UNIT TITLE: Readers Theater
... of erosion are water, wind, and ice (or glaciers). 8. The interior of Earth is hot. Convection currents in the mantle cause tectonic plates to move. This causes earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and the creation of mountain ranges. 9. The continents formed one large supercontinent called Pangaea that ...
... of erosion are water, wind, and ice (or glaciers). 8. The interior of Earth is hot. Convection currents in the mantle cause tectonic plates to move. This causes earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and the creation of mountain ranges. 9. The continents formed one large supercontinent called Pangaea that ...
Plate Tectonics - Mrs. DiLorenzo Earth Science
... 1. Appearance of Continents: the outlines of present-day continents appear to fit together like puzzle pieces. ...
... 1. Appearance of Continents: the outlines of present-day continents appear to fit together like puzzle pieces. ...
The Sandbox Experiment - Earth and Atmospheric Sciences
... piston, simulating tectonic deformation that one sees in many mountain ranges. The structures that you create are not unlike those that have been responsible for recent earthquakes in China and elsewhere. In the other experiment, you will observe some of the key mechanical features that allow great ...
... piston, simulating tectonic deformation that one sees in many mountain ranges. The structures that you create are not unlike those that have been responsible for recent earthquakes in China and elsewhere. In the other experiment, you will observe some of the key mechanical features that allow great ...
Bundle 1 - Humble ISD
... Fact: The majority of volcanoes are located along tectonic plate boundaries. “Ring of Fire” is the name given to an area along the border of the Pacific Plate with a high concentration of volcanoes. Earthquakes happen randomly across the earth’s surface. Fact: As with volcanoes, most of the world’ ...
... Fact: The majority of volcanoes are located along tectonic plate boundaries. “Ring of Fire” is the name given to an area along the border of the Pacific Plate with a high concentration of volcanoes. Earthquakes happen randomly across the earth’s surface. Fact: As with volcanoes, most of the world’ ...
Earth`s Interior Processes
... asthenosphere (upper mantle). • Alfred Wegener – proposed that the earth’s continents were once joined in a single supercontinent (known as Pangea) and broke apart into the continents – This process was known as continental drift ...
... asthenosphere (upper mantle). • Alfred Wegener – proposed that the earth’s continents were once joined in a single supercontinent (known as Pangea) and broke apart into the continents – This process was known as continental drift ...
DYNAMIC PLANET I
... • All the Earth’s oceans have a continuous mountain range, called a mid-ocean ridge • Located above rising currents in the mantle convection cells • Stand high because they are heated by hot rising material which expands the rocks ...
... • All the Earth’s oceans have a continuous mountain range, called a mid-ocean ridge • Located above rising currents in the mantle convection cells • Stand high because they are heated by hot rising material which expands the rocks ...
Soils Overview Part 1 - Massachusetts Envirothon
... Parent material can be rocks weathered in place (residuum) Or mineral material deposited by water (alluvium) wind (eolian) gravity (colluvium) lake bed sedimentation (lacustrine) ocean deposits (marine sediment) glacial deposits (till) Or organic material ...
... Parent material can be rocks weathered in place (residuum) Or mineral material deposited by water (alluvium) wind (eolian) gravity (colluvium) lake bed sedimentation (lacustrine) ocean deposits (marine sediment) glacial deposits (till) Or organic material ...
The Structure of the Earth
... Earthquakes/eclipses occur at plate boundaries. They are caused by plate movements/global warming ...
... Earthquakes/eclipses occur at plate boundaries. They are caused by plate movements/global warming ...
Fundamental Concepts and Skills
... building) occurs as a result of relative motion along plate boundaries. Hot spot volcanic activity is exceptional in that it is NOT related to plate boundaries. 5. There are three types of plate boundaries: ...
... building) occurs as a result of relative motion along plate boundaries. Hot spot volcanic activity is exceptional in that it is NOT related to plate boundaries. 5. There are three types of plate boundaries: ...
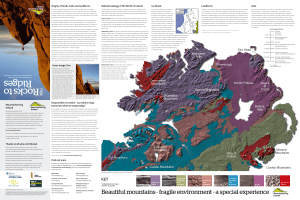
Rocks to Ridges - Mountaineering Ireland
... By studying rocks, soils and landforms in upland regions we discover how the ...
... By studying rocks, soils and landforms in upland regions we discover how the ...
How The Earth Works
... 1 hour+ to pyramids 3 hours to retreat of glaciers from Wisconsin 12 days = 1 million years 2 years to extinction of dinosaurs 14 years to age of Niagara Escarpment 31 years = 1 billion years ...
... 1 hour+ to pyramids 3 hours to retreat of glaciers from Wisconsin 12 days = 1 million years 2 years to extinction of dinosaurs 14 years to age of Niagara Escarpment 31 years = 1 billion years ...
GEOL 4110 Advanced Earth Science For Teachers Jim Miller
... Advanced Earth Science For Teachers ...
... Advanced Earth Science For Teachers ...
Layers of the Earth
... • Crust-Like the shell of an egg is very thin (roughly 5km thick). Mostly Silica and Oxygen. Very brittle. • Continental crust is thick. Made of granite. • Oceanic crust is thin. Made of basalt. ...
... • Crust-Like the shell of an egg is very thin (roughly 5km thick). Mostly Silica and Oxygen. Very brittle. • Continental crust is thick. Made of granite. • Oceanic crust is thin. Made of basalt. ...
Plate Tectonics – Study Guide
... 1. A_____ W______ found evidence of continental drift. When he proposed this theory at first he could not identify the force that would move tectonic plates; other _____ did not accept his theory because he could not explain what could move such large plates. Later scientists linked the idea of c___ ...
... 1. A_____ W______ found evidence of continental drift. When he proposed this theory at first he could not identify the force that would move tectonic plates; other _____ did not accept his theory because he could not explain what could move such large plates. Later scientists linked the idea of c___ ...
earthquakes and mountain building ppt
... – Although it is known where earthquakes and volcanic eruptions are likely to happen, there is currently no reliable way to predict precisely when an event will occur. – Volcanoes and earthquakes indicate the high temperatures and pressures that exist in earth's interior. – Volcanism(volcanic activi ...
... – Although it is known where earthquakes and volcanic eruptions are likely to happen, there is currently no reliable way to predict precisely when an event will occur. – Volcanoes and earthquakes indicate the high temperatures and pressures that exist in earth's interior. – Volcanism(volcanic activi ...
Earth Science Chapter 20: Mountain Building Chapter Overview
... As peaks are eroded, mass decreases, and the roots of the mountains become smaller. A balance between erosion and the decrease on the size of the root will continue for hundreds of millions of years until both the mountains and their roots disappear. This slow process of the crust’s rising as the re ...
... As peaks are eroded, mass decreases, and the roots of the mountains become smaller. A balance between erosion and the decrease on the size of the root will continue for hundreds of millions of years until both the mountains and their roots disappear. This slow process of the crust’s rising as the re ...
Weathering and Erosion
... Dunes- Hills of sand found in dry inland areas. Beach- Area of shoreline where waves have deposited sand and sediment from the ocean. Deltas- Area formed by sediment where a river flow into an ocean, sea, or lake. ...
... Dunes- Hills of sand found in dry inland areas. Beach- Area of shoreline where waves have deposited sand and sediment from the ocean. Deltas- Area formed by sediment where a river flow into an ocean, sea, or lake. ...
Discovery Education: Earth`s Spheres interactive text
... The Cryosphere is the part of the Hydrosphere that contains water in its solid form. Frozen water comes in a variety of forms. Snow, which is frozen precipitation, is found throughout the world. Ice is also found throughout the world in the form of glaciers, ice shelves, sea ice, icebergs, and perma ...
... The Cryosphere is the part of the Hydrosphere that contains water in its solid form. Frozen water comes in a variety of forms. Snow, which is frozen precipitation, is found throughout the world. Ice is also found throughout the world in the form of glaciers, ice shelves, sea ice, icebergs, and perma ...
GE1632013UFINALEXAM
... L. name for materials blown from a volcano M. point of origination in the Earth of an earthquake N. excessive erosion O. water below the potentiometric surface P. rate at which Earth’s temperature increases with depth R. A very large ocean wave caused by an underwater earthquake or volcanic eruption ...
... L. name for materials blown from a volcano M. point of origination in the Earth of an earthquake N. excessive erosion O. water below the potentiometric surface P. rate at which Earth’s temperature increases with depth R. A very large ocean wave caused by an underwater earthquake or volcanic eruption ...
Lesson 1: Earth Energy Lesson
... As the mantle moves around, the crust “floating” on top of it is “deformed” into different shapes and features! These features include: Mountains, valleys, canyons, volcanoes, oceans, deep sea trenches, etc… ...
... As the mantle moves around, the crust “floating” on top of it is “deformed” into different shapes and features! These features include: Mountains, valleys, canyons, volcanoes, oceans, deep sea trenches, etc… ...
Study Questions for Exam #2
... a. subduction zones; formation of sutured margins and uplifted mountains b. strong horizontal compression; folding and thrust faulting c. strong horizontal extension, folding and thrust faulting d. a mix of horizontal compression and transform faulting; production of oceanic crust 3. Why (or rather, ...
... a. subduction zones; formation of sutured margins and uplifted mountains b. strong horizontal compression; folding and thrust faulting c. strong horizontal extension, folding and thrust faulting d. a mix of horizontal compression and transform faulting; production of oceanic crust 3. Why (or rather, ...
26 Sep: Volcano Processes
... Obs: Earthquake “sequences” (Sumatra, Turkey) where large stress changes following one event favor another Obs: “Slow fault slip” events, harmonic (seismic) tremor May someday be possible to predict EQs; need improved understanding of physics & MUCH better measurements Today: • Volcanism ...
... Obs: Earthquake “sequences” (Sumatra, Turkey) where large stress changes following one event favor another Obs: “Slow fault slip” events, harmonic (seismic) tremor May someday be possible to predict EQs; need improved understanding of physics & MUCH better measurements Today: • Volcanism ...
Plate Tectonics Crossword
... 4. ______________ zones. Places where the seafloor is forced under continental plates. 5. Section of the Earth below the crust. 7. Paleontologists noticed that these were the same on different continents even though the continents were separated by oceans. 9. Source of heat in the mantle. 11. Seaflo ...
... 4. ______________ zones. Places where the seafloor is forced under continental plates. 5. Section of the Earth below the crust. 7. Paleontologists noticed that these were the same on different continents even though the continents were separated by oceans. 9. Source of heat in the mantle. 11. Seaflo ...
Post-glacial rebound
.jpg?width=300)
Post-glacial rebound (sometimes called continental rebound) is the rise of land masses that were depressed by the huge weight of ice sheets during the last glacial period, through a process known as isostatic depression. Post-glacial rebound and isostatic depression are different parts of a process known as either glacial isostasy, glacial isostatic adjustment, or glacioisostasy. Glacioisostasy is the solid Earth deformation associated with changes in ice mass distribution. The most obvious and direct affects of post-glacial rebound are readily apparent in northern Europe (especially Scotland, Estonia, Latvia, Fennoscandia, and northern Denmark), Siberia, Canada, the Great Lakes of Canada and the United States, the coastal region of the US state of Maine, parts of Patagonia, and Antarctica. However, through processes known as ocean siphoning and continental levering, the effects of post-glacial rebound on sea-level are felt globally far from the locations of current and former ice sheets.