A short, data oriented summary of
... (shallower water). Even before plate tectonics, this long linear feature was described as a “midocean ridge.” This is because the lithosphere is hottest at a spreading center, so thermal expansion makes its elevation higher. Hot mantle rocks rise into the space left by the separating plates and form ...
... (shallower water). Even before plate tectonics, this long linear feature was described as a “midocean ridge.” This is because the lithosphere is hottest at a spreading center, so thermal expansion makes its elevation higher. Hot mantle rocks rise into the space left by the separating plates and form ...
Activity EarthBeneath 150209
... For the questions below, please use the years on the Timeline Handout that correspond to the time periods listed on the key to the Geologic Map. For example on the Geologic Map, the light blue color by A in the Pacific or Atlantic Ocean is Pliocene (shown on the Ocean Geology Key). Then look up Plio ...
... For the questions below, please use the years on the Timeline Handout that correspond to the time periods listed on the key to the Geologic Map. For example on the Geologic Map, the light blue color by A in the Pacific or Atlantic Ocean is Pliocene (shown on the Ocean Geology Key). Then look up Plio ...
FREE Sample Here
... c. Represents 20 percent of Earth’s surface d. Winds through all major ocean basins ...
... c. Represents 20 percent of Earth’s surface d. Winds through all major ocean basins ...
plate tectonics review
... Notice that ALL of the major plates include both continental and oceanic crust ...
... Notice that ALL of the major plates include both continental and oceanic crust ...
Mantle & Crust
... Rudnick and Fountain, 1995 – first thorough study of upper and lower continental crust Based on seismic velocities, lower crust can be gabbro, ...
... Rudnick and Fountain, 1995 – first thorough study of upper and lower continental crust Based on seismic velocities, lower crust can be gabbro, ...
Plate Tectonics in a Nutshell Name
... the magma cools and solidifies as large bodies of plutonic (intrusive) rocks far below the Earth’s surface. These large bodies or rocks, when later exposed by erosion, commonly form cores of many great mountain ranges [such as the Sierra Nevada (California) or the Andes (South America)] that are cre ...
... the magma cools and solidifies as large bodies of plutonic (intrusive) rocks far below the Earth’s surface. These large bodies or rocks, when later exposed by erosion, commonly form cores of many great mountain ranges [such as the Sierra Nevada (California) or the Andes (South America)] that are cre ...
key terms
... passive continental margin (trailing edge) (183): The void created at divergent plate boundaries by the separating plates is filled with molten rock which rises from below the lithosphere and solidifies in the fissure. New crust is added to the trailing edge of each separating plate as it moves slow ...
... passive continental margin (trailing edge) (183): The void created at divergent plate boundaries by the separating plates is filled with molten rock which rises from below the lithosphere and solidifies in the fissure. New crust is added to the trailing edge of each separating plate as it moves slow ...
seafloorpapermodel_questions1_7
... About 40 years ago, scientists discovered that there are both age and magnetic patterns in the seafloor. This discovery allowed another piece of the puzzle about plate tectonics to fall into place. What scientists found was that new seafloor has continually been forming over millions of years at the ...
... About 40 years ago, scientists discovered that there are both age and magnetic patterns in the seafloor. This discovery allowed another piece of the puzzle about plate tectonics to fall into place. What scientists found was that new seafloor has continually been forming over millions of years at the ...
Oceanography Lecture 15
... Oceans’ depths are filled with cold water (colder than the ~17.5°C average T of the Oceans’ surface waters). ! Most of this water must have originated in polar latitudes, where it was chilled by losing heat to the frigid air. ! Uniformity of T and salinity of subsurface seawater from Ocean to Ocean ...
... Oceans’ depths are filled with cold water (colder than the ~17.5°C average T of the Oceans’ surface waters). ! Most of this water must have originated in polar latitudes, where it was chilled by losing heat to the frigid air. ! Uniformity of T and salinity of subsurface seawater from Ocean to Ocean ...
Name: Date: ______ Block:______ EARTH SYSTEMS QUIZ 1
... d. Rotation of liquid rock found within the core 17. Which layer of Earth’s structure is believed to make up the majority of its mass and volume? a. Mantle b. Magma ...
... d. Rotation of liquid rock found within the core 17. Which layer of Earth’s structure is believed to make up the majority of its mass and volume? a. Mantle b. Magma ...
1 Lecture 14 - Marine Sediments – Formation and Distribution
... Rachel Carson, The Sea Around Us. The sediments deposited in the ocean are an archive of historical information about the Earth and, specifically, they provide information about global biogeochemical cycles. The distribution of sediments in the ocean is determined by biological and chemical processe ...
... Rachel Carson, The Sea Around Us. The sediments deposited in the ocean are an archive of historical information about the Earth and, specifically, they provide information about global biogeochemical cycles. The distribution of sediments in the ocean is determined by biological and chemical processe ...
Ocean - Geological Society of India
... 1. Continental Rise 2. Continental Shelf 3. Abyssal plain 4. Canyon 5. Continental Slope 6. Island arc 7. Volcano 8. Oceanic trench 9. Guyot 10. Seamounts 11. Transform faults 12. Oceanic ridge 13. Volcanic island 14. Continent ...
... 1. Continental Rise 2. Continental Shelf 3. Abyssal plain 4. Canyon 5. Continental Slope 6. Island arc 7. Volcano 8. Oceanic trench 9. Guyot 10. Seamounts 11. Transform faults 12. Oceanic ridge 13. Volcanic island 14. Continent ...
Polymetallic Sulphides - International Seabed Authority
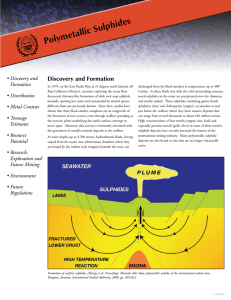
... Most sites have been located in mid-ocean at the East Pacific Rise, the Southeast Pacific Rise and the Northeast Pacific Rise. Several deposits are also known at the Mid-Atlantic Ridge but only one has so far been located at the ridge system of the Indian Ocean. The paucity of known sulphide deposit ...
... Most sites have been located in mid-ocean at the East Pacific Rise, the Southeast Pacific Rise and the Northeast Pacific Rise. Several deposits are also known at the Mid-Atlantic Ridge but only one has so far been located at the ridge system of the Indian Ocean. The paucity of known sulphide deposit ...
Texas Science Grade 8 Investigations
... drags the plates along with it as it moves. The heated material eventually cools enough to begin sinking back toward the core, where the process repeats itself. Different convection cells circulate in different directions, and this is the key to what happens at tectonic plate boundaries. The plates ...
... drags the plates along with it as it moves. The heated material eventually cools enough to begin sinking back toward the core, where the process repeats itself. Different convection cells circulate in different directions, and this is the key to what happens at tectonic plate boundaries. The plates ...
deep ocean/high seas resource use: understanding the legal issues
... The World Ocean Council (WOC) continues to provide information to the ocean business community on the legal and policy aspects of ocean sustainable development. The WOC is pleased to announce the following webinar: Go Deep: The Legal Implications of Deep Ocean Resource Exploration and Extraction Fri ...
... The World Ocean Council (WOC) continues to provide information to the ocean business community on the legal and policy aspects of ocean sustainable development. The WOC is pleased to announce the following webinar: Go Deep: The Legal Implications of Deep Ocean Resource Exploration and Extraction Fri ...
Plate Boundarieskouts
... MARIANAS /JAPAN TRENCH The Marianas/Japan Trench is a converging plate-subduction- boundary that is oceanic to oceanic. The Pacific plate (ocean) is sub ducted underneath the Mariana/Philippine Plate (ocean) ...
... MARIANAS /JAPAN TRENCH The Marianas/Japan Trench is a converging plate-subduction- boundary that is oceanic to oceanic. The Pacific plate (ocean) is sub ducted underneath the Mariana/Philippine Plate (ocean) ...
Possible Biological Consequences of Plate Tectonics
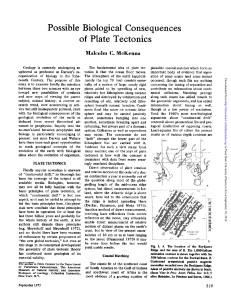
... offset of the ridge segments has been a major confirmation by seismology of the plate tectonics synthesis. First-motion studies of earthquakes occurring along ridge-ridge transform faults confirm the symmetrical spreading of oceanic lithosphere from mid-ocean ridges. Further evidence of the mobility ...
... offset of the ridge segments has been a major confirmation by seismology of the plate tectonics synthesis. First-motion studies of earthquakes occurring along ridge-ridge transform faults confirm the symmetrical spreading of oceanic lithosphere from mid-ocean ridges. Further evidence of the mobility ...
2How Is Continental Movement Explained by Plate Tectonics?
... map. Where are most of these boundaries located? The top picture on the right shows how plates move at a spreading boundary and what the result can be. The Great Rift Valley in Africa is one place where new crust is being added to the earth's surface. As the crust builds up, it forms a wider and dee ...
... map. Where are most of these boundaries located? The top picture on the right shows how plates move at a spreading boundary and what the result can be. The Great Rift Valley in Africa is one place where new crust is being added to the earth's surface. As the crust builds up, it forms a wider and dee ...
marine and esturian ecosystem-2012
... enhanced. The lower specific gravity of sea water is most beneficial to marine organisms. As the sea water contains large number of salts it is a most suitable, environment for living cells. Further it has been found that the ratio of total saIt content of seawater is almost same as that of body flu ...
... enhanced. The lower specific gravity of sea water is most beneficial to marine organisms. As the sea water contains large number of salts it is a most suitable, environment for living cells. Further it has been found that the ratio of total saIt content of seawater is almost same as that of body flu ...
22.4 Plate Tectonics
... sink into the mantle in the process of subduction. Subduction zones are near the edges of oceanic plates. As a plate sinks through a subduction zone, it bends, forming a depression in the ocean floor called a trench. ...
... sink into the mantle in the process of subduction. Subduction zones are near the edges of oceanic plates. As a plate sinks through a subduction zone, it bends, forming a depression in the ocean floor called a trench. ...
The Biosphere - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... determines what organisms live in a place. Key elements include: Temperature. Most organisms are adapted to live within a relatively narrow range of temperatures and will not thrive if temperatures are colder or warmer. The growing season of plants, for example, is importantly influenced by temperat ...
... determines what organisms live in a place. Key elements include: Temperature. Most organisms are adapted to live within a relatively narrow range of temperatures and will not thrive if temperatures are colder or warmer. The growing season of plants, for example, is importantly influenced by temperat ...
Geology First active hydrothermal vents on an ultraslow-spreading center: Southwest Indian Ridge
... The cumulative length of Earth’s ultraslowspreading ridges, where the full seafloor spreading rate is less than 16 mm/yr, is more than 15,000 km, representing ~20% of the global mid-ocean-ridge system (Solomon, 1989). Thus, ultraslow ridges constitute a major component of Earth’s tectonic plate boun ...
... The cumulative length of Earth’s ultraslowspreading ridges, where the full seafloor spreading rate is less than 16 mm/yr, is more than 15,000 km, representing ~20% of the global mid-ocean-ridge system (Solomon, 1989). Thus, ultraslow ridges constitute a major component of Earth’s tectonic plate boun ...
earth-10th-edition-tarbuck-solution-manual
... c. Represents 20 percent of Earth’s surface d. Winds through all major ocean basins ...
... c. Represents 20 percent of Earth’s surface d. Winds through all major ocean basins ...
The reflection seismic survey of project TIPTEQ—the inventory of the
... & Shreve (1988) is a zone with varying thickness above the oceanic crust in which material being transported downwards, exhibits a velocity gradient with respect to both plates. The material flowing within the subduction channel is derived from trench deposits, off scrapings from the base of the upp ...
... & Shreve (1988) is a zone with varying thickness above the oceanic crust in which material being transported downwards, exhibits a velocity gradient with respect to both plates. The material flowing within the subduction channel is derived from trench deposits, off scrapings from the base of the upp ...
Abyssal plain
An abyssal plain is an underwater plain on the deep ocean floor, usually found at depths between 3000 and 6000 m. Lying generally between the foot of a continental rise and a mid-ocean ridge, abyssal plains cover more than 50% of the Earth’s surface. They are among the flattest, smoothest and least explored regions on Earth. Abyssal plains are key geologic elements of oceanic basins (the other elements being an elevated mid-ocean ridge and flanking abyssal hills). In addition to these elements, active oceanic basins (those that are associated with a moving plate tectonic boundary) also typically include an oceanic trench and a subduction zone.Abyssal plains were not recognized as distinct physiographic features of the sea floor until the late 1940s and, until very recently, none had been studied on a systematic basis. They are poorly preserved in the sedimentary record, because they tend to be consumed by the subduction process. The creation of the abyssal plain is the end result of spreading of the seafloor (plate tectonics) and melting of the lower oceanic crust. Magma rises from above the asthenosphere (a layer of the upper mantle) and as this basaltic material reaches the surface at mid-ocean ridges it forms new oceanic crust. This is constantly pulled sideways by spreading of the seafloor. Abyssal plains result from the blanketing of an originally uneven surface of oceanic crust by fine-grained sediments, mainly clay and silt. Much of this sediment is deposited by turbidity currents that have been channelled from the continental margins along submarine canyons down into deeper water. The remainder of the sediment is composed chiefly of pelagic sediments. Metallic nodules are common in some areas of the plains, with varying concentrations of metals, including manganese, iron, nickel, cobalt, and copper. These nodules may provide a significant resource for future mining ventures.Owing in part to their vast size, abyssal plains are currently believed to be a major reservoir of biodiversity. The abyss also exerts significant influence upon ocean carbon cycling, dissolution of calcium carbonate, and atmospheric CO2 concentrations over timescales of 100–1000 years. The structure and function of abyssal ecosystems are strongly influenced by the rate of flux of food to the seafloor and the composition of the material that settles. Factors such as climate change, fishing practices, and ocean fertilization are expected to have a substantial effect on patterns of primary production in the euphotic zone. This will undoubtedly impact the flux of organic material to the abyss in a similar manner and thus have a profound effect on the structure, function and diversity of abyssal ecosystems.