What is Weather.
... Others … He, H, neon, ozone and krypton. This air thins out quickly as you increase altitude. Air always contains some water vapor. Humidity. ...
... Others … He, H, neon, ozone and krypton. This air thins out quickly as you increase altitude. Air always contains some water vapor. Humidity. ...
Final Exam Study Guide Terms Constantinople Republic Confucius
... Climate changes gradually over time. During the last one to two million years, for example, the earth passed through four eras when large areas were covered with glaciers. Geographers have developed several possible explanations for what caused glacial eras in history. One explanation is that variat ...
... Climate changes gradually over time. During the last one to two million years, for example, the earth passed through four eras when large areas were covered with glaciers. Geographers have developed several possible explanations for what caused glacial eras in history. One explanation is that variat ...
ps 2-7-08 - elyceum-beta
... • Build Mountains • Keep building as long as pushing occurs • No volcanos ...
... • Build Mountains • Keep building as long as pushing occurs • No volcanos ...
Study Guide Answers
... Oceanic crust is denser so when it converges with the continental plate causes subduction. The oceanic plate melts and convection currents recycle it back to point A 5. What is the main cause for earthquakes and volcanoes? Plate tectonics, plate movement, one plate moving past another either by conv ...
... Oceanic crust is denser so when it converges with the continental plate causes subduction. The oceanic plate melts and convection currents recycle it back to point A 5. What is the main cause for earthquakes and volcanoes? Plate tectonics, plate movement, one plate moving past another either by conv ...
The Dunedin Volcano
... Use the resource “The Dunedin Volcano” to answer the following questions. Include pictures sourced from the internet where appropriate (eg harbour cone). ALL pictures should have a caption. 1a. What kind of volcano is the Dunedin Volcano? 1b. How long has it been extinct for? 2. Fill in the gaps: Be ...
... Use the resource “The Dunedin Volcano” to answer the following questions. Include pictures sourced from the internet where appropriate (eg harbour cone). ALL pictures should have a caption. 1a. What kind of volcano is the Dunedin Volcano? 1b. How long has it been extinct for? 2. Fill in the gaps: Be ...
Atmospheric
... envelope of transparent, odourless gases held to the earth by gravitational attraction. Most of our weather happens in the first 16km ( it extends to ...
... envelope of transparent, odourless gases held to the earth by gravitational attraction. Most of our weather happens in the first 16km ( it extends to ...
8.4 Earth`s Layers
... Lithosphere – Earth’s outermost layer that consists of the crust and uppermost mantle. It forms a relatively cool, rigid shell Asthenosphere – located below the lithosphere. Relatively soft, and weaker layer. Warmer than the lithosphere ...
... Lithosphere – Earth’s outermost layer that consists of the crust and uppermost mantle. It forms a relatively cool, rigid shell Asthenosphere – located below the lithosphere. Relatively soft, and weaker layer. Warmer than the lithosphere ...
Click on image to content
... Plate Tectonics means that the crust of the earth is divided into large connected units, all of which are moving relative to one another and colliding with one another in various ways. The idea of Plate Tectonics was first published by the German geologist, Alfred Wegener in 1915 but this theory was ...
... Plate Tectonics means that the crust of the earth is divided into large connected units, all of which are moving relative to one another and colliding with one another in various ways. The idea of Plate Tectonics was first published by the German geologist, Alfred Wegener in 1915 but this theory was ...
Backward Design Learning Plan - UNC
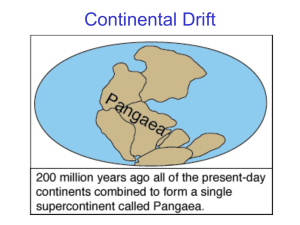
... The theory of continental drift was not accepted until the 1960s because scientists were not sure what force could move continents and how the could move without shattering (they thought the continents plowed through the sea floor). With the invention of SONAR, scientists discovered that the ocean f ...
... The theory of continental drift was not accepted until the 1960s because scientists were not sure what force could move continents and how the could move without shattering (they thought the continents plowed through the sea floor). With the invention of SONAR, scientists discovered that the ocean f ...
Name
... the exact distance between the satellites and the ground station. Over time, these distances change slightly. By recording the time it takes for the GPS ground stations to move a given distance, scientists can measure the speed at which each tectonic plate moves. What happens when plates separate on ...
... the exact distance between the satellites and the ground station. Over time, these distances change slightly. By recording the time it takes for the GPS ground stations to move a given distance, scientists can measure the speed at which each tectonic plate moves. What happens when plates separate on ...
study guide – unit 9 – plate tectonics
... magnetic reversal: magnetic minerals create same pattern on both sides, Earth’s polarity has reversed ...
... magnetic reversal: magnetic minerals create same pattern on both sides, Earth’s polarity has reversed ...
Slide 1
... A volcano is an opening (or rupture) in the Earth's surface or crust, which allows hot, molten rock, ash, and gases to escape from deep below the surface. Volcanic activity involving the extrusion of rock tends to form mountains or features like mountains over a period of time. Volcanoes are genera ...
... A volcano is an opening (or rupture) in the Earth's surface or crust, which allows hot, molten rock, ash, and gases to escape from deep below the surface. Volcanic activity involving the extrusion of rock tends to form mountains or features like mountains over a period of time. Volcanoes are genera ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Introduction to Earthquakes EASA
... ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ...
... ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ...
Great Ideas in Science: Lecture 9 – Earth as a Planet
... Air mass: Uniform temperature and moisture Weather: State of the atmosphere Climate: Long-term average of weather ...
... Air mass: Uniform temperature and moisture Weather: State of the atmosphere Climate: Long-term average of weather ...
Chemistry C1a file
... An experiment where the mixture of gases believed to be present in the early atmosphere were mixed together and given a high voltage spark to simulate lightning What did they find? They found that they could produce the building blocks of life know as amino acids Why was this not definite proof ...
... An experiment where the mixture of gases believed to be present in the early atmosphere were mixed together and given a high voltage spark to simulate lightning What did they find? They found that they could produce the building blocks of life know as amino acids Why was this not definite proof ...
The Forces of Weathering and Erosion
... night, the rock’s surface cools. The repeated change from hot to cold may cause the rock to peel or flake layers that are parallel to the rock’s surface. This peeling or flaking is known as exfoliation. ...
... night, the rock’s surface cools. The repeated change from hot to cold may cause the rock to peel or flake layers that are parallel to the rock’s surface. This peeling or flaking is known as exfoliation. ...
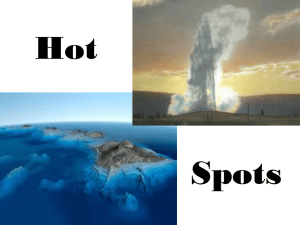
Hot Spots
... constant, as the plate continues to move over it. • The result is a trail of volcanoes left behind, with older volcanoes moving away from the hot spot, and newer ones forming over top of the hot spot. ...
... constant, as the plate continues to move over it. • The result is a trail of volcanoes left behind, with older volcanoes moving away from the hot spot, and newer ones forming over top of the hot spot. ...
Pachamama Geography Consultants
... from MT. Rainer National Park. Sections of the town are composed of solidified mud flows that originated on Mt.Ranier. ...
... from MT. Rainer National Park. Sections of the town are composed of solidified mud flows that originated on Mt.Ranier. ...
Tectonic–climatic interaction

Tectonic–climatic interaction is the interrelationship between tectonic processes and the climate system. The tectonic processes in question include orogenesis, volcanism, and erosion, while relevant climatic processes include atmospheric circulation, orographic lift, monsoon circulation and the rain shadow effect. As the geological record of past climate changes over millions of years is sparse and poorly resolved, many questions remain unresolved regarding the nature of tectonic-climate interaction, although it is an area of active research by geologists and palaeoclimatologists.