
Plate Tectonics Assignment(3-27-13)
... Click me for the animation Right Side: Ocean Convergent Boundary Situation 1: 1. Hit play in the animation and observe: (2 pts) Write down two observations as it applies to trench, volcanoes, subduction a. b. 2. Use the density tool at the bottom to find the density of the magma and the mantle aroun ...
... Click me for the animation Right Side: Ocean Convergent Boundary Situation 1: 1. Hit play in the animation and observe: (2 pts) Write down two observations as it applies to trench, volcanoes, subduction a. b. 2. Use the density tool at the bottom to find the density of the magma and the mantle aroun ...
Plate Tectonics Lecture Notes
... •In the mantle, temperatures range between 500-900 degrees Celsius at the upper boundary with the crust to over 4,000 degrees Celsius at the boundary with the core. •Due to the temperature difference between the Earth's surface and outer core, and the ability of the crystalline rocks at high pressur ...
... •In the mantle, temperatures range between 500-900 degrees Celsius at the upper boundary with the crust to over 4,000 degrees Celsius at the boundary with the core. •Due to the temperature difference between the Earth's surface and outer core, and the ability of the crystalline rocks at high pressur ...
What is a Lithospheric Plate?
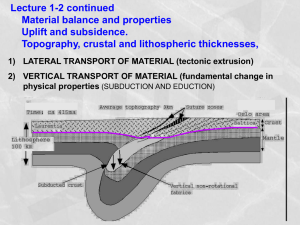
... dies down and lithosphere cools. Volcano sinks beneath the sea 35 becomes a seamount. ...
... dies down and lithosphere cools. Volcano sinks beneath the sea 35 becomes a seamount. ...
Plate Tectonics Lecture Notes: Slide 1. Title
... •In the mantle, temperatures range between 500-900 degrees Celsius at the upper boundary with the crust to over 4,000 degrees Celsius at the boundary with the core. •Due to the temperature difference between the Earth's surface and outer core, and the ability of the crystalline rocks at high pressur ...
... •In the mantle, temperatures range between 500-900 degrees Celsius at the upper boundary with the crust to over 4,000 degrees Celsius at the boundary with the core. •Due to the temperature difference between the Earth's surface and outer core, and the ability of the crystalline rocks at high pressur ...
Ch 4 PPT - Blountstown Middle School
... energy from the core produce the energy for convection. ...
... energy from the core produce the energy for convection. ...
Peruvian anchovy landings and El Niño events
... Ocean Fronts and Eddies FRONT: the interface between two water masses with differing physical characteristics (temperature and salinity) with resulting variations in density. Some fronts which have weak boundaries at the surface have strong “walls” below the surface. The boundary zones are sites of ...
... Ocean Fronts and Eddies FRONT: the interface between two water masses with differing physical characteristics (temperature and salinity) with resulting variations in density. Some fronts which have weak boundaries at the surface have strong “walls” below the surface. The boundary zones are sites of ...
Langmuir circulations and enhanced turbulence beneath wind
... presented in Figures 8 and 10. These transects are situated near 11oS and 21oS, respectively. Positive values indicate northward currents in both situations. Figure 8 shows the intense near shore northward transport induced by the NBUC pointed out by the horizontal velocity fields (Figures 5 to 7). ...
... presented in Figures 8 and 10. These transects are situated near 11oS and 21oS, respectively. Positive values indicate northward currents in both situations. Figure 8 shows the intense near shore northward transport induced by the NBUC pointed out by the horizontal velocity fields (Figures 5 to 7). ...
Layers of the Earth By Mr. Lee Yeah, uh huh, you know what it is
... I’mma hop up on this fresh beat so I can teach you About the layers of the earth, first Thing’s first The ourtermost layer is called the Crust, filled with dirt And rocks and sand, I hope you Understand The crust is the layer on top of which We stand It’s made out of rocks, mostly igneous Oceanic cr ...
... I’mma hop up on this fresh beat so I can teach you About the layers of the earth, first Thing’s first The ourtermost layer is called the Crust, filled with dirt And rocks and sand, I hope you Understand The crust is the layer on top of which We stand It’s made out of rocks, mostly igneous Oceanic cr ...
FIS 310
... ii. The Atlantic ocean iii. The Indian ocean iv. The arctic ocean The Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Ocean are the three oceanic extensions of the Antarctic Ocean which surrounds the Antarctic continent, but they are separated by the continental barrier into these three oceans. The other small oceans ...
... ii. The Atlantic ocean iii. The Indian ocean iv. The arctic ocean The Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Ocean are the three oceanic extensions of the Antarctic Ocean which surrounds the Antarctic continent, but they are separated by the continental barrier into these three oceans. The other small oceans ...
Print - National Geographic Society
... and salinity. Also known as thermohaline circulation, the conveyor belt is a system in which water moves between the cold depths and warm surface in oceans throughout the world. Have students draw the Ocean Conveyor Belt on the World Physical MapMaker Kit. ...
... and salinity. Also known as thermohaline circulation, the conveyor belt is a system in which water moves between the cold depths and warm surface in oceans throughout the world. Have students draw the Ocean Conveyor Belt on the World Physical MapMaker Kit. ...
Metamorphic Processes Associated with Orogenic Belts of India
... subduction, ophiolite, island arc formation and progressive metamorphism attendant with syn- to late-tectonic granites as a result of collision of lithospheric plates. The Himalayan rocks preserve evidence of all the internal processes that occurred during its evolution by the global plate tectonics ...
... subduction, ophiolite, island arc formation and progressive metamorphism attendant with syn- to late-tectonic granites as a result of collision of lithospheric plates. The Himalayan rocks preserve evidence of all the internal processes that occurred during its evolution by the global plate tectonics ...
Continental Margins and Marginal Seas
... edges of diverging tectonic plates, while along the Pacific, active margins with earthquake and volcanic activities are found near the edges of the different converging plates. Waters on the shelves and in the marginal seas are in constant motion, even more than those in the open oceans, and this is ...
... edges of diverging tectonic plates, while along the Pacific, active margins with earthquake and volcanic activities are found near the edges of the different converging plates. Waters on the shelves and in the marginal seas are in constant motion, even more than those in the open oceans, and this is ...
Deep Sea Drilling Project Initial Reports Volume 22
... south of the Java Trench. The Wharton Basin is bounded on the west by the Ninetyeast Ridge, on the south by Broken Ridge, and on the east by the Java Trench. This basin is divided into north and south by the Cocos Seamount Chain which trends roughly east-west along latitude 12°S. The Wharton Basin i ...
... south of the Java Trench. The Wharton Basin is bounded on the west by the Ninetyeast Ridge, on the south by Broken Ridge, and on the east by the Java Trench. This basin is divided into north and south by the Cocos Seamount Chain which trends roughly east-west along latitude 12°S. The Wharton Basin i ...
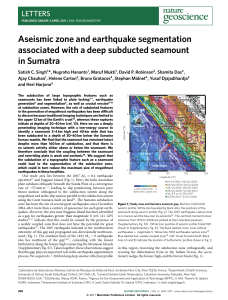
Aseismic zone and earthquake segmentation associated with a
... oceanic plate, a veneer of thin sediments (200 ms) is present, which gradually thickens to 800 ms at the subduction front. The first 25 km of the frontal part of the accretionary prism consists of folded and faulted accreted sediments sloping gently seaward. The top of the oceanic crust is imaged al ...
... oceanic plate, a veneer of thin sediments (200 ms) is present, which gradually thickens to 800 ms at the subduction front. The first 25 km of the frontal part of the accretionary prism consists of folded and faulted accreted sediments sloping gently seaward. The top of the oceanic crust is imaged al ...
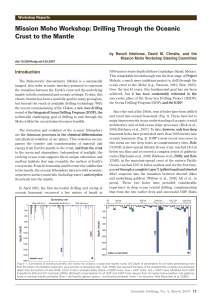
Mission Moho Workshop: Drilling Through the Oceanic Crust to the
... a wide range of water-rock reactions that change the physical properties of the crust on a variety of temporal and spatial scales. One strategy for studying the aging of oceanic crust is to drill multi-hole transects along seafloor spreading flow lines to examine the time-integrated changes in physi ...
... a wide range of water-rock reactions that change the physical properties of the crust on a variety of temporal and spatial scales. One strategy for studying the aging of oceanic crust is to drill multi-hole transects along seafloor spreading flow lines to examine the time-integrated changes in physi ...
Scripps Scientists Explore the Mysteries and Challenges of the
... Scripps Institution of Oceanography: scripps.ucsd.edu Scripps News: scrippsnews.ucsd.edu About Scripps Institution of Oceanography Scripps Institution of Oceanography at University of California, San Diego, is one of the oldest, largest and most important centers for global science research and educ ...
... Scripps Institution of Oceanography: scripps.ucsd.edu Scripps News: scrippsnews.ucsd.edu About Scripps Institution of Oceanography Scripps Institution of Oceanography at University of California, San Diego, is one of the oldest, largest and most important centers for global science research and educ ...
An Entirely New 3D-View of the Crustal and Mantle Structure of a
... Espírito Santo; sometimes attaining significant widths (Figure 3). Serpentinization of the exhumed mantle can be deduced from the gravimetric modeling (mantle densities gradually decreasing to as low as 2.60 g/cm3) to occur down to several kilometers (6-8) deep (Figure 5 and Figure 8). This is in sh ...
... Espírito Santo; sometimes attaining significant widths (Figure 3). Serpentinization of the exhumed mantle can be deduced from the gravimetric modeling (mantle densities gradually decreasing to as low as 2.60 g/cm3) to occur down to several kilometers (6-8) deep (Figure 5 and Figure 8). This is in sh ...
nakamoto4
... acid-base equilibrium and biological processes. From ocean drilling cores, it is suggested that the enhanced deposition of organic matter to the deep ocean may have ...
... acid-base equilibrium and biological processes. From ocean drilling cores, it is suggested that the enhanced deposition of organic matter to the deep ocean may have ...
Chapter 13 Section 3 Life in the Ocean
... • The Oceanic Zone The oceanic zone includes the volume of water that covers the entire sea floor except for the continental shelf. • The deeper parts of the oceanic zone have colder water temperatures and much greater pressure than the neritic zone. • Organisms are more spread out in the oceanic zo ...
... • The Oceanic Zone The oceanic zone includes the volume of water that covers the entire sea floor except for the continental shelf. • The deeper parts of the oceanic zone have colder water temperatures and much greater pressure than the neritic zone. • Organisms are more spread out in the oceanic zo ...
[Subramaniam et al. 2008]
... cells at 4,000 m in late July/early August. They calculated that these DDAs had settling rates of 100–200 m d⫺1 with little remineralization along the way. Deuser et al. (24) observed that total material flux into a deep trap (3200 m) deployed just east of Barbados (13°13⬘ N, 57°41⬘ W) ranged betwee ...
... cells at 4,000 m in late July/early August. They calculated that these DDAs had settling rates of 100–200 m d⫺1 with little remineralization along the way. Deuser et al. (24) observed that total material flux into a deep trap (3200 m) deployed just east of Barbados (13°13⬘ N, 57°41⬘ W) ranged betwee ...
Lab 4
... from the ridge, older oceanic lithosphere cools and becomes more dense. Eventually, the ocean floor spreads away from the ridge crest and sinks to depths below the CCD, where only abyssal clays are preserved. This pattern may be modified if the plate motion brings a region of the ocean floor under a ...
... from the ridge, older oceanic lithosphere cools and becomes more dense. Eventually, the ocean floor spreads away from the ridge crest and sinks to depths below the CCD, where only abyssal clays are preserved. This pattern may be modified if the plate motion brings a region of the ocean floor under a ...
Scientists-testimoni..
... Deep-sea trawling is widely known to be the most destructive kind of fishing in history. The scientific literature has repeatedly demonstrated that this method of fishing destroys the habitats of fishes and invertebrates, is non-selective for any species, and has long-term impact. The United Nations ...
... Deep-sea trawling is widely known to be the most destructive kind of fishing in history. The scientific literature has repeatedly demonstrated that this method of fishing destroys the habitats of fishes and invertebrates, is non-selective for any species, and has long-term impact. The United Nations ...
Chapter 11 What about continental drift?
... This higher sea level floods the continental surfaces and makes possible the deposition of large areas of sedimentary deposits on top of the normally high-standing continents. The Grand Canyon provides a spectacular window into the amazing layer-cake character of these sediment deposits that in many ...
... This higher sea level floods the continental surfaces and makes possible the deposition of large areas of sedimentary deposits on top of the normally high-standing continents. The Grand Canyon provides a spectacular window into the amazing layer-cake character of these sediment deposits that in many ...
Abyssal plain
An abyssal plain is an underwater plain on the deep ocean floor, usually found at depths between 3000 and 6000 m. Lying generally between the foot of a continental rise and a mid-ocean ridge, abyssal plains cover more than 50% of the Earth’s surface. They are among the flattest, smoothest and least explored regions on Earth. Abyssal plains are key geologic elements of oceanic basins (the other elements being an elevated mid-ocean ridge and flanking abyssal hills). In addition to these elements, active oceanic basins (those that are associated with a moving plate tectonic boundary) also typically include an oceanic trench and a subduction zone.Abyssal plains were not recognized as distinct physiographic features of the sea floor until the late 1940s and, until very recently, none had been studied on a systematic basis. They are poorly preserved in the sedimentary record, because they tend to be consumed by the subduction process. The creation of the abyssal plain is the end result of spreading of the seafloor (plate tectonics) and melting of the lower oceanic crust. Magma rises from above the asthenosphere (a layer of the upper mantle) and as this basaltic material reaches the surface at mid-ocean ridges it forms new oceanic crust. This is constantly pulled sideways by spreading of the seafloor. Abyssal plains result from the blanketing of an originally uneven surface of oceanic crust by fine-grained sediments, mainly clay and silt. Much of this sediment is deposited by turbidity currents that have been channelled from the continental margins along submarine canyons down into deeper water. The remainder of the sediment is composed chiefly of pelagic sediments. Metallic nodules are common in some areas of the plains, with varying concentrations of metals, including manganese, iron, nickel, cobalt, and copper. These nodules may provide a significant resource for future mining ventures.Owing in part to their vast size, abyssal plains are currently believed to be a major reservoir of biodiversity. The abyss also exerts significant influence upon ocean carbon cycling, dissolution of calcium carbonate, and atmospheric CO2 concentrations over timescales of 100–1000 years. The structure and function of abyssal ecosystems are strongly influenced by the rate of flux of food to the seafloor and the composition of the material that settles. Factors such as climate change, fishing practices, and ocean fertilization are expected to have a substantial effect on patterns of primary production in the euphotic zone. This will undoubtedly impact the flux of organic material to the abyss in a similar manner and thus have a profound effect on the structure, function and diversity of abyssal ecosystems.

















![[Subramaniam et al. 2008]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/017997148_1-17e663b2a353d7b5751f9bd2c3bc762c-300x300.png)


