Nerve Physiology
... resulting depolarization is called an Excitatory Post Synaptic Potential (EPSP). These individual potentials are sub-threshold. If the transmitter opens an anion influx, the resulting hyperpolarization is called an Inhibitory Post Synaptic Potential (IPSP All these potentials are additive. ...
... resulting depolarization is called an Excitatory Post Synaptic Potential (EPSP). These individual potentials are sub-threshold. If the transmitter opens an anion influx, the resulting hyperpolarization is called an Inhibitory Post Synaptic Potential (IPSP All these potentials are additive. ...
The Nervous System (Chapter 7)
... Clusters of neuron cell bodies and collection of nerve fibers are named differently when they are in the CNS than when they are part of the PNS. 12. What are nuclei? _____________________________________________________________________________ 13. What is the difference between white matter and gray ...
... Clusters of neuron cell bodies and collection of nerve fibers are named differently when they are in the CNS than when they are part of the PNS. 12. What are nuclei? _____________________________________________________________________________ 13. What is the difference between white matter and gray ...
1
... Long Lived, amitotic (don’t divide), and have a high metabolic rate Their plasma membrane functions in electrical signaling and cell-to-cell signaling during development ...
... Long Lived, amitotic (don’t divide), and have a high metabolic rate Their plasma membrane functions in electrical signaling and cell-to-cell signaling during development ...
THE NEuRoN - Big Picture
... Many neurons are insulated by myelin: multiple layers of cell membrane that wrap around the axon. The sheath is interrupted at regular intervals ( ‘nodes of Ranvier’), where the channels that generate the electrical signal are located. Myelin reduces leakage of electrical charge from the axon, resul ...
... Many neurons are insulated by myelin: multiple layers of cell membrane that wrap around the axon. The sheath is interrupted at regular intervals ( ‘nodes of Ranvier’), where the channels that generate the electrical signal are located. Myelin reduces leakage of electrical charge from the axon, resul ...
Types of neurons - Brigham Young University
... to 1m) process designed to convey info away from the cell body. Transmit APs from the soma toward the end of the axon where they cause NT release. Often branch sparsely, forming collaterals. Each collateral may split into telodendria which end in a synaptic knob, which contains synaptic vesicl ...
... to 1m) process designed to convey info away from the cell body. Transmit APs from the soma toward the end of the axon where they cause NT release. Often branch sparsely, forming collaterals. Each collateral may split into telodendria which end in a synaptic knob, which contains synaptic vesicl ...
Histology of the Peripheral Nervous System
... axons of small diameter are usually unmyelinated in CNS; not embedded in oligodendrocytes in PNS; enveloped within simple grooves of the Schwann cells A single axon or a group of axons may be enclosed in a single invagination of the Schwann cell surface. ...
... axons of small diameter are usually unmyelinated in CNS; not embedded in oligodendrocytes in PNS; enveloped within simple grooves of the Schwann cells A single axon or a group of axons may be enclosed in a single invagination of the Schwann cell surface. ...
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM - Coast Colleges Home Page
... Sodium-Potassium Pump moves Na+ out & K+ in (Requires Energy) ...
... Sodium-Potassium Pump moves Na+ out & K+ in (Requires Energy) ...
Document
... _ Maintain ionic homeostasis _ Take up neurotransmitters _ Form glial scars (gliosis) _ Oligodendrocytes _ Present in white and gray matter _ Interfascicular oligodendrocytes are located in the white matter ofthe CNS, where they produce the myelin sheath. _ Ependymal cells. Line ventricles _ Microgl ...
... _ Maintain ionic homeostasis _ Take up neurotransmitters _ Form glial scars (gliosis) _ Oligodendrocytes _ Present in white and gray matter _ Interfascicular oligodendrocytes are located in the white matter ofthe CNS, where they produce the myelin sheath. _ Ependymal cells. Line ventricles _ Microgl ...
Neurology - wsscience
... a) Astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia, ependymal cells b) unipolar, bipolar, multipolar cells c) Efferent, afferent, association cells d) Motor, sensory, interneuron cells ...
... a) Astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia, ependymal cells b) unipolar, bipolar, multipolar cells c) Efferent, afferent, association cells d) Motor, sensory, interneuron cells ...
The Nervous System- Nervous Tissue
... in the PNS creating a neurilemma around them. Neurilemma allows for potential regeneration of damaged axons • creates myelin sheath around most axons of PNS ...
... in the PNS creating a neurilemma around them. Neurilemma allows for potential regeneration of damaged axons • creates myelin sheath around most axons of PNS ...
Your Name Here______________________________
... b. Na+ diffusing into it. c. K+ diffusing out of it d. Na+ diffusing out of it. 3. The velocity of nerve impulse conduction is greatest in nerve fibers that are _______ in diameter and _______. a. large; myelinated b. small; myelinated c. large; unmyelinated d. small; unmyelinated 4. Neurotransmitte ...
... b. Na+ diffusing into it. c. K+ diffusing out of it d. Na+ diffusing out of it. 3. The velocity of nerve impulse conduction is greatest in nerve fibers that are _______ in diameter and _______. a. large; myelinated b. small; myelinated c. large; unmyelinated d. small; unmyelinated 4. Neurotransmitte ...
file - Athens Academy
... In addition to helping us maintain our sanity, having an imbalance in this neurotransmitter plays a role in the development of Parkinson’s Disease. ...
... In addition to helping us maintain our sanity, having an imbalance in this neurotransmitter plays a role in the development of Parkinson’s Disease. ...
Nervous Systems
... Bind to receptors on neurons, muscle cells, or gland cells Broken down by enzymes or taken back up into surrounding cells Types of neurotransmitters: Excitatory: speed up impulses by causing depolarization of postsynaptic membrane Inhibitory: slow impulses by causing hyperpolarization of postsyn ...
... Bind to receptors on neurons, muscle cells, or gland cells Broken down by enzymes or taken back up into surrounding cells Types of neurotransmitters: Excitatory: speed up impulses by causing depolarization of postsynaptic membrane Inhibitory: slow impulses by causing hyperpolarization of postsyn ...
Overview of the Nervous System (the most important system in the
... Saltatory Conduction (myelinated axons) Depolarization only at nodes of Ranvier where there is a high density of voltagegated ion channels The myelin sheath and nodes of Ranvier act like a capacitor, and the impulse “leaps” down the axon, regenerating itself at each node ...
... Saltatory Conduction (myelinated axons) Depolarization only at nodes of Ranvier where there is a high density of voltagegated ion channels The myelin sheath and nodes of Ranvier act like a capacitor, and the impulse “leaps” down the axon, regenerating itself at each node ...
Nervous System - APBio
... • Tropomyosin – regulatory proteins that blocks the myosin binding sites on the thin filaments • Depolarization of neuron allows Ca+ in the cell. • Ca+ binds to troponin complex which controls the position of the tropomyosin on the thin filaments, uncovering the binding sites – allowing ...
... • Tropomyosin – regulatory proteins that blocks the myosin binding sites on the thin filaments • Depolarization of neuron allows Ca+ in the cell. • Ca+ binds to troponin complex which controls the position of the tropomyosin on the thin filaments, uncovering the binding sites – allowing ...
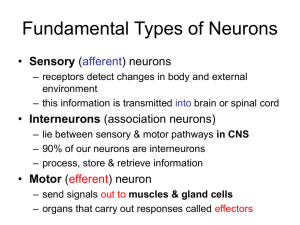
Fundamental Types of Neurons
... mechanisms for producing electrical potentials & currents – electrical potential - difference in concentration of charged particles between different parts of the cell – electrical current - flow of charged particles from one point to another ...
... mechanisms for producing electrical potentials & currents – electrical potential - difference in concentration of charged particles between different parts of the cell – electrical current - flow of charged particles from one point to another ...
3.E.2 Nervous System - kromko
... The sodium-potassium pump, powered by ATP, counters the effect of the leak channels, working to maintain the resting membrane potential at -70 mV. ...
... The sodium-potassium pump, powered by ATP, counters the effect of the leak channels, working to maintain the resting membrane potential at -70 mV. ...
Biology 12 - Chapter 17 - Biology12-Lum
... send it to your central nervous system (CNS) (which is your brain and spinal cord). This is then sent back to the PNS so your body can respond ...
... send it to your central nervous system (CNS) (which is your brain and spinal cord). This is then sent back to the PNS so your body can respond ...
The Nervous System: Neural Tissue
... 1. The minimum stimulus needed to trigger a depolarization and an impulse is called a Threshold stimulus. 2. The All – or – None Law says that action potentials will happen completely or not at all. 3. All action potentials are alike no matter the strength of the stimulus. 4. Frequency of impulse tr ...
... 1. The minimum stimulus needed to trigger a depolarization and an impulse is called a Threshold stimulus. 2. The All – or – None Law says that action potentials will happen completely or not at all. 3. All action potentials are alike no matter the strength of the stimulus. 4. Frequency of impulse tr ...
The Nervous System - Downtown Magnets High School
... • Increases with myelin (80% lipid, 20% protein) • Myelin surrounds axon; acts as electric insulator • Created from Schwann cells. ...
... • Increases with myelin (80% lipid, 20% protein) • Myelin surrounds axon; acts as electric insulator • Created from Schwann cells. ...
Node of Ranvier

The nodes of Ranvier also known as myelin sheath gaps, are the gaps (approximately 1 micrometer in length) formed between the myelin sheaths generated by different cells. A myelin sheath is a many-layered coating, largely composed of a fatty substance called myelin, that wraps around the axon of a neuron and very efficiently insulates it. At nodes of Ranvier, the axonal membrane is uninsulated and, therefore, capable of generating electrical activity.