C. The Action Potential
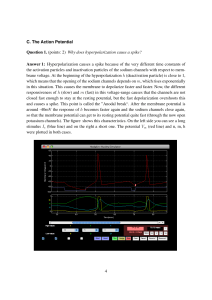
... in this situation. This causes the membrane to depolarize faster and faster. Now, the different responsiveness of h (slow) and m (fast) in this voltage-range causes that the channels are not closed fast enough to stay at the resting potential, but the fast depolarization overshoots this and causes a ...
... in this situation. This causes the membrane to depolarize faster and faster. Now, the different responsiveness of h (slow) and m (fast) in this voltage-range causes that the channels are not closed fast enough to stay at the resting potential, but the fast depolarization overshoots this and causes a ...
Lab 11 Nervous System I
... Describe the organization of the nervous system. Identify the structure and function of the neuroglia. Identify the differences between glial cells in the central nervous system and in the peripheral nervous system. Identify the structures of a typical neuron Compare the location and function of the ...
... Describe the organization of the nervous system. Identify the structure and function of the neuroglia. Identify the differences between glial cells in the central nervous system and in the peripheral nervous system. Identify the structures of a typical neuron Compare the location and function of the ...
193 CHAPTER 10: NERVOUS SYSTEM I OBJECTIVES: 1. Name
... Sensory receptors (located at the ends of peripheral neurons) detect changes (i.e. are stimulated) occurring in their surroundings; Once stimulated, sensory receptors transmit a sensory impulse to the CNS. A sensory impulse is carried on a sensory neuron. ...
... Sensory receptors (located at the ends of peripheral neurons) detect changes (i.e. are stimulated) occurring in their surroundings; Once stimulated, sensory receptors transmit a sensory impulse to the CNS. A sensory impulse is carried on a sensory neuron. ...
receptors and ion channels - The Company of Biologists
... Throughout this symposium a unifying idea is the interactions of receptors and ion channels and the modifiability of this connection. In recent years our knowledge of the different types of second messengers turned on by receptor activation and of their effects on the conductances of ion channels ha ...
... Throughout this symposium a unifying idea is the interactions of receptors and ion channels and the modifiability of this connection. In recent years our knowledge of the different types of second messengers turned on by receptor activation and of their effects on the conductances of ion channels ha ...
Concept Mapping Back Print
... A fibers. Motor impulses to skeletal muscles are also carried by A fibers. These types of impulses relay information about the external surroundings and how the body will respond to external stimuli. The speed with which these impulses are carried could reduce the incidence of injury to the body by ...
... A fibers. Motor impulses to skeletal muscles are also carried by A fibers. These types of impulses relay information about the external surroundings and how the body will respond to external stimuli. The speed with which these impulses are carried could reduce the incidence of injury to the body by ...
12-2cut
... This repolarizes membrane 3) Refractory period: time during which original state is regenerated by Na-K pumps. During this time, neuron __________ fire again. ...
... This repolarizes membrane 3) Refractory period: time during which original state is regenerated by Na-K pumps. During this time, neuron __________ fire again. ...
Nervous System
... same _________________ of signal transmission. More stimulus (i.e. more painful) = more impulses generated, NOT a stronger impulse. An impulse does not diminish in strength as it travels along a neuron. We already know that having a myelin insulation on an axon will __________ its impulse tran ...
... same _________________ of signal transmission. More stimulus (i.e. more painful) = more impulses generated, NOT a stronger impulse. An impulse does not diminish in strength as it travels along a neuron. We already know that having a myelin insulation on an axon will __________ its impulse tran ...
CNS Cellular Components - Johns Hopkins Medicine
... biochemical changes in the neuronal cell body following axonal damage. They include retraction of dendrites, cellular swelling and dispersion of Nissl bodies (chromatolysis), and accumulation of intermediate filaments. In the PNS, but not in the CNS, axonal regeneration and restoration of normal neu ...
... biochemical changes in the neuronal cell body following axonal damage. They include retraction of dendrites, cellular swelling and dispersion of Nissl bodies (chromatolysis), and accumulation of intermediate filaments. In the PNS, but not in the CNS, axonal regeneration and restoration of normal neu ...
Tutorial 4: Shapes and Roles of Glial Cells Figure 4: Shapes and
... In addition to neurons, the nervous system is populated with a category of cells that support the functions of neurons. These support cells are called glial cells in the central nervous system and satellite cells in the peripheral nervous system. Glial cells are approximately 10 times more plentiful ...
... In addition to neurons, the nervous system is populated with a category of cells that support the functions of neurons. These support cells are called glial cells in the central nervous system and satellite cells in the peripheral nervous system. Glial cells are approximately 10 times more plentiful ...
Human Anatomy & Physiology I
... depolarization to threshold level, the impulse will travel the entire length of the neuron at a constant and maximum strength. ...
... depolarization to threshold level, the impulse will travel the entire length of the neuron at a constant and maximum strength. ...
Candy Neurons
... Draw a picture of the neuron (with direction of a signal indicated) below: (must have candy neuron checked by me BEFORE DRAWING) ...
... Draw a picture of the neuron (with direction of a signal indicated) below: (must have candy neuron checked by me BEFORE DRAWING) ...
CONDUCTION INTRODUCTION
... Conduction of an action potential in myelinated fibers occurs by a process known as saltatory conduction. By this we mean that the action potential is conducted with great speed between nodes (due to greatly decreased time constant for conduction) and pauses to regenerate itself only at the nodes of ...
... Conduction of an action potential in myelinated fibers occurs by a process known as saltatory conduction. By this we mean that the action potential is conducted with great speed between nodes (due to greatly decreased time constant for conduction) and pauses to regenerate itself only at the nodes of ...
Components of Cell Membranes
... One of the main components of membranes are phospholipids, a type of lipid made from two fatty acid chain ‘tails’ attached to a phosphate group ‘head’. The phosphate group head is polar and hydrophilic (‘water-loving’), while the fatty acid chains of the tail are nonpolar and hydrophobic (‘water-hat ...
... One of the main components of membranes are phospholipids, a type of lipid made from two fatty acid chain ‘tails’ attached to a phosphate group ‘head’. The phosphate group head is polar and hydrophilic (‘water-loving’), while the fatty acid chains of the tail are nonpolar and hydrophobic (‘water-hat ...
Chapter 12
... Electrochemical Gradients for Potassium and Sodium Ions The electrochemical gradient for a specific ion is the sum of the chemical and electrical forces acting on the ion across the plasma membrane. The electrochemical gradients for K+ and Na+ are the primary factors affecting the resting membrane ...
... Electrochemical Gradients for Potassium and Sodium Ions The electrochemical gradient for a specific ion is the sum of the chemical and electrical forces acting on the ion across the plasma membrane. The electrochemical gradients for K+ and Na+ are the primary factors affecting the resting membrane ...
BIO201 Crimando Vocab 6 BIO201 Nervous System I Vocabulary
... Change in membrane voltage shifting to more positive value: ____________________ or ____________________ Change in membrane voltage shifting to more negative value: ____________________ or ____________________ Membrane potential level at which voltage-gated Na+ channels open: ____________________ Pe ...
... Change in membrane voltage shifting to more positive value: ____________________ or ____________________ Change in membrane voltage shifting to more negative value: ____________________ or ____________________ Membrane potential level at which voltage-gated Na+ channels open: ____________________ Pe ...
- Annals of Eye Science
... optic nerve is gradual and silent. And it’s hard to detect a clear anatomical abnormality of optic nerve in glaucoma. So re-growth of axon and redirection of axon to its original spatial position is quite hard. Without accurate localization of axon back to the central nervous system (CNS), it’s impo ...
... optic nerve is gradual and silent. And it’s hard to detect a clear anatomical abnormality of optic nerve in glaucoma. So re-growth of axon and redirection of axon to its original spatial position is quite hard. Without accurate localization of axon back to the central nervous system (CNS), it’s impo ...
Slide 1 - AccessPharmacy
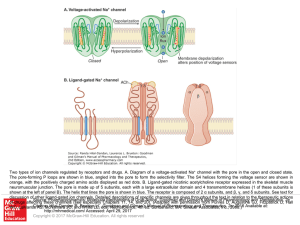
... Two types of ion channels regulated by receptors and drugs. A. Diagram of a voltage-activated Na+ channel with the pore in the open and closed state. The pore-forming P loops are shown in blue, angled into the pore to form the selectivity filter. The S4 helices forming the voltage sensor are shown i ...
... Two types of ion channels regulated by receptors and drugs. A. Diagram of a voltage-activated Na+ channel with the pore in the open and closed state. The pore-forming P loops are shown in blue, angled into the pore to form the selectivity filter. The S4 helices forming the voltage sensor are shown i ...
Learning Objectives
... 3. Distinguish among sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons. 4. List and describe the major parts of a neuron and explain the function of each. 5. Describe the function of astrocytes, radial glia, oligodendrocytes, and Schwann cells. ...
... 3. Distinguish among sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons. 4. List and describe the major parts of a neuron and explain the function of each. 5. Describe the function of astrocytes, radial glia, oligodendrocytes, and Schwann cells. ...
Slide ()
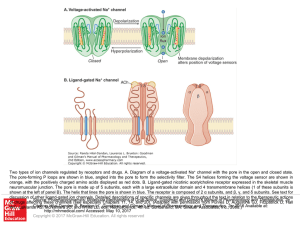
... Two types of ion channels regulated by receptors and drugs. A. Diagram of a voltage-activated Na+ channel with the pore in the open and closed state. The pore-forming P loops are shown in blue, angled into the pore to form the selectivity filter. The S4 helices forming the voltage sensor are shown i ...
... Two types of ion channels regulated by receptors and drugs. A. Diagram of a voltage-activated Na+ channel with the pore in the open and closed state. The pore-forming P loops are shown in blue, angled into the pore to form the selectivity filter. The S4 helices forming the voltage sensor are shown i ...
Technical Definitions
... and to other parts of the body. Expanded Definition: History: The term “neuron” was first introduced in an article by German anatomist Heinrich Wilhelm Waldeyer in 1891. Waldeyer proposed neurons to be specialized cells that make up the nervous system (Anctil, 2015). Spanish anatomist Ramon y Cajal ...
... and to other parts of the body. Expanded Definition: History: The term “neuron” was first introduced in an article by German anatomist Heinrich Wilhelm Waldeyer in 1891. Waldeyer proposed neurons to be specialized cells that make up the nervous system (Anctil, 2015). Spanish anatomist Ramon y Cajal ...
301 Definitions – Revised Shannon Benson
... and to other parts of the body. Expanded Definition: History: The term “neuron” was first introduced in an article by German anatomist Heinrich Wilhelm Waldeyer in 1891. Waldeyer proposed neurons to be specialized cells that make up the nervous system (Anctil, 2015). Spanish anatomist Ramon y Cajal ...
... and to other parts of the body. Expanded Definition: History: The term “neuron” was first introduced in an article by German anatomist Heinrich Wilhelm Waldeyer in 1891. Waldeyer proposed neurons to be specialized cells that make up the nervous system (Anctil, 2015). Spanish anatomist Ramon y Cajal ...
PowerPoint version
... Chapter 49 (part 2): Sensory Systems 1. A fish detects vibrations in the water around it by means of its lateral lines, rows of sensory receptors along each side of the body. Based on what you know about sensory receptors, the lateral line receptors are probably which of the following? a. hair cell ...
... Chapter 49 (part 2): Sensory Systems 1. A fish detects vibrations in the water around it by means of its lateral lines, rows of sensory receptors along each side of the body. Based on what you know about sensory receptors, the lateral line receptors are probably which of the following? a. hair cell ...
Node of Ranvier

The nodes of Ranvier also known as myelin sheath gaps, are the gaps (approximately 1 micrometer in length) formed between the myelin sheaths generated by different cells. A myelin sheath is a many-layered coating, largely composed of a fatty substance called myelin, that wraps around the axon of a neuron and very efficiently insulates it. At nodes of Ranvier, the axonal membrane is uninsulated and, therefore, capable of generating electrical activity.