* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lesson 11 - Subduction Boundary Volcanism
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Deep sea community wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
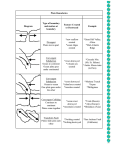
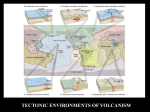
Plate Boundary Volcanism Volcanoes are associated with two of the three types of plate boundaries, these being convergent and divergent boundaries. Very little volcanic activity is seen at transform fault boundaries. Volcanism associated with plate tectonic activity are found in three areas on Earth; 1) Ridges (or spreading centers) Reference: 2) Subduction zones 3) Interior of tectonic plates. Tarbuck and Lutgens Pages 232 - 235 Subduction Zone Volcanism At trenches, ocean floor bends and moves downward into the upper mantle. At depths of 100 km partial melting of the ocean crust and mantle takes place. Basaltic and andesitic magmas are produced at subduction zones. After great quantities of magma are produced, the molten rock moves upward toward the surface because it is less dense than the surrounding rock. Ocean – Ocean convergent boundaries and Ocean – Continent convergent boundaries have this type of volcanism. Subduction Zone Volcanism 1) Ocean – Ocean Volcanism Ocean crust subducts beneath ocean crust. Basaltic magmas are produced and burns upward toward the surface forming a chain of volcanoes called a “volcanic island arc” parallel to the trench. Examples include; Islands of Japan. Ocean Plate Asthenosphere Ocean Plate Subduction Zone Volcanism 2) Ocean – Continent Volcanism Ocean crust subducts beneath continental crust. Andesitic and Granitic magmas burns upward into the continental crust adding to mountain systems. This type of volcanism is very explosive and is mainly found surrounding the Pacific Ocean. Examples include; volcanoes in the Andes mountains. Ocean Plate Asthenosphere Continental Plate Subduction Zone Volcanism 2) Ocean – Continent Volcanism At a depths of 100 km, the subducting ocean crust starts to melt. This generates magmas that are thick and contains large amounts of gases. As a result, subduction eruptions at ocean-continent boundaries are very explosive and produce composite volcanic cones. most of the world’s volcanoes are of this type and border the Pacific Ocean, called the Pacific Ring of Fire. Ocean Plate Asthenosphere Continental Plate Sample Problem With the aid of a diagram describe the volcanic features formed at a ocean-ocean convergent boundary. Answer: At an ocean-ocean convergent boundary, one oceanic plate subducts beneath another and melts when it descends into the mantle at approximately 100km depth. This molten material moves up through the oceanic plate located above and erupts onto the ocean floor. This forms a chain of volcanic islands parallel to the trench called a “volcanic island arc.” Ocean Plate Asthenosphere Ocean Plate