Power Point print view
... • As the plate subducts into the mantle, – it is heated and partially melted – generating magma of ~ andesitic composition – that rises to the surface – because it is less dense than the surrounding ...
... • As the plate subducts into the mantle, – it is heated and partially melted – generating magma of ~ andesitic composition – that rises to the surface – because it is less dense than the surrounding ...
Lecture 4:the observed mean circulation
... •The strong currents on the western side of ocean basins transport warm water from low to high latitude in the subtropics and cool water from high to low latitudes in the subpolar regions. ...
... •The strong currents on the western side of ocean basins transport warm water from low to high latitude in the subtropics and cool water from high to low latitudes in the subpolar regions. ...
seafloor-spreading
... relationship between heat flow rate and distance from the mid ocean ridge? A) ...
... relationship between heat flow rate and distance from the mid ocean ridge? A) ...
Mantle flow drives the subsidence of oceanic plates - HAL
... In order to test that the structure of the oceanic lithosphere is indeed determined by the underlying mantle convection, we analyzed more than 770 depth profiles, leading to a complete coverage of the Pacific plate (23). Several kinematic models have been tested to compute the trajectories represen ...
... In order to test that the structure of the oceanic lithosphere is indeed determined by the underlying mantle convection, we analyzed more than 770 depth profiles, leading to a complete coverage of the Pacific plate (23). Several kinematic models have been tested to compute the trajectories represen ...
seafloor-spreading
... relationship between heat flow rate and distance from the mid ocean ridge? A) ...
... relationship between heat flow rate and distance from the mid ocean ridge? A) ...
Plate Tectonics - Londonderry School District
... Coal exists under the ice in the rock of Antarctica – yet coal can only form from plants that grow in warm climates. ...
... Coal exists under the ice in the rock of Antarctica – yet coal can only form from plants that grow in warm climates. ...
the earth`s life support systems - sohs
... • Tends to wear down Earth’s surface and produce a variety of landforms by the buildup of eroded sediment ...
... • Tends to wear down Earth’s surface and produce a variety of landforms by the buildup of eroded sediment ...
8_Plate_Tectonics_n_Layers_of_the_Earth
... 1. The continental crust is composed of granite while the oceanic crust is composed of basalt. 2. The density of the continental crust is less than the oceanic crust, thus it floats higher on the mantle. ...
... 1. The continental crust is composed of granite while the oceanic crust is composed of basalt. 2. The density of the continental crust is less than the oceanic crust, thus it floats higher on the mantle. ...
Theory of Plate Tectonics
... As two tectonic plates slowly separate, molten material rises from within the mantle to fill the opening. As the ocean floor slowly separates, new rocks form at the mid-ocean ridge that is ...
... As two tectonic plates slowly separate, molten material rises from within the mantle to fill the opening. As the ocean floor slowly separates, new rocks form at the mid-ocean ridge that is ...
Three distinct margins of the North American and Eurasian Plates
... Lecture 8. Historic Earthquakes I: San Francisco 1906, Alaska 1964, Lisbon 1755 Three distinct margins of the North American and Eurasian Plates 1. San Francisco, CA: 18 April 1906 [“Earthquake City”] Fault & Plate Tectonics San Andreas Fault (NW-trending, 1200 km long, Right-Lateral Strike-Slip Fau ...
... Lecture 8. Historic Earthquakes I: San Francisco 1906, Alaska 1964, Lisbon 1755 Three distinct margins of the North American and Eurasian Plates 1. San Francisco, CA: 18 April 1906 [“Earthquake City”] Fault & Plate Tectonics San Andreas Fault (NW-trending, 1200 km long, Right-Lateral Strike-Slip Fau ...
File - Champion`s Champs
... Ponds and Lakes range in size from just a few square meters to thousands of square kilometers ponds may be seasonal, lasting just a couple of months (such as sessile pools) lakes may exist for hundreds of years or more may have limited species diversity since they are often isolated from one anothe ...
... Ponds and Lakes range in size from just a few square meters to thousands of square kilometers ponds may be seasonal, lasting just a couple of months (such as sessile pools) lakes may exist for hundreds of years or more may have limited species diversity since they are often isolated from one anothe ...
Plate Tectonics _2010
... • Where lithospheric plates are moving towards one another at their boundary, lithospheric area must be consumed. This is accomplished by subduction or thickening and delamination. ...
... • Where lithospheric plates are moving towards one another at their boundary, lithospheric area must be consumed. This is accomplished by subduction or thickening and delamination. ...
The Theory of Plate Tectonics
... Earth’s lithosphere (the crust and the upper mantle) is broken into separate sections called plates. The plates fit closely together along cracks in the crust. They carry the continents, or parts of the ocean floor, or both. The geological theory of plate tectonics states that pieces of Earth’s lith ...
... Earth’s lithosphere (the crust and the upper mantle) is broken into separate sections called plates. The plates fit closely together along cracks in the crust. They carry the continents, or parts of the ocean floor, or both. The geological theory of plate tectonics states that pieces of Earth’s lith ...
continental drift theory Now called PLATE TECTONICS
... • Transform faults – occur when plates slide past one another along a fracture (fault) in the lithosphere ...
... • Transform faults – occur when plates slide past one another along a fracture (fault) in the lithosphere ...
Intertidal Zone
... disposal can harm species that feed on the ocean's bottom. Manmade or natural oil seepage can clog tidepool animals so they are unable to live or avoid being eaten. Careless tidepool explorers can crush animals and leave others exposed. Unfortunately, the intertidal zone is a place where changes to ...
... disposal can harm species that feed on the ocean's bottom. Manmade or natural oil seepage can clog tidepool animals so they are unable to live or avoid being eaten. Careless tidepool explorers can crush animals and leave others exposed. Unfortunately, the intertidal zone is a place where changes to ...
File
... lower solid layer of the mantle. The movement of the uuper mantle (asthenosphere) is the reason that the crustal plates of the Earth move. ...
... lower solid layer of the mantle. The movement of the uuper mantle (asthenosphere) is the reason that the crustal plates of the Earth move. ...
Oceans, Lakes and Coasts
... Rotation deflects prevailing winds and currents. The sense of deflection depends upon the initial direction of motion and the position relative to the equator. A projectile shot from the North Pole to the ! equator deflects to the west. Winds and ! currents moving north to south are likewise deflect ...
... Rotation deflects prevailing winds and currents. The sense of deflection depends upon the initial direction of motion and the position relative to the equator. A projectile shot from the North Pole to the ! equator deflects to the west. Winds and ! currents moving north to south are likewise deflect ...
File
... Why is molten magma rising to the surface at divergent plate boundaries? A. because it is more dense than the hotter rock around it B. because it is affected by anti-gravity C. because it is less dense than the cooler rock surrounding ...
... Why is molten magma rising to the surface at divergent plate boundaries? A. because it is more dense than the hotter rock around it B. because it is affected by anti-gravity C. because it is less dense than the cooler rock surrounding ...
Plate Tectonics - Welcome to Ms. Duff's Classroom!
... Difference between continental drift & plate tectonics. Evidence used to support plate tectonics. Earth’s oceanic crust is broken into 7 large (& several smaller) pieces or “plates”; pieces of continental crust “ride” on some of these plates ...
... Difference between continental drift & plate tectonics. Evidence used to support plate tectonics. Earth’s oceanic crust is broken into 7 large (& several smaller) pieces or “plates”; pieces of continental crust “ride” on some of these plates ...
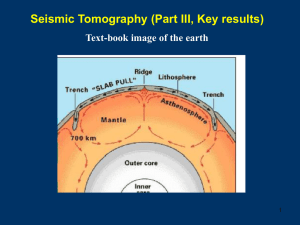
lecture7_tomo
... 2. Other arcs show the effect of addition of different continental components to source, most likely Atlantic sediment (Antilles) or Pacific sediment (Banda, New Zealand). The basaltic lavas are more enriched in radioactive elements (more “original” or “primordial”) and more gassed. These are often ...
... 2. Other arcs show the effect of addition of different continental components to source, most likely Atlantic sediment (Antilles) or Pacific sediment (Banda, New Zealand). The basaltic lavas are more enriched in radioactive elements (more “original” or “primordial”) and more gassed. These are often ...
GSL abstract, K. H. James
... 1555049: crystalline crust thins significantly across the continental shelf and Florida Escarpment from ~25 km to ~7 km in the deep-water eastern Gulf of Mexico. Multi-channel seismic reflection data coincident to GUMBO 3 displays seaward-dipping reflectors (SDRs) within this zone of crustal thinnin ...
... 1555049: crystalline crust thins significantly across the continental shelf and Florida Escarpment from ~25 km to ~7 km in the deep-water eastern Gulf of Mexico. Multi-channel seismic reflection data coincident to GUMBO 3 displays seaward-dipping reflectors (SDRs) within this zone of crustal thinnin ...
Continental Drift and Sea Floor Spreading Notes
... developed the idea that the continents had been once joined together in one land mass? 2) What was the name given to supercontinent that once existed? 3) The idea that the continents have slowly shifted over time is know as ________. 4-5) Give two pieces of evidence used to support this theory. 6) W ...
... developed the idea that the continents had been once joined together in one land mass? 2) What was the name given to supercontinent that once existed? 3) The idea that the continents have slowly shifted over time is know as ________. 4-5) Give two pieces of evidence used to support this theory. 6) W ...
Abyssal plain
An abyssal plain is an underwater plain on the deep ocean floor, usually found at depths between 3000 and 6000 m. Lying generally between the foot of a continental rise and a mid-ocean ridge, abyssal plains cover more than 50% of the Earth’s surface. They are among the flattest, smoothest and least explored regions on Earth. Abyssal plains are key geologic elements of oceanic basins (the other elements being an elevated mid-ocean ridge and flanking abyssal hills). In addition to these elements, active oceanic basins (those that are associated with a moving plate tectonic boundary) also typically include an oceanic trench and a subduction zone.Abyssal plains were not recognized as distinct physiographic features of the sea floor until the late 1940s and, until very recently, none had been studied on a systematic basis. They are poorly preserved in the sedimentary record, because they tend to be consumed by the subduction process. The creation of the abyssal plain is the end result of spreading of the seafloor (plate tectonics) and melting of the lower oceanic crust. Magma rises from above the asthenosphere (a layer of the upper mantle) and as this basaltic material reaches the surface at mid-ocean ridges it forms new oceanic crust. This is constantly pulled sideways by spreading of the seafloor. Abyssal plains result from the blanketing of an originally uneven surface of oceanic crust by fine-grained sediments, mainly clay and silt. Much of this sediment is deposited by turbidity currents that have been channelled from the continental margins along submarine canyons down into deeper water. The remainder of the sediment is composed chiefly of pelagic sediments. Metallic nodules are common in some areas of the plains, with varying concentrations of metals, including manganese, iron, nickel, cobalt, and copper. These nodules may provide a significant resource for future mining ventures.Owing in part to their vast size, abyssal plains are currently believed to be a major reservoir of biodiversity. The abyss also exerts significant influence upon ocean carbon cycling, dissolution of calcium carbonate, and atmospheric CO2 concentrations over timescales of 100–1000 years. The structure and function of abyssal ecosystems are strongly influenced by the rate of flux of food to the seafloor and the composition of the material that settles. Factors such as climate change, fishing practices, and ocean fertilization are expected to have a substantial effect on patterns of primary production in the euphotic zone. This will undoubtedly impact the flux of organic material to the abyss in a similar manner and thus have a profound effect on the structure, function and diversity of abyssal ecosystems.