Channels active in the excitability of nerves and skeletal muscles
... following an action potential and reach steady state over 100 –200 ms (15). Thus, they are involved in the last phase of recovery toward resting membrane potential following an action potential or series of action potentials (Fig. 1). Their two major physiological roles are stabilizing the resting p ...
... following an action potential and reach steady state over 100 –200 ms (15). Thus, they are involved in the last phase of recovery toward resting membrane potential following an action potential or series of action potentials (Fig. 1). Their two major physiological roles are stabilizing the resting p ...
Chapter 02 - Neurons and Glia
... altered gene expression would be useful. Samples of mRNA were collected from Nicolas’s brain and from a normal brain so that comparisons could be made. mRNAs from the two brains were labeled green and red, respectively. 1) Why is it useful to test differences in gene expression? 2) What happens when ...
... altered gene expression would be useful. Samples of mRNA were collected from Nicolas’s brain and from a normal brain so that comparisons could be made. mRNAs from the two brains were labeled green and red, respectively. 1) Why is it useful to test differences in gene expression? 2) What happens when ...
Structure of the Planarian Central Nervous System (CNS)
... gene of human (Furukubo-Tokunaga, personal communication), it is still difficult to imagine the common genetic programs between them, since the position and the structure as * Corresponding author: Tel. +81-7915-8-0187; FAX. +81-7915-8-0187. ...
... gene of human (Furukubo-Tokunaga, personal communication), it is still difficult to imagine the common genetic programs between them, since the position and the structure as * Corresponding author: Tel. +81-7915-8-0187; FAX. +81-7915-8-0187. ...
Channels active in the excitability of nerves and skeletal muscles
... following an action potential and reach steady state over 100 –200 ms (15). Thus, they are involved in the last phase of recovery toward resting membrane potential following an action potential or series of action potentials (Fig. 1). Their two major physiological roles are stabilizing the resting p ...
... following an action potential and reach steady state over 100 –200 ms (15). Thus, they are involved in the last phase of recovery toward resting membrane potential following an action potential or series of action potentials (Fig. 1). Their two major physiological roles are stabilizing the resting p ...
Chapter 7 The Nervous System - Mrs. heninger
... Nerve fibers that carry impulses away from the central nervous system to organs, muscles, & glands. The impulses “effect” (bring about) a motor response. ...
... Nerve fibers that carry impulses away from the central nervous system to organs, muscles, & glands. The impulses “effect” (bring about) a motor response. ...
Neurons and Nervous Tissue
... An action potential is an all-or-none event because voltage-gated Na+ channels have a positive feedback mechanism that ensures the maximum value of the action potential. An action potential is selfregenerating because it spreads to adjacent membrane regions. ...
... An action potential is an all-or-none event because voltage-gated Na+ channels have a positive feedback mechanism that ensures the maximum value of the action potential. An action potential is selfregenerating because it spreads to adjacent membrane regions. ...
The Lymphatic System
... Lymph capillaries Closed-ended vessels Lined by endothelium 1-way flaps into capillary Allows passage of tissue fluid, large proteins, bacteria, viruses, cancer cells, cell debris ...
... Lymph capillaries Closed-ended vessels Lined by endothelium 1-way flaps into capillary Allows passage of tissue fluid, large proteins, bacteria, viruses, cancer cells, cell debris ...
The Cell Membrane - Libreria Universo
... ample, insulin increases glucose transport into cells by moving glucose transporters from an intracellular reservoir into the membrane. Primary-active carrier-mediated transport involves energy expenditure. The energy comes mostly from ATP that is hydrolyzed by the carrier protein itself, which also ...
... ample, insulin increases glucose transport into cells by moving glucose transporters from an intracellular reservoir into the membrane. Primary-active carrier-mediated transport involves energy expenditure. The energy comes mostly from ATP that is hydrolyzed by the carrier protein itself, which also ...
Second cause of hidden hearing loss identified
... hidden hearing loss. Even after the myelin regenerated, damage to a nerve structure called the heminode remained. Synapse loss versus myelin disruption ...
... hidden hearing loss. Even after the myelin regenerated, damage to a nerve structure called the heminode remained. Synapse loss versus myelin disruption ...
1 Electrophysiology and pacemaker function of the - AJP
... and lower mammals also have highlighted that the fibroblast, and therefore collagen, content of the heart is subject to strong developmental regulation: it is low during initial embryogenesis, and increases during late embryogenesis and postnatal growth (3, 19, 27, 103). After this period of expansi ...
... and lower mammals also have highlighted that the fibroblast, and therefore collagen, content of the heart is subject to strong developmental regulation: it is low during initial embryogenesis, and increases during late embryogenesis and postnatal growth (3, 19, 27, 103). After this period of expansi ...
A microfluidic culture platform for CNS axonal injury, regeneration
... MAP2). Frames including the longest dendrites in each chamber were imaged. Dashed lines indicate the protein synthesis occurs and is important barrier region. in the development, maintenance and plasticity of synapses22. Much of this work uses invertebrate models such as Aplysia and squid giant axon ...
... MAP2). Frames including the longest dendrites in each chamber were imaged. Dashed lines indicate the protein synthesis occurs and is important barrier region. in the development, maintenance and plasticity of synapses22. Much of this work uses invertebrate models such as Aplysia and squid giant axon ...
A Functional Role for Intra-Axonal Protein Synthesis during Axonal
... (Steward, 1997; Schuman, 1999; Martin et al., 2000). Although mRNAs are thought to be excluded from most adult vertebrate axons, intra-axonal translation has been demonstrated in neurons of several invertebrate species (Giuditta et al., 1991; Davis et al., 1992; van Minnen et al., 1997). There is ev ...
... (Steward, 1997; Schuman, 1999; Martin et al., 2000). Although mRNAs are thought to be excluded from most adult vertebrate axons, intra-axonal translation has been demonstrated in neurons of several invertebrate species (Giuditta et al., 1991; Davis et al., 1992; van Minnen et al., 1997). There is ev ...
E3R Game 1 Order That Student Copy
... A. Receptors are ligand gated sodium ion channels which allow Na+ to enter the postsynaptic neuron (or muscle) and triggers an action potential in the postsynaptic neuron (or muscle contraction) B. Action potential gets to the end of the presynaptic axon C. The Ca++ triggers synaptic vesicles locate ...
... A. Receptors are ligand gated sodium ion channels which allow Na+ to enter the postsynaptic neuron (or muscle) and triggers an action potential in the postsynaptic neuron (or muscle contraction) B. Action potential gets to the end of the presynaptic axon C. The Ca++ triggers synaptic vesicles locate ...
The Domino Effect
... and does not vary in intensity. This reversal of polarity causes the same change in the neighboring area of the membrane, which causes a reversal of polarity further along, and so on. In this way, the impulse propagates along the length of the neuron as a cascade of ionic exchanges. It does not lose ...
... and does not vary in intensity. This reversal of polarity causes the same change in the neighboring area of the membrane, which causes a reversal of polarity further along, and so on. In this way, the impulse propagates along the length of the neuron as a cascade of ionic exchanges. It does not lose ...
Release of neurotransmitters from glia
... that the kinetics of calcium response are important in neurotransmitter release from astrocytes, and that slow calcium oscillation rather than large increases in calcium can be important, as well as differences between submembrane calcium transients versus bulk cytoplasmic calcium changes. Differenc ...
... that the kinetics of calcium response are important in neurotransmitter release from astrocytes, and that slow calcium oscillation rather than large increases in calcium can be important, as well as differences between submembrane calcium transients versus bulk cytoplasmic calcium changes. Differenc ...
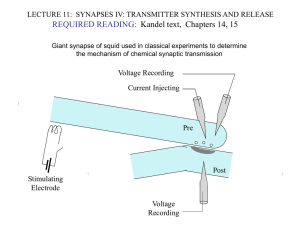
LECTURE11.SynapsesIV
... AXONAL ACTION POTENTIAL MODIFIES NEUROTRANSMITTER EXOCYTOSIS AND EPSP An action potential normally produces a transient increase in presynaptic calcium, which is dissipated by diffusion and calcium buffers. A high-frequency train of spike (tetanus) saturates the buffering capacity, creating a period ...
... AXONAL ACTION POTENTIAL MODIFIES NEUROTRANSMITTER EXOCYTOSIS AND EPSP An action potential normally produces a transient increase in presynaptic calcium, which is dissipated by diffusion and calcium buffers. A high-frequency train of spike (tetanus) saturates the buffering capacity, creating a period ...
Use the following information to answer the next question.
... Nerve impulses would also be reduced because of the axonopathy. While the speed of nerve impulse conduction could be normal, defects within the axons themselves would inhibit conduction. As a result, fewer nerve impulses would be transmitted. • Describe two kinds of evidence that could be obtained f ...
... Nerve impulses would also be reduced because of the axonopathy. While the speed of nerve impulse conduction could be normal, defects within the axons themselves would inhibit conduction. As a result, fewer nerve impulses would be transmitted. • Describe two kinds of evidence that could be obtained f ...
VGIchan: Prediction and Classification of Voltage-Gated Ion
... proteins that enable the passage of selected inorganic ions across cell membranes. They open and close in response to changes in transmembrane voltage, and play a key role in electric signaling by excitable cells such as neurons (1 ). They also have a critical role in the function of the nervous sys ...
... proteins that enable the passage of selected inorganic ions across cell membranes. They open and close in response to changes in transmembrane voltage, and play a key role in electric signaling by excitable cells such as neurons (1 ). They also have a critical role in the function of the nervous sys ...
The Pathology of Multiple Sclerosis and Its Variants
... activity to plaques that are active only at their margin, to chronic, inactive demyelinated shrunken glial scars. Although plaques can appear anywhere there is central myelin, there is a predilection for the periventricular white matter, optic nerves, spinal cord, and juxtacortical areas. Areas of w ...
... activity to plaques that are active only at their margin, to chronic, inactive demyelinated shrunken glial scars. Although plaques can appear anywhere there is central myelin, there is a predilection for the periventricular white matter, optic nerves, spinal cord, and juxtacortical areas. Areas of w ...
Contribution of calcium-conducting channels to the transport of
... capable of permeating other types of cations such as barium (Ba) and strontium (Sr) [27, 46, 54]. Although Zn ions exert inhibitory actions on VGCC [41], they can nevertheless permeate through them. One of the first indication that Ca-conducting channels can transport Zn ions came from electrophysio ...
... capable of permeating other types of cations such as barium (Ba) and strontium (Sr) [27, 46, 54]. Although Zn ions exert inhibitory actions on VGCC [41], they can nevertheless permeate through them. One of the first indication that Ca-conducting channels can transport Zn ions came from electrophysio ...
The Nervous System
... by both the sympathetic and the parasympathetic divisions. The two systems work antagonistically to maintain homeostasis, with only one system stimulating the organ at any given time. Determining which system is in control is easy, based on the organ’s activity. If the organ is burning energy, relea ...
... by both the sympathetic and the parasympathetic divisions. The two systems work antagonistically to maintain homeostasis, with only one system stimulating the organ at any given time. Determining which system is in control is easy, based on the organ’s activity. If the organ is burning energy, relea ...
Sample
... Objective: Factual LO: 2.2 APA: 1.2 36) The ________ are important for the process of myelination of nerve axon membranes in brain. A) oligodendrocytes B) microglia C) astrocytes D) neurocytes E) Schwann cells Answer: A Diff: 1 Page Ref: 27 Objective: Factual LO: 2.2 APA:1.1 37) Which of the followi ...
... Objective: Factual LO: 2.2 APA: 1.2 36) The ________ are important for the process of myelination of nerve axon membranes in brain. A) oligodendrocytes B) microglia C) astrocytes D) neurocytes E) Schwann cells Answer: A Diff: 1 Page Ref: 27 Objective: Factual LO: 2.2 APA:1.1 37) Which of the followi ...
Neuronal polarity: from extracellular signals to
... undergo Y-shaped branching1,2. Axons contain synaptic vesicles from which they release neurotransmitters at axon terminals in response to electrical signals from the cell body. Dendrites, especially dendritic spines, contain receptors for these neurotransmitters, as well as organelles and signalling ...
... undergo Y-shaped branching1,2. Axons contain synaptic vesicles from which they release neurotransmitters at axon terminals in response to electrical signals from the cell body. Dendrites, especially dendritic spines, contain receptors for these neurotransmitters, as well as organelles and signalling ...
Slow Changes in the Availability of Voltage
... systems that go through periods of long lasting depolarization. However, for the more general case, where depolarizing input occurs in episodes of various (mostly short) duration and frequencies, inactivation must accumulate and persist between repetitive action potentials in order to become biologi ...
... systems that go through periods of long lasting depolarization. However, for the more general case, where depolarizing input occurs in episodes of various (mostly short) duration and frequencies, inactivation must accumulate and persist between repetitive action potentials in order to become biologi ...
Node of Ranvier

The nodes of Ranvier also known as myelin sheath gaps, are the gaps (approximately 1 micrometer in length) formed between the myelin sheaths generated by different cells. A myelin sheath is a many-layered coating, largely composed of a fatty substance called myelin, that wraps around the axon of a neuron and very efficiently insulates it. At nodes of Ranvier, the axonal membrane is uninsulated and, therefore, capable of generating electrical activity.