Chapter 11 Section 2
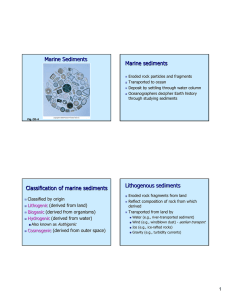
... Types of Mountains, continued Volcanic Mountains • Mountains that form when magma erupts onto Earth’s surface are called volcanic mountains, which commonly form along convergent plate boundaries. • Some of the largest volcanic mountains are part of the midocean ridges along divergent plate boundarie ...
... Types of Mountains, continued Volcanic Mountains • Mountains that form when magma erupts onto Earth’s surface are called volcanic mountains, which commonly form along convergent plate boundaries. • Some of the largest volcanic mountains are part of the midocean ridges along divergent plate boundarie ...
Glaciers caused zooplankton mortality?
... frontal zones is commonly reported as a main cause of marine organism mortality, and a range between 5 and 8 PSU is regarded as the critical salinity for both marine and freshwater species (Khlebovitsch, 1990). On the other hand, numerous neritic species withstand a salinity decrease from 30 to 1 PS ...
... frontal zones is commonly reported as a main cause of marine organism mortality, and a range between 5 and 8 PSU is regarded as the critical salinity for both marine and freshwater species (Khlebovitsch, 1990). On the other hand, numerous neritic species withstand a salinity decrease from 30 to 1 PS ...
Episodic crustal growth and mantle evolution
... intermittent. This interpretation is certainly controversial, and it may be that the 'quiescent' periods merely represent missing continental material, which has been recycled back into the mantle. However, Reymer and Schubert (1984, 1986) have shown that crust formation rates during some geological ...
... intermittent. This interpretation is certainly controversial, and it may be that the 'quiescent' periods merely represent missing continental material, which has been recycled back into the mantle. However, Reymer and Schubert (1984, 1986) have shown that crust formation rates during some geological ...
III. Continental intraplate alkaline series
... Intraplate magmatism Most of the magmas are produced on plate boundaries (mid-ocean ridges and subductions); but significant production also in intra-plate conditions. How significant? Intraplate activity is typically discontinuous, so it is difficult to integrate on a long time period and assess it ...
... Intraplate magmatism Most of the magmas are produced on plate boundaries (mid-ocean ridges and subductions); but significant production also in intra-plate conditions. How significant? Intraplate activity is typically discontinuous, so it is difficult to integrate on a long time period and assess it ...
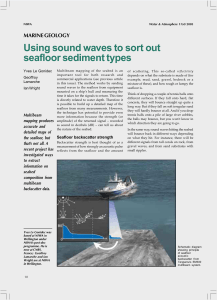
Using sound waves to sort out seafloor sediment types
... geological formations on land, images of seafloor backscatter can help us to identify different submarine geological processes. It can also distinguish different substrate types (mud, gravel) and associated biological habitats. Until recently the images produced by the multibeam backscatter were gre ...
... geological formations on land, images of seafloor backscatter can help us to identify different submarine geological processes. It can also distinguish different substrate types (mud, gravel) and associated biological habitats. Until recently the images produced by the multibeam backscatter were gre ...
Alpine–Himalayan orogenic belt
... move west from the East Pacific Rise only to be consumed at subduction zones in Central and South America ...
... move west from the East Pacific Rise only to be consumed at subduction zones in Central and South America ...
mid-ocean ridges: mantle convection
... mantle matrix and buoyantly rises toward the surface, where it forms new, basaltic, oceanic crust. The crust and mantle cool at the surface by thermal conduction and hydrothermal circulation. This cooling generates a thermal boundary layer, which is rigid to convection and is the newly created edge ...
... mantle matrix and buoyantly rises toward the surface, where it forms new, basaltic, oceanic crust. The crust and mantle cool at the surface by thermal conduction and hydrothermal circulation. This cooling generates a thermal boundary layer, which is rigid to convection and is the newly created edge ...
The Hindu Kush Seismic Zone as a Paradigm
... other than Himalayan-type crustal stacking is required to produce UHP rocks in collisional mountain belts. Platt (1987) suggested a mechanism whereby extension in the upper part of an accretionary wedge thickened by underplating could account for the exhumation of some Alpine HP rocks. Extensional f ...
... other than Himalayan-type crustal stacking is required to produce UHP rocks in collisional mountain belts. Platt (1987) suggested a mechanism whereby extension in the upper part of an accretionary wedge thickened by underplating could account for the exhumation of some Alpine HP rocks. Extensional f ...
Hyperextended continental margins—Knowns and
... margins: (1) limited crustal stretching, (2) hyperextension, (3) exhumed mantle, and (4) ultraslow or normal oceanic crust (cf. Péron-Pinvidic and Manatschal, 2009). The zones probably formed as the rift propagated, a common mode of continental break-up (e.g., the South Atlantic, Heine et al., 2013; ...
... margins: (1) limited crustal stretching, (2) hyperextension, (3) exhumed mantle, and (4) ultraslow or normal oceanic crust (cf. Péron-Pinvidic and Manatschal, 2009). The zones probably formed as the rift propagated, a common mode of continental break-up (e.g., the South Atlantic, Heine et al., 2013; ...
Hyperextended continental margins—Knowns and
... margins: (1) limited crustal stretching, (2) hyperextension, (3) exhumed mantle, and (4) ultraslow or normal oceanic crust (cf. Péron-Pinvidic and Manatschal, 2009). The zones probably formed as the rift propagated, a common mode of continental break-up (e.g., the South Atlantic, Heine et al., 2013; ...
... margins: (1) limited crustal stretching, (2) hyperextension, (3) exhumed mantle, and (4) ultraslow or normal oceanic crust (cf. Péron-Pinvidic and Manatschal, 2009). The zones probably formed as the rift propagated, a common mode of continental break-up (e.g., the South Atlantic, Heine et al., 2013; ...
SEDIMENTARY BASINS BASIN TYPES ACCORDING TO
... B. Convergent plate margins • Deep-sea trench floors are composed of descending oceanic crust. Therefore, some of them represent the deepest elongate basins present on the globe. In areas of very high sediment influx from the neighboring continent, however, they are for the most part filled up and ...
... B. Convergent plate margins • Deep-sea trench floors are composed of descending oceanic crust. Therefore, some of them represent the deepest elongate basins present on the globe. In areas of very high sediment influx from the neighboring continent, however, they are for the most part filled up and ...
The Submarine Volcano Eruption off El Hierro Island: Effects on the
... the euphotic or epipelagic zone (100–200 m depth) and the top of the bathypelagic zone (1000 m depth) [10]. Part of this biota feeds during the night in the epipelagic zone, forming what we here refer to as the MSL. This so-called Diel Vertical Migration (DVM) occurs on a daily basis around the worl ...
... the euphotic or epipelagic zone (100–200 m depth) and the top of the bathypelagic zone (1000 m depth) [10]. Part of this biota feeds during the night in the epipelagic zone, forming what we here refer to as the MSL. This so-called Diel Vertical Migration (DVM) occurs on a daily basis around the worl ...
The deep sea is a major sink for microplastic debris
... environment. As an additional precaution, those handling the samples wore only natural fibre clothing, and were protected with 100% cotton laboratory coats and headwear, and latex gloves, for all laboratory processing and during the JC76T research cruise. Microplastics were extracted from the sedimen ...
... environment. As an additional precaution, those handling the samples wore only natural fibre clothing, and were protected with 100% cotton laboratory coats and headwear, and latex gloves, for all laboratory processing and during the JC76T research cruise. Microplastics were extracted from the sedimen ...
Seamount Census Reveals New and Poorly Known Marine Life
... A newly discovered species of midwater fish is being described from the 2002 cruise. Both Vecchione and Heyl consider their most exciting find a cephalopod species called the ram’s horn squid. “This is a very unusual kind of deep- ...
... A newly discovered species of midwater fish is being described from the 2002 cruise. Both Vecchione and Heyl consider their most exciting find a cephalopod species called the ram’s horn squid. “This is a very unusual kind of deep- ...
You Can`t Catch a Fish with a Robot
... Abstract: In this essay I will relate the challenges associated with deep sea ocean exploration as well as the advantages and disadvantages of today’s ocean technologies based on experience with most of these systems. After nearly 5 decades using robotic vehicles (Remotely Operated Vehicles = ROVs a ...
... Abstract: In this essay I will relate the challenges associated with deep sea ocean exploration as well as the advantages and disadvantages of today’s ocean technologies based on experience with most of these systems. After nearly 5 decades using robotic vehicles (Remotely Operated Vehicles = ROVs a ...
Kimberlites and the start of plate tectonics
... powers plate motions. Although subduction the mantle was low, mostly delivered by delamizones are not part of the formal definition of PT, nation and lithospheric drips, so fluid pressure we now know that convergent plate margins are at the top of asthenosphere was mostly low and surficial expressio ...
... powers plate motions. Although subduction the mantle was low, mostly delivered by delamizones are not part of the formal definition of PT, nation and lithospheric drips, so fluid pressure we now know that convergent plate margins are at the top of asthenosphere was mostly low and surficial expressio ...
Ch13Pres - Leornian.org
... – With the development of reliable methods of navigation, oceangoing vessels provided access to all continents and commercially important trade routes were established. – Beginning with the Challenger Expedition of the 1870s, understanding of the ocean’s properties and processes rapidly grew during ...
... – With the development of reliable methods of navigation, oceangoing vessels provided access to all continents and commercially important trade routes were established. – Beginning with the Challenger Expedition of the 1870s, understanding of the ocean’s properties and processes rapidly grew during ...
history_Oceanography..
... the AMSR-E sea ice product from the University of Bremen (Figure 4). The most recent operational analysis from the Canadian Ice Service and the U.S. National Ice Center on August 8 showed a small section of Amundsen’s historic path still blocked by a 50kilometer (31-mile) stretch of sea ice, althoug ...
... the AMSR-E sea ice product from the University of Bremen (Figure 4). The most recent operational analysis from the Canadian Ice Service and the U.S. National Ice Center on August 8 showed a small section of Amundsen’s historic path still blocked by a 50kilometer (31-mile) stretch of sea ice, althoug ...
benthic marine habitats in antarctica
... Ocean reveals vast areas of seabed at abyssal depths (Figure 2). In contras~ a careful sean:h of the literature on Antanotic benthic marine biology will fail to uncover much data on these areas; we know almost nothing of the biology of the deep sea in Antarctica. Most of what we have learned has com ...
... Ocean reveals vast areas of seabed at abyssal depths (Figure 2). In contras~ a careful sean:h of the literature on Antanotic benthic marine biology will fail to uncover much data on these areas; we know almost nothing of the biology of the deep sea in Antarctica. Most of what we have learned has com ...
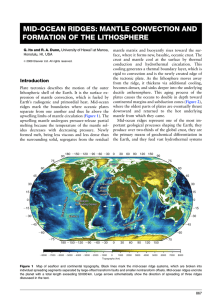
Mid-Ocean Ridges: Mantle Convection and Formation
... of the mantle solidus decreases with decreasing pressure. Newly formed melt, being less viscous and less dense than the surrounding solid, segregates from the residual mantle matrix and buoyantly rises toward the surface, where it forms new, basaltic, oceanic crust. The crust and mantle cool at the ...
... of the mantle solidus decreases with decreasing pressure. Newly formed melt, being less viscous and less dense than the surrounding solid, segregates from the residual mantle matrix and buoyantly rises toward the surface, where it forms new, basaltic, oceanic crust. The crust and mantle cool at the ...
IOC/SC-WESTPAC
... Supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of China, the Natural Science Foundation of China and the Qingdao National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology, systematic observations in the Northwestern Pacific Ocean are carried out during four cruises from 2014 to 2016 conducted by OU ...
... Supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of China, the Natural Science Foundation of China and the Qingdao National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology, systematic observations in the Northwestern Pacific Ocean are carried out during four cruises from 2014 to 2016 conducted by OU ...
Abyssal plain
An abyssal plain is an underwater plain on the deep ocean floor, usually found at depths between 3000 and 6000 m. Lying generally between the foot of a continental rise and a mid-ocean ridge, abyssal plains cover more than 50% of the Earth’s surface. They are among the flattest, smoothest and least explored regions on Earth. Abyssal plains are key geologic elements of oceanic basins (the other elements being an elevated mid-ocean ridge and flanking abyssal hills). In addition to these elements, active oceanic basins (those that are associated with a moving plate tectonic boundary) also typically include an oceanic trench and a subduction zone.Abyssal plains were not recognized as distinct physiographic features of the sea floor until the late 1940s and, until very recently, none had been studied on a systematic basis. They are poorly preserved in the sedimentary record, because they tend to be consumed by the subduction process. The creation of the abyssal plain is the end result of spreading of the seafloor (plate tectonics) and melting of the lower oceanic crust. Magma rises from above the asthenosphere (a layer of the upper mantle) and as this basaltic material reaches the surface at mid-ocean ridges it forms new oceanic crust. This is constantly pulled sideways by spreading of the seafloor. Abyssal plains result from the blanketing of an originally uneven surface of oceanic crust by fine-grained sediments, mainly clay and silt. Much of this sediment is deposited by turbidity currents that have been channelled from the continental margins along submarine canyons down into deeper water. The remainder of the sediment is composed chiefly of pelagic sediments. Metallic nodules are common in some areas of the plains, with varying concentrations of metals, including manganese, iron, nickel, cobalt, and copper. These nodules may provide a significant resource for future mining ventures.Owing in part to their vast size, abyssal plains are currently believed to be a major reservoir of biodiversity. The abyss also exerts significant influence upon ocean carbon cycling, dissolution of calcium carbonate, and atmospheric CO2 concentrations over timescales of 100–1000 years. The structure and function of abyssal ecosystems are strongly influenced by the rate of flux of food to the seafloor and the composition of the material that settles. Factors such as climate change, fishing practices, and ocean fertilization are expected to have a substantial effect on patterns of primary production in the euphotic zone. This will undoubtedly impact the flux of organic material to the abyss in a similar manner and thus have a profound effect on the structure, function and diversity of abyssal ecosystems.