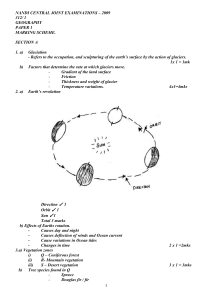
nandi central joint examinations – 2009
... frictional drag on that crustal rocks forcing them to move. When continental coast are pulled towards each other they force sediments between them to fold Folding of such sediments leads to formation of folds that have often caused the formation of fold mountains. (3x1marks) d) Significance of foldi ...
... frictional drag on that crustal rocks forcing them to move. When continental coast are pulled towards each other they force sediments between them to fold Folding of such sediments leads to formation of folds that have often caused the formation of fold mountains. (3x1marks) d) Significance of foldi ...
Sample
... 4. What does a porphyritic texture indicate about the history of an igneous rock? Porphyritic texture tells a more complicated cooling history of the magma/lava. A melt that has already formed large crystals at some depth will continue to cool and crystallize more rapidly if it then erupts at surfac ...
... 4. What does a porphyritic texture indicate about the history of an igneous rock? Porphyritic texture tells a more complicated cooling history of the magma/lava. A melt that has already formed large crystals at some depth will continue to cool and crystallize more rapidly if it then erupts at surfac ...
Land Formations - Library Video Company
... deep trenches — Long and re l a t i ve ly narrow underwater va l l eys. Deep ocean trenches are formed where one plate slides under another. mountains — Natural land formations with steep slopes and a peak that rise above the surrounding landscape to high elevations. volcano — An opening in the Eart ...
... deep trenches — Long and re l a t i ve ly narrow underwater va l l eys. Deep ocean trenches are formed where one plate slides under another. mountains — Natural land formations with steep slopes and a peak that rise above the surrounding landscape to high elevations. volcano — An opening in the Eart ...
Slide 1
... Earth’s mantle and crust generate regions of uplift and subsidence, which respectively act as sources and sinks for sediment. Weathering and erosion processes acting on bedrock exposed in uplifted regions are strongly controlled by climate and topography. ...
... Earth’s mantle and crust generate regions of uplift and subsidence, which respectively act as sources and sinks for sediment. Weathering and erosion processes acting on bedrock exposed in uplifted regions are strongly controlled by climate and topography. ...
03-10_plate_invest_worksheet10.v2
... To complete this worksheet, see the instructions in the textbook (Chapter 3 Investigation). Table 1. Plate Boundaries of an Unknown Ocean and Continents This perspective view shows two continents, labeled A and B, separated by an ocean. Use the topography to identify possible plate boundaries and ...
... To complete this worksheet, see the instructions in the textbook (Chapter 3 Investigation). Table 1. Plate Boundaries of an Unknown Ocean and Continents This perspective view shows two continents, labeled A and B, separated by an ocean. Use the topography to identify possible plate boundaries and ...
Study Guide Geology 303, SDSU Spring PEOPLE for TEST 1: 1
... particles or radiation and energy is released. Source of energy keeping Earth’s interior hot. The early Earth was transformed by this heat along with impact and gravitational energy. 18.(2)-ridge: A volcanic mountain range that lies along the spreading centers on the floors of the oceans. 19.(2)-sea ...
... particles or radiation and energy is released. Source of energy keeping Earth’s interior hot. The early Earth was transformed by this heat along with impact and gravitational energy. 18.(2)-ridge: A volcanic mountain range that lies along the spreading centers on the floors of the oceans. 19.(2)-sea ...
12.2 Note Outline
... When tectonic plates move apart (diverge), rifts (on land) and ridges (under the ocean) widen. When tectonic plates move past each other at a transform boundary, pressure may build until an earthquake releases the pressure. Volcanoes occur at tectonic plate boundaries or over geologic hot spots. ...
... When tectonic plates move apart (diverge), rifts (on land) and ridges (under the ocean) widen. When tectonic plates move past each other at a transform boundary, pressure may build until an earthquake releases the pressure. Volcanoes occur at tectonic plate boundaries or over geologic hot spots. ...
Q. What is the concept of plate tectonics theory?
... - It is a scientific theory which describes the large scale motion of Earth’s lithosphere. The theory builds on the older concepts of continental drift developed by Alfred Wegner and seafloor spreading. Where the plates are relatively moving towards each others and changing their sizes and shapes. T ...
... - It is a scientific theory which describes the large scale motion of Earth’s lithosphere. The theory builds on the older concepts of continental drift developed by Alfred Wegner and seafloor spreading. Where the plates are relatively moving towards each others and changing their sizes and shapes. T ...
Metamorphic Rocks
... Extreme pressure may also lead to foliation, the flat layers that form in rocks as the rocks are squeezed by pressure ( Figure 1.1). Foliation normally forms when pressure is exerted in only one direction. Metamorphic rocks may also be non-foliated. Quartzite and marble, shown in the concept "Metamo ...
... Extreme pressure may also lead to foliation, the flat layers that form in rocks as the rocks are squeezed by pressure ( Figure 1.1). Foliation normally forms when pressure is exerted in only one direction. Metamorphic rocks may also be non-foliated. Quartzite and marble, shown in the concept "Metamo ...
Second Hour Exam, Fall, 2007
... 18. "Greenstone belts" in the continental shields are often important mining areas, but in the history of the Earth represent ancient a. island arc systems. c. oceanic crust (ophiolites). b. segments of the MORRS. d. remnants of continental blocks. 19. Which of the following earthquake predictors is ...
... 18. "Greenstone belts" in the continental shields are often important mining areas, but in the history of the Earth represent ancient a. island arc systems. c. oceanic crust (ophiolites). b. segments of the MORRS. d. remnants of continental blocks. 19. Which of the following earthquake predictors is ...
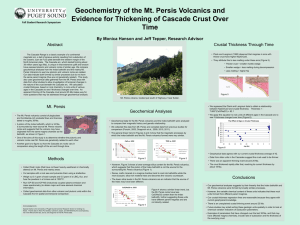
hanson_summer_2011_poster - Sound Ideas
... 38 million years ago (Ma), is unique in that extensive uplift and erosion have exposed plutonic and volcanic rocks of similar age. We compare geochemical analyses from the Index batholith and the nearby Mt. Persis Volcanics to see how plutonic and volcanic rocks are related. Our data indicate both f ...
... 38 million years ago (Ma), is unique in that extensive uplift and erosion have exposed plutonic and volcanic rocks of similar age. We compare geochemical analyses from the Index batholith and the nearby Mt. Persis Volcanics to see how plutonic and volcanic rocks are related. Our data indicate both f ...
Makayla Vogel
... place is the famous San Andreas Fault. The San Andreas Fault is a strikeslip boundary. Even though it has some earthquakes it has very little ones to add to it. It has had some that are over 4.0. The San Andreas Fault lives on the Pacific and Northern Plate. The easiest way to find out which area is ...
... place is the famous San Andreas Fault. The San Andreas Fault is a strikeslip boundary. Even though it has some earthquakes it has very little ones to add to it. It has had some that are over 4.0. The San Andreas Fault lives on the Pacific and Northern Plate. The easiest way to find out which area is ...
Oceanic Crust
... convergent, divergent and transform. • Wegener hypothesized that continents drifted apart from one another and did so in the past. • As tectonic plates separate, the sea-floor spreads apart and magma fills in the new gap. • Magnetic reversals is one way to measure the age and movement of the tectoni ...
... convergent, divergent and transform. • Wegener hypothesized that continents drifted apart from one another and did so in the past. • As tectonic plates separate, the sea-floor spreads apart and magma fills in the new gap. • Magnetic reversals is one way to measure the age and movement of the tectoni ...
Volcanoes, Earthquakes, Islands . . . Oh My!
... What lies beneath the tectonic plates? • Below the lithosphere is the asthenosphere, a layer that is solid, but flows. ...
... What lies beneath the tectonic plates? • Below the lithosphere is the asthenosphere, a layer that is solid, but flows. ...
Faults, Fossils, Rocks and Minerals Review:
... 13. Tell where the thermal energy for the rock cycle originates? ...
... 13. Tell where the thermal energy for the rock cycle originates? ...
Tectonic–climatic interaction

Tectonic–climatic interaction is the interrelationship between tectonic processes and the climate system. The tectonic processes in question include orogenesis, volcanism, and erosion, while relevant climatic processes include atmospheric circulation, orographic lift, monsoon circulation and the rain shadow effect. As the geological record of past climate changes over millions of years is sparse and poorly resolved, many questions remain unresolved regarding the nature of tectonic-climate interaction, although it is an area of active research by geologists and palaeoclimatologists.