
Lecture 9 and 10
... Many of the red areas are the result of ancient rift systems that contain denser basalts. ...
... Many of the red areas are the result of ancient rift systems that contain denser basalts. ...
Plate tectonics
... Understand the processes that are continuously changing Earth’s surface as lithospheric plates move relative to one another. Identify the role of oceanic ridges, transform faults and deep-sea trenches in defining the edges of lithospheric plates. Understand the importance of asthenospheric thermal c ...
... Understand the processes that are continuously changing Earth’s surface as lithospheric plates move relative to one another. Identify the role of oceanic ridges, transform faults and deep-sea trenches in defining the edges of lithospheric plates. Understand the importance of asthenospheric thermal c ...
Warm deep-water ocean conveyor during
... heat transport in the intermediate scenario, whereas there is almost no cross-equatorial heat transport in the warm scenario. It is important that in this scenario the southern and northern deep-water sources trade places in driving the conveyor. The warmer Southern Ocean is saltier and therefore de ...
... heat transport in the intermediate scenario, whereas there is almost no cross-equatorial heat transport in the warm scenario. It is important that in this scenario the southern and northern deep-water sources trade places in driving the conveyor. The warmer Southern Ocean is saltier and therefore de ...
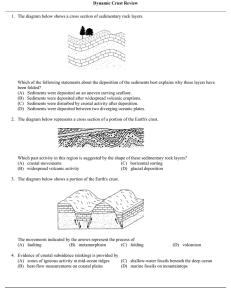
Dynamic Crust Review
... 7. Fossils of organisms that lived in shallow water can be found in horizontal sedimentary rock layers at great ocean depths. This fact is generally interpreted by most Earth scientists as evidence that (A) the cold water deep in the ocean kills shallow-water organisms (B) sunlight once penetrated t ...
... 7. Fossils of organisms that lived in shallow water can be found in horizontal sedimentary rock layers at great ocean depths. This fact is generally interpreted by most Earth scientists as evidence that (A) the cold water deep in the ocean kills shallow-water organisms (B) sunlight once penetrated t ...
Plate Tectonics
... equator, steeper at high latitudes, and vertical at the magnetic poles. The magnetic field is inclined downward in the Northern Hemisphere and upward in the Southern Hemisphere. Magnetic minerals, most commonly those with a high iron content, align parallel to Earth's magnetic field when they form d ...
... equator, steeper at high latitudes, and vertical at the magnetic poles. The magnetic field is inclined downward in the Northern Hemisphere and upward in the Southern Hemisphere. Magnetic minerals, most commonly those with a high iron content, align parallel to Earth's magnetic field when they form d ...
S6E5e. Recognize that lithospheric plates constantly move and
... • A colder, older, denser oceanic plate subducts (goes down), under another oceanic plate into the mantle. • A deep sea trench is created where one plate bends and sinks. • High temperatures cause rock to melt around the subducting plate as it goes under the other plate • Newly formed magma is force ...
... • A colder, older, denser oceanic plate subducts (goes down), under another oceanic plate into the mantle. • A deep sea trench is created where one plate bends and sinks. • High temperatures cause rock to melt around the subducting plate as it goes under the other plate • Newly formed magma is force ...
MASTER SYLLABUS
... 20-6.describe a food web and give an example. 21-1.recognize the physical factors that influence the penetration of light in the sea; 21-2.describe the relationships between plants and light in the sea; 21-3.indicate the interactions between animals and light in the sea; 21-4.discuss bioluminescence ...
... 20-6.describe a food web and give an example. 21-1.recognize the physical factors that influence the penetration of light in the sea; 21-2.describe the relationships between plants and light in the sea; 21-3.indicate the interactions between animals and light in the sea; 21-4.discuss bioluminescence ...
Hirn and Laigle [2004]
... Kodaira et al. (6). In their simple earthquake-slip model, the block unclamped by pore-fluid pressure under the forearc crust would experience silent earthquakes before the megathrust earthquake. The absence of silent earthquakes on the other segments of Nankai is then consistent with more recent ru ...
... Kodaira et al. (6). In their simple earthquake-slip model, the block unclamped by pore-fluid pressure under the forearc crust would experience silent earthquakes before the megathrust earthquake. The absence of silent earthquakes on the other segments of Nankai is then consistent with more recent ru ...
Evolution of magma-poor continental margins from rifting to sea¯oor
... anomalies (Fig. 1a, c and e) indicate that ZECM basement magnetizations are typically much lower than those of oceanic basement further west, and the spectral properties of the anomalies suggest that most source bodies, equated here with syn-rift ma®c intrusions (for example, ref. 24), lie not at to ...
... anomalies (Fig. 1a, c and e) indicate that ZECM basement magnetizations are typically much lower than those of oceanic basement further west, and the spectral properties of the anomalies suggest that most source bodies, equated here with syn-rift ma®c intrusions (for example, ref. 24), lie not at to ...
Plate Tectonics
... type of movment? •Convergent = Collide •Divergent = Divide •Transform = Slide ...
... type of movment? •Convergent = Collide •Divergent = Divide •Transform = Slide ...
MS Plate Tectonics
... the center of the Atlantic Ocean. Deep sea trenches are found along the west coast of Central and South America and in the mid-Atlantic, east of the southern tip of South America. Isolated mountains and flat, featureless regions can also be spotted. ...
... the center of the Atlantic Ocean. Deep sea trenches are found along the west coast of Central and South America and in the mid-Atlantic, east of the southern tip of South America. Isolated mountains and flat, featureless regions can also be spotted. ...
Plate tectonics
... Plate Tectonics - evidence for theory of continental drift by Hess, Heezen and Tharp (1960’s) found lithospheres plate boundaries that can be 3 types: 1) ridges (spreading centers) 2) trenches (subduction zones) 3) transform faults (plates sliding past one another) ...
... Plate Tectonics - evidence for theory of continental drift by Hess, Heezen and Tharp (1960’s) found lithospheres plate boundaries that can be 3 types: 1) ridges (spreading centers) 2) trenches (subduction zones) 3) transform faults (plates sliding past one another) ...
Snacktectonics
... Purpose of Activity: To model the interactions of Earth’s lithosphere (tectonic plates) as they slowly move on the Earth’s mantle (asthenosphere), through the use of snack foods. Background for Activity: The theory of plate tectonics says that the crust of the Earth is composed of separate plates wh ...
... Purpose of Activity: To model the interactions of Earth’s lithosphere (tectonic plates) as they slowly move on the Earth’s mantle (asthenosphere), through the use of snack foods. Background for Activity: The theory of plate tectonics says that the crust of the Earth is composed of separate plates wh ...
turbulence @ ocean observatories - Center for Coastal Physical
... The location of the LEO observatory is characteristic of the very gently sloping continental shelves that extend along most of the eastern seaboard of the United States, in places extending 100s of km offshore. LEO is also characteristic of strongly surface-wave-influenced shelf environments with si ...
... The location of the LEO observatory is characteristic of the very gently sloping continental shelves that extend along most of the eastern seaboard of the United States, in places extending 100s of km offshore. LEO is also characteristic of strongly surface-wave-influenced shelf environments with si ...
... most of the world’s oceans lies a massive, dynamic plumbing system that is a central component of our planet’s inner workings. Heated and under pressure, seawater and other fluids flow and percolate up, down, and through myriad layers of subseafloor rock formations. At volcanically active mid-ocean ...
Plate Tectonics - Flushing High School
... 1, a map of the major plates and boundaries, and Figure 2, a map of earthquake distribution and depth. There are three basic types of plate boundaries: DIVERGENT (constructive) plate boundaries form when two plates are moving away from one another. This occurs along mid-ocean ridge systems (e.g., th ...
... 1, a map of the major plates and boundaries, and Figure 2, a map of earthquake distribution and depth. There are three basic types of plate boundaries: DIVERGENT (constructive) plate boundaries form when two plates are moving away from one another. This occurs along mid-ocean ridge systems (e.g., th ...
SGES 1302 Lecture3
... continental crust, from which he inferred that there must be a strong upper layer (which he called the lithosphere) above a weaker layer which could flow (which he called the asthenosphere). These ideas were enlarged by Daly (1940), and have been broadly accepted by geologists and geophysicists. Alt ...
... continental crust, from which he inferred that there must be a strong upper layer (which he called the lithosphere) above a weaker layer which could flow (which he called the asthenosphere). These ideas were enlarged by Daly (1940), and have been broadly accepted by geologists and geophysicists. Alt ...
Inside Earth: Layers of the Earth
... Continental crust is much thicker than oceanic crust. It is 35 kilometers (22 miles) thick on average, but it varies a lot. Continental crust is made up of many different rocks but mainly igneous granite rock. All three major rock types — igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary — are found in the crus ...
... Continental crust is much thicker than oceanic crust. It is 35 kilometers (22 miles) thick on average, but it varies a lot. Continental crust is made up of many different rocks but mainly igneous granite rock. All three major rock types — igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary — are found in the crus ...
Extremely thin crust in the Indian Ocean possibly resulting from
... basement, which Dean et al. (2010) interpret to be due to a predecollement surface (seaward propagation of the megathrust). On profile WG3, which is at about 60 km from the subduction front, this reflector also has a negative polarity and is present along the most part of the profile, interrupted by ...
... basement, which Dean et al. (2010) interpret to be due to a predecollement surface (seaward propagation of the megathrust). On profile WG3, which is at about 60 km from the subduction front, this reflector also has a negative polarity and is present along the most part of the profile, interrupted by ...
Inside Earth: Layers of the Earth - Maria Montessori Academy Blog
... Continental crust is much thicker than oceanic crust. It is 35 kilometers (22 miles) thick on average, but it varies a lot. Continental crust is made up of many different rocks but mainly igneous granite rock. All three major rock types — igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary — are found in the crus ...
... Continental crust is much thicker than oceanic crust. It is 35 kilometers (22 miles) thick on average, but it varies a lot. Continental crust is made up of many different rocks but mainly igneous granite rock. All three major rock types — igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary — are found in the crus ...
Inside Earth: Layers of the Earth
... Continental crust is much thicker than oceanic crust. It is 35 kilometers (22 miles) thick on average, but it varies a lot. Continental crust is made up of many different rocks but mainly igneous granite rock. All three major rock types — igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary — are found in the crus ...
... Continental crust is much thicker than oceanic crust. It is 35 kilometers (22 miles) thick on average, but it varies a lot. Continental crust is made up of many different rocks but mainly igneous granite rock. All three major rock types — igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary — are found in the crus ...
Supplemental Readings on Plate Tectonics and
... mantle lithosphere at the spreading ridge3; the oceanic crust sits directly on the asthenosphere. But Figure 7.9 also shows that, at a significant distance away from the spreading ridge, there is an impressive thickness of mantle lithosphere (which is denser than asthenosphere) attached to the botto ...
... mantle lithosphere at the spreading ridge3; the oceanic crust sits directly on the asthenosphere. But Figure 7.9 also shows that, at a significant distance away from the spreading ridge, there is an impressive thickness of mantle lithosphere (which is denser than asthenosphere) attached to the botto ...
Abyssal plain
An abyssal plain is an underwater plain on the deep ocean floor, usually found at depths between 3000 and 6000 m. Lying generally between the foot of a continental rise and a mid-ocean ridge, abyssal plains cover more than 50% of the Earth’s surface. They are among the flattest, smoothest and least explored regions on Earth. Abyssal plains are key geologic elements of oceanic basins (the other elements being an elevated mid-ocean ridge and flanking abyssal hills). In addition to these elements, active oceanic basins (those that are associated with a moving plate tectonic boundary) also typically include an oceanic trench and a subduction zone.Abyssal plains were not recognized as distinct physiographic features of the sea floor until the late 1940s and, until very recently, none had been studied on a systematic basis. They are poorly preserved in the sedimentary record, because they tend to be consumed by the subduction process. The creation of the abyssal plain is the end result of spreading of the seafloor (plate tectonics) and melting of the lower oceanic crust. Magma rises from above the asthenosphere (a layer of the upper mantle) and as this basaltic material reaches the surface at mid-ocean ridges it forms new oceanic crust. This is constantly pulled sideways by spreading of the seafloor. Abyssal plains result from the blanketing of an originally uneven surface of oceanic crust by fine-grained sediments, mainly clay and silt. Much of this sediment is deposited by turbidity currents that have been channelled from the continental margins along submarine canyons down into deeper water. The remainder of the sediment is composed chiefly of pelagic sediments. Metallic nodules are common in some areas of the plains, with varying concentrations of metals, including manganese, iron, nickel, cobalt, and copper. These nodules may provide a significant resource for future mining ventures.Owing in part to their vast size, abyssal plains are currently believed to be a major reservoir of biodiversity. The abyss also exerts significant influence upon ocean carbon cycling, dissolution of calcium carbonate, and atmospheric CO2 concentrations over timescales of 100–1000 years. The structure and function of abyssal ecosystems are strongly influenced by the rate of flux of food to the seafloor and the composition of the material that settles. Factors such as climate change, fishing practices, and ocean fertilization are expected to have a substantial effect on patterns of primary production in the euphotic zone. This will undoubtedly impact the flux of organic material to the abyss in a similar manner and thus have a profound effect on the structure, function and diversity of abyssal ecosystems.







![Hirn and Laigle [2004]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/016241152_1-94ccf91c94bda93b4db1ea9c4d06f8a2-300x300.png)














