Benchmark 3 Answer Key
... 16. What geological features are created at convergent boundaries with subduction? Volcanic islands, volcanoes, trenches 17. What causes plate tectonic movement? Convection currents and heat 18. What are plates that move beneath another plate called? Why does this occur? Subduction… it happens becau ...
... 16. What geological features are created at convergent boundaries with subduction? Volcanic islands, volcanoes, trenches 17. What causes plate tectonic movement? Convection currents and heat 18. What are plates that move beneath another plate called? Why does this occur? Subduction… it happens becau ...
PlateTec1617 - Biloxi Public Schools
... middle of a tectonic plate located beneath a plate remains in one place as plate above it moves creates chain of small volcanoes no longer active when not over the hot spot Hawaiian Islands--different ages of islands a wave of energy that travels away from the center of an earthquake in all directio ...
... middle of a tectonic plate located beneath a plate remains in one place as plate above it moves creates chain of small volcanoes no longer active when not over the hot spot Hawaiian Islands--different ages of islands a wave of energy that travels away from the center of an earthquake in all directio ...
Petrography of Basaltic Rocks Field Relations
... • Typically more evolved composition than MORB – Higher Si, K, Ti, P, and Ba – Lower Mg, and Ni • Evolved, olivine-poor compositions – Suggest some fractionation prior to eruption ...
... • Typically more evolved composition than MORB – Higher Si, K, Ti, P, and Ba – Lower Mg, and Ni • Evolved, olivine-poor compositions – Suggest some fractionation prior to eruption ...
3_GC1_Plates2_09
... 3. HOW DOES THE FORMATION OF NEW OCEAN FLOOR RELATE TO THE DEFORMATION OF THE EARTH’S ...
... 3. HOW DOES THE FORMATION OF NEW OCEAN FLOOR RELATE TO THE DEFORMATION OF THE EARTH’S ...
Igneous Rocks Power Point
... Shore, some of the best places to hunt for agates are in gravel pits scattered across the state. • Agates can be found where there are gravel deposits associated ...
... Shore, some of the best places to hunt for agates are in gravel pits scattered across the state. • Agates can be found where there are gravel deposits associated ...
The age of the Solar system
... - Atmosphere rich in carbon dioxide, no oxygen - Probably no water 9. How was the atmosphere changed 2 billion years after the earth’s formation? - The tiny blue-green algae (a life-form very important in the evolution of life on Earth) takes in the carbon dioxide from the environment and releases o ...
... - Atmosphere rich in carbon dioxide, no oxygen - Probably no water 9. How was the atmosphere changed 2 billion years after the earth’s formation? - The tiny blue-green algae (a life-form very important in the evolution of life on Earth) takes in the carbon dioxide from the environment and releases o ...
Lesson 11 - Subduction Boundary Volcanism
... At trenches, ocean floor bends and moves downward into the upper mantle. At depths of 100 km partial melting of the ocean crust and mantle takes place. Basaltic and andesitic magmas are produced at subduction zones. After great quantities of magma are produced, the molten rock moves upward tow ...
... At trenches, ocean floor bends and moves downward into the upper mantle. At depths of 100 km partial melting of the ocean crust and mantle takes place. Basaltic and andesitic magmas are produced at subduction zones. After great quantities of magma are produced, the molten rock moves upward tow ...
Science Study Guide - Thomas C. Cario Middle School
... P-Waves move back and forth. S-Waves move at right angles to direction. Surface Waves move in a side-to-side swaying motion. 13. Which waves can go through liquids or solids? P Waves 14. Explain the Ring of Fire. Plate boundaries around the Pacific Ocean where there are many volcanoes and earthquake ...
... P-Waves move back and forth. S-Waves move at right angles to direction. Surface Waves move in a side-to-side swaying motion. 13. Which waves can go through liquids or solids? P Waves 14. Explain the Ring of Fire. Plate boundaries around the Pacific Ocean where there are many volcanoes and earthquake ...
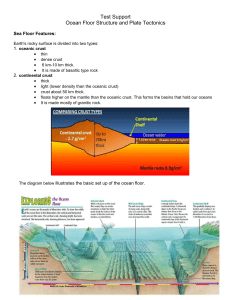
Unit 5: Ocean Floor Structure and Plate Tectonics
... a seamount with a flat top created by wave action when the seamount was at sea level ...
... a seamount with a flat top created by wave action when the seamount was at sea level ...
Mantle Convection
... generated from Earth’s interior. A convection current occurs when a liquid or gas is heated, becomes less dense, and rises. When cooling makes the liquid or gas dense again, it eventually sinks. This cyclical process forms a convection cell, with material within the cell continually moving in respon ...
... generated from Earth’s interior. A convection current occurs when a liquid or gas is heated, becomes less dense, and rises. When cooling makes the liquid or gas dense again, it eventually sinks. This cyclical process forms a convection cell, with material within the cell continually moving in respon ...
Tect.EQ.Oceans.S04 - SC4 Geography MainPage
... flat areas of the ocean floor that are on the continental shelf flat areas of the ocean floor that are in very deep water flat areas of the moon Surface waves on the ocean are typically caused by: ...
... flat areas of the ocean floor that are on the continental shelf flat areas of the ocean floor that are in very deep water flat areas of the moon Surface waves on the ocean are typically caused by: ...
Chapter 9: Earth`s Changing Surface
... a. Sand on the beach is created by waves which are a source of erosion and deposition. b. The constant action of waves is a major source of erosion along shorelines. c. Harbors and inlets form when some areas erode more quickly than others. d. Deltas are a place where heavy sediments are deposited w ...
... a. Sand on the beach is created by waves which are a source of erosion and deposition. b. The constant action of waves is a major source of erosion along shorelines. c. Harbors and inlets form when some areas erode more quickly than others. d. Deltas are a place where heavy sediments are deposited w ...
earth space science review problem sheet
... ___ 8. What plate boundary involves plates moving together and is associated with the formation of mountain ranges? a. subduction zone b. divergent boundary c. convergent boundary d. transform boundary ___ 9. One major agent of erosion that has shaped Earth’s land surface is a. mass movement. b. mov ...
... ___ 8. What plate boundary involves plates moving together and is associated with the formation of mountain ranges? a. subduction zone b. divergent boundary c. convergent boundary d. transform boundary ___ 9. One major agent of erosion that has shaped Earth’s land surface is a. mass movement. b. mov ...
Inside the Restless Earth
... 11. Draw and label a diagram of each of the three main types of plate boundaries. Use arrows to show direction plate is moving. ...
... 11. Draw and label a diagram of each of the three main types of plate boundaries. Use arrows to show direction plate is moving. ...
Rock Cycle
... 21. __________ is the process by which sediments get pressed together. 22. Sand grains, pebbles, mud, shells and leaves are all examples of ____________. 23. Any rock formed when another rock is changed by heat or _________ is a metamorphic rock. 24. The series of processes that slowly change Earth’ ...
... 21. __________ is the process by which sediments get pressed together. 22. Sand grains, pebbles, mud, shells and leaves are all examples of ____________. 23. Any rock formed when another rock is changed by heat or _________ is a metamorphic rock. 24. The series of processes that slowly change Earth’ ...
Chapter 10 Section 3
... and is the driving force for plate tectonics. It is also known as the cycle of heating, rising, and cooling. ...
... and is the driving force for plate tectonics. It is also known as the cycle of heating, rising, and cooling. ...
Minerals • Mineral is a substance that is: • Solid • Formed in Nature
... o Line – changes over time o Bar – compare sets of data o Histogram – show ranges of large sets of data ...
... o Line – changes over time o Bar – compare sets of data o Histogram – show ranges of large sets of data ...
Final Review - Academic Computer Center
... The greater the grain size of an Earth material sample, the greater the water ...
... The greater the grain size of an Earth material sample, the greater the water ...
Background
... ROCKS In other cases, the accumulation of large amounts of dead plant material may, over millions of years, turn into coal which is another type of sedimentary rock It may be that some dead sea creatures are not fragmented and become buried in their original condition. When this happens they can bec ...
... ROCKS In other cases, the accumulation of large amounts of dead plant material may, over millions of years, turn into coal which is another type of sedimentary rock It may be that some dead sea creatures are not fragmented and become buried in their original condition. When this happens they can bec ...
cenozoic1
... This sedimentary material is more easily eroded than crystalline rock, so the eastern boundary is a “fall zone”, where the gradients of rivers steepen suddenly as they dig into the softer material of the coastal plain. ...
... This sedimentary material is more easily eroded than crystalline rock, so the eastern boundary is a “fall zone”, where the gradients of rivers steepen suddenly as they dig into the softer material of the coastal plain. ...
Rocks
... ________________ – rocks are made of mixtures of minerals and other materials. Some contain a single mineral. Others contain several minerals. _________ – color provides clues to the rock’s mineral composition. (Ex: granite = light basalt = dark) _________- the look and feel of the rock’s surface. T ...
... ________________ – rocks are made of mixtures of minerals and other materials. Some contain a single mineral. Others contain several minerals. _________ – color provides clues to the rock’s mineral composition. (Ex: granite = light basalt = dark) _________- the look and feel of the rock’s surface. T ...
Tectonic–climatic interaction

Tectonic–climatic interaction is the interrelationship between tectonic processes and the climate system. The tectonic processes in question include orogenesis, volcanism, and erosion, while relevant climatic processes include atmospheric circulation, orographic lift, monsoon circulation and the rain shadow effect. As the geological record of past climate changes over millions of years is sparse and poorly resolved, many questions remain unresolved regarding the nature of tectonic-climate interaction, although it is an area of active research by geologists and palaeoclimatologists.