuide1
... 1. A characteristic that improves an organism’s ability to survive is an adaptation_. Over time, this may be an animal’s response to changes in the environment. 2. The process by which populations slowly change over time is called __Evolution . 3. A characteristic that can be passed from parent to o ...
... 1. A characteristic that improves an organism’s ability to survive is an adaptation_. Over time, this may be an animal’s response to changes in the environment. 2. The process by which populations slowly change over time is called __Evolution . 3. A characteristic that can be passed from parent to o ...
Name: Period: ____ Date: ______ Population Genetics and
... determine whether or not the remains were different species? a. geographic isolation. b. allopatric speciation. c. the biological species concept. d. the morphological concept of species. 22. Two closely related species of salamanders that live in the same area, but mate at different times of the ye ...
... determine whether or not the remains were different species? a. geographic isolation. b. allopatric speciation. c. the biological species concept. d. the morphological concept of species. 22. Two closely related species of salamanders that live in the same area, but mate at different times of the ye ...
MECHANISMS FOR EVOLUTION
... • GENETIC DRIFT – in small populations the frequencies of alleles can be drastically affected by chance events – BOTTLENECK EFFECT – if populations are driven to the point of extinction the remaining individuals do not carry a true representation of the original gene pool. – FOUNDER EFFECT – when a ...
... • GENETIC DRIFT – in small populations the frequencies of alleles can be drastically affected by chance events – BOTTLENECK EFFECT – if populations are driven to the point of extinction the remaining individuals do not carry a true representation of the original gene pool. – FOUNDER EFFECT – when a ...
Biology Objectives for Evolution Unit Test
... 11. Explain what is meant by the term survival of the fittest 12. Define speciation and give examples 13. Explain the different forms of isolation and how they may lead to speciation and give examples 14. Define adaptive radiation. Explain why this occurs and give two examples. 15. Compare and under ...
... 11. Explain what is meant by the term survival of the fittest 12. Define speciation and give examples 13. Explain the different forms of isolation and how they may lead to speciation and give examples 14. Define adaptive radiation. Explain why this occurs and give two examples. 15. Compare and under ...
Prostacyclin Synthase Overexpression Prevents Mouse Lung
... •Alzheimer’s and other dementia •Traumatic brain injury •Stroke •Fetal Alcohol Syndrome •Gene profiling provides a molecular fingerprint for susceptibility and cause of specific cognitive disorders. ...
... •Alzheimer’s and other dementia •Traumatic brain injury •Stroke •Fetal Alcohol Syndrome •Gene profiling provides a molecular fingerprint for susceptibility and cause of specific cognitive disorders. ...
Evolution . . . .
... characteristics that help an organism survive. Sharp teeth help to eat meat ...
... characteristics that help an organism survive. Sharp teeth help to eat meat ...
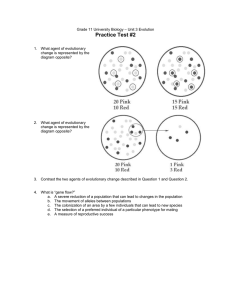
Grade 11 University Biology – Unit 3 Evolution
... 14. Which of the following statements best represents the power of Artificial Selection? a. Artificial selection reduces the number of harmful mutations that may occur b. Individuals that are very different from the original species can be produced in a controlled fashion c. Breeders typically breed ...
... 14. Which of the following statements best represents the power of Artificial Selection? a. Artificial selection reduces the number of harmful mutations that may occur b. Individuals that are very different from the original species can be produced in a controlled fashion c. Breeders typically breed ...
Natural Selection Lab 2
... one generation to the next • Mutation: any change in the genes from one population to the next • Natural selection: individuals best suited to their environment will survive and reproduce ...
... one generation to the next • Mutation: any change in the genes from one population to the next • Natural selection: individuals best suited to their environment will survive and reproduce ...
Script 3
... [4] Darwin first thought of this idea because of what he knew about artificial selection. [5] Darwin knew nothing about genes. / But he did know that dog breeders could influence the kinds of traits dogs had by carefully choosing to breed only the dogs with certain traits. [6] He did the same thing ...
... [4] Darwin first thought of this idea because of what he knew about artificial selection. [5] Darwin knew nothing about genes. / But he did know that dog breeders could influence the kinds of traits dogs had by carefully choosing to breed only the dogs with certain traits. [6] He did the same thing ...
Chapter 23: Evolution of Populations / Lecture
... Their descendent population will then show differences from the original B. Natural Selection – Differential reproductive success C. Gene Flow – Flow of genes in and out of a population by migration of individuals D. Mutation – Change in a gene code which may lead to a phenotypic change. III. The Im ...
... Their descendent population will then show differences from the original B. Natural Selection – Differential reproductive success C. Gene Flow – Flow of genes in and out of a population by migration of individuals D. Mutation – Change in a gene code which may lead to a phenotypic change. III. The Im ...
evolution notes
... likely to survive and therefore reproduce passing off genetic variances to their offspring. ...
... likely to survive and therefore reproduce passing off genetic variances to their offspring. ...
File - Lucinda Supernavage
... a)Bottleneck effect may lead to reduced genetic variability following some large disturbance that removes a large portion of the population. b) Founder effect may lead to reduced variability when a few individuals from a large population colonize an isolated habitat. ...
... a)Bottleneck effect may lead to reduced genetic variability following some large disturbance that removes a large portion of the population. b) Founder effect may lead to reduced variability when a few individuals from a large population colonize an isolated habitat. ...