The evolution of the martian elastic lithosphere and implications for
... et al., 2004; Belleguic et al., 2005) and this general trend is well understood in terms of planetary cooling as predicted by thermal evolution models (Hauck and Phillips, 2002; Schumacher and Breuer, 2006). However, the data also implies that the lithospheric thickness rapidly increased during the ...
... et al., 2004; Belleguic et al., 2005) and this general trend is well understood in terms of planetary cooling as predicted by thermal evolution models (Hauck and Phillips, 2002; Schumacher and Breuer, 2006). However, the data also implies that the lithospheric thickness rapidly increased during the ...
Geomorphology_Dics
... distinct, but the materials used to construct them may still be a significant portion of the soil zone. Railroad cut A common anthropogenic feature, typically a microfeature, consisting of the sloping, cut surface flanking a railroad bed on one or both sides, that remains after local topography is m ...
... distinct, but the materials used to construct them may still be a significant portion of the soil zone. Railroad cut A common anthropogenic feature, typically a microfeature, consisting of the sloping, cut surface flanking a railroad bed on one or both sides, that remains after local topography is m ...
Rheology and Tectonic Significance of Serpentinite
... that control the dynamics of great subduction earthquakes, which likely propagate across patches that creep during interseismic periods. When the asperity-contact lifetime during frictional slip is short compared to the time it takes to diffuse heat away from asperities, the resulting “flash heating ...
... that control the dynamics of great subduction earthquakes, which likely propagate across patches that creep during interseismic periods. When the asperity-contact lifetime during frictional slip is short compared to the time it takes to diffuse heat away from asperities, the resulting “flash heating ...
Teleseismic imaging of subaxial flow at midocean ridges: traveltime
... Deformation of peridotite caused by mantle flow beneath an oceanic spreading centre can result in the development of seismic anisotropy. Traveltime anomalies and shearwave splitting will develop as seismic energy propagates through such an anisotropic region, thus providing a signature of the deform ...
... Deformation of peridotite caused by mantle flow beneath an oceanic spreading centre can result in the development of seismic anisotropy. Traveltime anomalies and shearwave splitting will develop as seismic energy propagates through such an anisotropic region, thus providing a signature of the deform ...
Geology: Effect of subducting sea-floor roughness on fore
... We suggest, however, that the shorter-wavelength roughness related to seamounts superimposes local variability on this overall uplift pattern. Below we report data used to evaluate the vertical separation across block-bounding faults, the tilting within blocks, and the Holocene uplift rates from nor ...
... We suggest, however, that the shorter-wavelength roughness related to seamounts superimposes local variability on this overall uplift pattern. Below we report data used to evaluate the vertical separation across block-bounding faults, the tilting within blocks, and the Holocene uplift rates from nor ...
Mechanical (de-)coupling of the lithosphere in the Valencia Trough
... the low-viscosity layer, which would £ow horizontally in order to compensate isostatic disequilibrium. We will refer to this mode as vertical decoupling. For this extreme situation for a continental extensional basin, it could be the case that, as lithosphere stretches, the upper crust could deform ...
... the low-viscosity layer, which would £ow horizontally in order to compensate isostatic disequilibrium. We will refer to this mode as vertical decoupling. For this extreme situation for a continental extensional basin, it could be the case that, as lithosphere stretches, the upper crust could deform ...
Laramide crustal thickening event in the Rocky Mountain Foreland
... huge regional "root" that now supports the foreland and Great Plains at up to 2 km average elevation. The same shear tractions that Brewer et al. [1980] invoked to cause the Wind River range overthrust may also have dragged and transported ductile lower crust from within the Sevier orogen in the Sou ...
... huge regional "root" that now supports the foreland and Great Plains at up to 2 km average elevation. The same shear tractions that Brewer et al. [1980] invoked to cause the Wind River range overthrust may also have dragged and transported ductile lower crust from within the Sevier orogen in the Sou ...
Global mass wasting during the Middle Ordovician: Meteoritic trigger
... is a continued flux of meteorites onto the Earth unrelated to large impact events (French and Koeberl, 2010). Furthermore, like for any other heavy mineral, the possibility of polyphase recycling has to be kept in mind. 4. Ordovician mass wasting localities Parnell (2009) described 12 megabreccia loc ...
... is a continued flux of meteorites onto the Earth unrelated to large impact events (French and Koeberl, 2010). Furthermore, like for any other heavy mineral, the possibility of polyphase recycling has to be kept in mind. 4. Ordovician mass wasting localities Parnell (2009) described 12 megabreccia loc ...
Finite-frequency wave propagation through outer rise fault zones
... media overtaking slower guided waves within joints (Figure 2). This anisotropy is qualitatively similar to effective-media theory for thin joints (i.e., long wavelengths) [e.g., Hudson, 1981]. That theory also predicts fastest wave speeds in the joint-parallel direction with slowest wave speeds in t ...
... media overtaking slower guided waves within joints (Figure 2). This anisotropy is qualitatively similar to effective-media theory for thin joints (i.e., long wavelengths) [e.g., Hudson, 1981]. That theory also predicts fastest wave speeds in the joint-parallel direction with slowest wave speeds in t ...
Some remarks about the degree-one deformation of the Earth
... Degree-one deformation involving a translation of the external surface may have some geodetic consequences. I n fact, observation stations, being located on the external surface, undergo the surface translation. If these stations are used t o define il reference frame, the centre of this frame will ...
... Degree-one deformation involving a translation of the external surface may have some geodetic consequences. I n fact, observation stations, being located on the external surface, undergo the surface translation. If these stations are used t o define il reference frame, the centre of this frame will ...
Plate tectonic controls on atmospheric CO2 levels since the Triassic
... estimating atmospheric CO2 levels, and test these against previous modeling results and available proxy data (18). ...
... estimating atmospheric CO2 levels, and test these against previous modeling results and available proxy data (18). ...
Non-hotspot volcano chains from small
... deformation is characterized by much smaller wavelengths (50-500 km) than that, which are commonly expected for PLI (>1000 km); (2) plume head flattening is asymmetric below intra-plate boundaries, which leads to mechanical decoupling of crust from mantle lithosphere, and to localized faulting at t ...
... deformation is characterized by much smaller wavelengths (50-500 km) than that, which are commonly expected for PLI (>1000 km); (2) plume head flattening is asymmetric below intra-plate boundaries, which leads to mechanical decoupling of crust from mantle lithosphere, and to localized faulting at t ...
Abstract Title - SWISS GEOSCIENCE MEETINGs
... to high stresses in the bending area. The plastic deformation and dislocation creep fields are, respectively, characterized by extension and compression in a horizontal direction. These two fields are clearly separated by the narrow nondeforming area in the core of the slab characterized by low devi ...
... to high stresses in the bending area. The plastic deformation and dislocation creep fields are, respectively, characterized by extension and compression in a horizontal direction. These two fields are clearly separated by the narrow nondeforming area in the core of the slab characterized by low devi ...
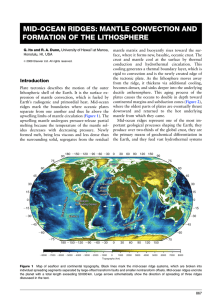
mid-ocean ridges: mantle convection
... rigid to convection and is the newly created edge of the tectonic plate. As the lithosphere moves away from the ridge, it thickens via additional cooling, becomes denser, and sinks deeper into the underlying ductile asthenosphere. This aging process of the plates causes the oceans to double in depth ...
... rigid to convection and is the newly created edge of the tectonic plate. As the lithosphere moves away from the ridge, it thickens via additional cooling, becomes denser, and sinks deeper into the underlying ductile asthenosphere. This aging process of the plates causes the oceans to double in depth ...
the fate of subducted oceanic crust and the origin
... unresolved problems with the model. These include uncertainties as to whether oceanic crust should be stored at the core-mantle boundary or base of the upper mantle, and the number of plumes (e.g. Anderson 2005a). Advocates of the plume model have argued that the uncertainties reflect a theory in it ...
... unresolved problems with the model. These include uncertainties as to whether oceanic crust should be stored at the core-mantle boundary or base of the upper mantle, and the number of plumes (e.g. Anderson 2005a). Advocates of the plume model have argued that the uncertainties reflect a theory in it ...
Geo-neutrino Overview - University of Hawaii Physics and Astronomy
... • Correlation matrix used by GNSM (Fogli et al (2006)) could be extended ?? if correlation coefficients among different crustal types are given. ...
... • Correlation matrix used by GNSM (Fogli et al (2006)) could be extended ?? if correlation coefficients among different crustal types are given. ...
A Lithospheric CrossSection Through the Swiss AlpsI
... they are documented in continent-continent collisional zones, and other tectonically active areas. The fundamental idea of the mathematical description is based on the theorem of vector addition. According to this theorem, complex velocity fields are built up by superposing simple velocity fields wh ...
... they are documented in continent-continent collisional zones, and other tectonically active areas. The fundamental idea of the mathematical description is based on the theorem of vector addition. According to this theorem, complex velocity fields are built up by superposing simple velocity fields wh ...
Geology of Svalbard
... Geology in the society Geology is all around us and is, quite simply, about the ground on which we live. Geological processes have formed the bedrock, deposited the superficial sediments and modified and sculpted landscapes. Some of these processes are global and very slow measured on a human time ...
... Geology in the society Geology is all around us and is, quite simply, about the ground on which we live. Geological processes have formed the bedrock, deposited the superficial sediments and modified and sculpted landscapes. Some of these processes are global and very slow measured on a human time ...
Earthquakes
... • Tiltmeter – measures tilting or raising of the ground • Creep meter – uses a wire stretched across a fault to measure horizontal movement of the ground • Laser-ranging device – uses a laser beam to detect horizontal fault movements ...
... • Tiltmeter – measures tilting or raising of the ground • Creep meter – uses a wire stretched across a fault to measure horizontal movement of the ground • Laser-ranging device – uses a laser beam to detect horizontal fault movements ...
Earthquakes
... • Tiltmeter – measures tilting or raising of the ground • Creep meter – uses a wire stretched across a fault to measure horizontal movement of the ground • Laser-ranging device – uses a laser beam to detect horizontal fault movements ...
... • Tiltmeter – measures tilting or raising of the ground • Creep meter – uses a wire stretched across a fault to measure horizontal movement of the ground • Laser-ranging device – uses a laser beam to detect horizontal fault movements ...
Whole-mantle convection and the transition
... OIB originate from different source regions. The terrestrial heat flow also suggests the presence of different source regions. In particular, the approximately 36 TW of heat output from the mantle cannot be produced by a mantle entirely composed of MORB source materials, because it has so few radioa ...
... OIB originate from different source regions. The terrestrial heat flow also suggests the presence of different source regions. In particular, the approximately 36 TW of heat output from the mantle cannot be produced by a mantle entirely composed of MORB source materials, because it has so few radioa ...
Earthquakes
... seismograph, scientists measure the difference between the arrival times of the P waves and S waves. – The longer the time difference, the further the epicenter is from the seismograph station. ...
... seismograph, scientists measure the difference between the arrival times of the P waves and S waves. – The longer the time difference, the further the epicenter is from the seismograph station. ...
Effects of Sea-Level Rise on Coral Reefs
... and subsided as they moved. At the same time the old Tethys ocean floor was replaced with younger, warmer, more buoyant oceanic crust squeezed up at the new spreading centers, and the overall elevation of the seafloor rose. Coral reefs came and went. The breakup of Pangea was accompanied by increase ...
... and subsided as they moved. At the same time the old Tethys ocean floor was replaced with younger, warmer, more buoyant oceanic crust squeezed up at the new spreading centers, and the overall elevation of the seafloor rose. Coral reefs came and went. The breakup of Pangea was accompanied by increase ...
Grade 4 Earth Science Unit (4.E.2.)
... environment existing when the rock was being formed. For example, most limestone represents marine environments, whereas, sandstones with ripple marks might indicate a shoreline habitat or riverbed. The study and comparison of exposed rock layers or strata in different areas of Earth led scientists ...
... environment existing when the rock was being formed. For example, most limestone represents marine environments, whereas, sandstones with ripple marks might indicate a shoreline habitat or riverbed. The study and comparison of exposed rock layers or strata in different areas of Earth led scientists ...
Post-glacial rebound
.jpg?width=300)
Post-glacial rebound (sometimes called continental rebound) is the rise of land masses that were depressed by the huge weight of ice sheets during the last glacial period, through a process known as isostatic depression. Post-glacial rebound and isostatic depression are different parts of a process known as either glacial isostasy, glacial isostatic adjustment, or glacioisostasy. Glacioisostasy is the solid Earth deformation associated with changes in ice mass distribution. The most obvious and direct affects of post-glacial rebound are readily apparent in northern Europe (especially Scotland, Estonia, Latvia, Fennoscandia, and northern Denmark), Siberia, Canada, the Great Lakes of Canada and the United States, the coastal region of the US state of Maine, parts of Patagonia, and Antarctica. However, through processes known as ocean siphoning and continental levering, the effects of post-glacial rebound on sea-level are felt globally far from the locations of current and former ice sheets.