- Maheshtala College
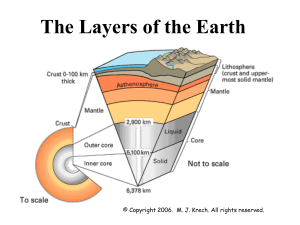
... different layers. The crust is the layer that you live on, and it is the most widely studied and understood. The mantle is much hotter and has the ability to flow. The outer core and inner core are even hotter with pressures so great you would be squeezed into a ball smaller than a marble if you wer ...
... different layers. The crust is the layer that you live on, and it is the most widely studied and understood. The mantle is much hotter and has the ability to flow. The outer core and inner core are even hotter with pressures so great you would be squeezed into a ball smaller than a marble if you wer ...
I. Divergent Boundaries A. Moving apart B. Sea Floor spreading at
... c. few quakes below 700 km are recorded: 1) perhaps plate loses rigidity to have quakes below this depth 2) perhaps plate become assimilated into underlying material at this ...
... c. few quakes below 700 km are recorded: 1) perhaps plate loses rigidity to have quakes below this depth 2) perhaps plate become assimilated into underlying material at this ...
2nd Nine Weeks Study Guide
... 42.The land between two normal faults moves upward to form a _________________________ mountain. 43.The rating system that rates an earthquake based on its magnitude is called the _____________________ scale. 44.What type of earthquake wave can only travel through solids? 45.Which scale would most l ...
... 42.The land between two normal faults moves upward to form a _________________________ mountain. 43.The rating system that rates an earthquake based on its magnitude is called the _____________________ scale. 44.What type of earthquake wave can only travel through solids? 45.Which scale would most l ...
Continental drift: An idea before its time Pangaea approximately 200
... spreading has come from drilling directly into ocean-floor sediment – Age of deepest sediments – Thickness of ocean-floor sediments verifies seafloor spreading ...
... spreading has come from drilling directly into ocean-floor sediment – Age of deepest sediments – Thickness of ocean-floor sediments verifies seafloor spreading ...
Intrusive Igneous Activity
... As a plate descends, the pressures and temperatures it experiences increase, and the water-laden sediments are baked (metamorphosed) and squeezed into new types of rock. The released water immediately vaporizes at these temperatures and pressures, and the vapor rises. As the vapor moves upward, it e ...
... As a plate descends, the pressures and temperatures it experiences increase, and the water-laden sediments are baked (metamorphosed) and squeezed into new types of rock. The released water immediately vaporizes at these temperatures and pressures, and the vapor rises. As the vapor moves upward, it e ...
Planet Earth11aw
... sinking into the mantle (subduction). Mountains are squeezed up here by the collision. Most earthquakes occur here. ...
... sinking into the mantle (subduction). Mountains are squeezed up here by the collision. Most earthquakes occur here. ...
Nature of the Earth and Universe Spring 2011 Exam 2 Name: April
... B. higher C. lower 19. A magma's viscosity is directly related to its iron content. A. True B. False 20. Current models for mantle convection indicate convection may occur _____. A. within the asthenosphere B. within the lower mantle C. mantle plumes D. throughout the whole or entire mantle E. all o ...
... B. higher C. lower 19. A magma's viscosity is directly related to its iron content. A. True B. False 20. Current models for mantle convection indicate convection may occur _____. A. within the asthenosphere B. within the lower mantle C. mantle plumes D. throughout the whole or entire mantle E. all o ...
Name___________________________ Date______________
... 6.E.2.2 Explain how crustal plates and ocean basins are formed, move and interact using earthquakes, heat flow and volcanoes to reflect forces within the earth. The earth's plates sit on a dense, hot, somewhat melted layer of the earth. The plates move very slowly, pressing against one another in so ...
... 6.E.2.2 Explain how crustal plates and ocean basins are formed, move and interact using earthquakes, heat flow and volcanoes to reflect forces within the earth. The earth's plates sit on a dense, hot, somewhat melted layer of the earth. The plates move very slowly, pressing against one another in so ...
The importance of the Earth`s biosphere in stabilizing the large
... contribute to its interior evolution? By harvesting solar energy and converting it to chemical energy, photosynthetic life plays an important role in the energy budget of Earth [4], leading to alterations of chemical reservoirs [1,3]. Since the surface is recycled into its interior at subduction zon ...
... contribute to its interior evolution? By harvesting solar energy and converting it to chemical energy, photosynthetic life plays an important role in the energy budget of Earth [4], leading to alterations of chemical reservoirs [1,3]. Since the surface is recycled into its interior at subduction zon ...
Complete Earth.s struct
... kilometres long. They cut through the abyssal plains. They can be so high that they emerge from the water and create islands, as is the case of Iceland. • Ridges have a fissure down their middle, called a rift. Rift ...
... kilometres long. They cut through the abyssal plains. They can be so high that they emerge from the water and create islands, as is the case of Iceland. • Ridges have a fissure down their middle, called a rift. Rift ...
Gluep-Honors
... Introduction: The interior of the Earth is complex. While it is made of 3 major layers, some of these layers can be subdivided or grouped into regions. The mantle of the Earth, and more specifically the asthenosphere, is a unique substance. Its composition is different from that of any other layer o ...
... Introduction: The interior of the Earth is complex. While it is made of 3 major layers, some of these layers can be subdivided or grouped into regions. The mantle of the Earth, and more specifically the asthenosphere, is a unique substance. Its composition is different from that of any other layer o ...
(composed of the continental crust and oceanic crust).
... Geologists use the term lithosphere to mean an outer Earth zone, or shell, of rigid, brittle rock. It includes not only the crust, but also the cooler, upper part of the mantle that is composed of brittle rock. The rigid, brittle lithosphere rests on top of a soft, plastic underlayer named the asthe ...
... Geologists use the term lithosphere to mean an outer Earth zone, or shell, of rigid, brittle rock. It includes not only the crust, but also the cooler, upper part of the mantle that is composed of brittle rock. The rigid, brittle lithosphere rests on top of a soft, plastic underlayer named the asthe ...
chapter 11 -- plate tectonics
... • The theory states that hot, less dense material in the mantle is forced upward to the surface at the ______-________ ridges. • As magma is forced upward at mid-ocean ridges, it flows in ________ directions away from the ridge. • As it moves away from the ridge, the magma cools, solidifies, gets __ ...
... • The theory states that hot, less dense material in the mantle is forced upward to the surface at the ______-________ ridges. • As magma is forced upward at mid-ocean ridges, it flows in ________ directions away from the ridge. • As it moves away from the ridge, the magma cools, solidifies, gets __ ...
to Ch. 9 Notes
... 8. oceanic ridge: a continuous elevated zone on the floor of all major ocean basins and varying in width from 1,000 to 4,000km; the rifts at the crests of the ridges represent divergent plate boundaries 9. rift valley: deep faulted structure found along the axes of divergent plate boundaries, rift v ...
... 8. oceanic ridge: a continuous elevated zone on the floor of all major ocean basins and varying in width from 1,000 to 4,000km; the rifts at the crests of the ridges represent divergent plate boundaries 9. rift valley: deep faulted structure found along the axes of divergent plate boundaries, rift v ...
3.4 Seismic waves in a spherical earth 3.5 Body wave travel time study
... • Even nearby • The Discontinuity has large topographic hi variations i i over small ll spatial wavelengths the focus and defocus waves. • There is no actual discontinuity, but that complex three dimensional velocity heterogeneities give the appearance of discontinuity ...
... • Even nearby • The Discontinuity has large topographic hi variations i i over small ll spatial wavelengths the focus and defocus waves. • There is no actual discontinuity, but that complex three dimensional velocity heterogeneities give the appearance of discontinuity ...
Document
... The Earth is made up of 3 main layers (core, mantle, crust) On the surface of the Earth are tectonic plates that slowly move around the globe Plates are made of crust and upper mantle (lithosphere) There are 2 types of plate There are 3 types of plate boundaries Volcanoes and Earthquakes are closely ...
... The Earth is made up of 3 main layers (core, mantle, crust) On the surface of the Earth are tectonic plates that slowly move around the globe Plates are made of crust and upper mantle (lithosphere) There are 2 types of plate There are 3 types of plate boundaries Volcanoes and Earthquakes are closely ...
Canaries
... Gurenko, A. A., Hoernle, K. A., Hauff, F., Schmincke, H. U., Han, D., Miura, Y. N., & Kaneoka, I. (2006). Major, trace element and Nd–Sr– Pb–O–He–Ar isotope signatures of shield stage lavas from the central and western Canary Islands: Insights into mantle and crustal processes. Chemical Geology, 75- ...
... Gurenko, A. A., Hoernle, K. A., Hauff, F., Schmincke, H. U., Han, D., Miura, Y. N., & Kaneoka, I. (2006). Major, trace element and Nd–Sr– Pb–O–He–Ar isotope signatures of shield stage lavas from the central and western Canary Islands: Insights into mantle and crustal processes. Chemical Geology, 75- ...
Where Volcanoes Are Located
... Most volcanoes are found at convergent or divergent plate boundaries, but there are some intraplate volcanoes. The Hawaiian Islands are examples. The islands are the exposed peaks of a great chain of volcanoes that lie in the middle of the Pacific plate. The youngest of the Hawaiian Islands sits dir ...
... Most volcanoes are found at convergent or divergent plate boundaries, but there are some intraplate volcanoes. The Hawaiian Islands are examples. The islands are the exposed peaks of a great chain of volcanoes that lie in the middle of the Pacific plate. The youngest of the Hawaiian Islands sits dir ...
Mantle plume
A mantle plume is a mechanism proposed in 1971 to explain volcanic regions of the earth that were not thought to be explicable by the then-new theory of plate tectonics. Some such volcanic regions lie far from tectonic plate boundaries, for example, Hawaii. Others represent unusually large-volume volcanism, whether on plate boundaries, e.g. Iceland, or basalt floods such as the Deccan or Siberian traps.A mantle plume is posited to exist where hot rock nucleates at the core-mantle boundary and rises through the Earth's mantle becoming a diapir in the Earth's crust. The currently active volcanic centers are known as ""hot spots"". In particular, the concept that mantle plumes are fixed relative to one another, and anchored at the core-mantle boundary, was thought to provide a natural explanation for the time-progressive chains of older volcanoes seen extending out from some such hot spots, such as the Hawaiian–Emperor seamount chain.The hypothesis of mantle plumes from depth is not universally accepted as explaining all such volcanism. It has required progressive hypothesis-elaboration leading to variant propositions such as mini-plumes and pulsing plumes. Another hypothesis for unusual volcanic regions is the ""Plate model"". This proposes shallower, passive leakage of magma from the mantle onto the Earth's surface where extension of the lithosphere permits it, attributing most volcanism to plate tectonic processes, with volcanoes far from plate boundaries resulting from intraplate extension.