Document
... c. What ion enters the cell at the axon terminals and initiates the process of neurotransmitter release? Ca+ d. When acetylcholines(neurotransmitters) bind to muscarinic, Which ion channels will be open? Cause depolarization, repolarization, or hyperpolarization? The ion in or out of the cell? K+; h ...
... c. What ion enters the cell at the axon terminals and initiates the process of neurotransmitter release? Ca+ d. When acetylcholines(neurotransmitters) bind to muscarinic, Which ion channels will be open? Cause depolarization, repolarization, or hyperpolarization? The ion in or out of the cell? K+; h ...
Nerve tissue File
... Slender processes of uniform diameter arising from the hillock, carrying information away from the cell Long axons are called nerve fibers One leads from the big toe up the leg, past the cell body near the spinal cord, into the cord and up to the brainstem, a couple meters or more. ...
... Slender processes of uniform diameter arising from the hillock, carrying information away from the cell Long axons are called nerve fibers One leads from the big toe up the leg, past the cell body near the spinal cord, into the cord and up to the brainstem, a couple meters or more. ...
Module Worksheet - Germantown School District
... This activity explains the way that neurons communicate with each other. Neuron Parts Match the part of the neuron identified with its description: o ...
... This activity explains the way that neurons communicate with each other. Neuron Parts Match the part of the neuron identified with its description: o ...
PsychSim 5: NEURAL MESSAGES Name: Section: Date: ______
... This activity explains the way that neurons communicate with each other. Neuron Parts Match the part of the neuron identified with its description: o ...
... This activity explains the way that neurons communicate with each other. Neuron Parts Match the part of the neuron identified with its description: o ...
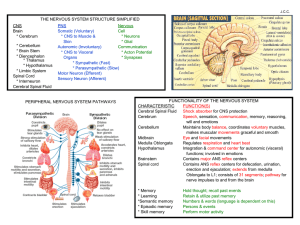
CNS Brain * Cerebrum * Cerebellum * Brain Stem * Diencephalon
... erection and ejaculation; extends from medulla Oblongata to L1; consists of 31 segments; pathway for nerve impulses to and from the brain * Memory * Learning *Semantic memory * Episodic memory * Skill memory ...
... erection and ejaculation; extends from medulla Oblongata to L1; consists of 31 segments; pathway for nerve impulses to and from the brain * Memory * Learning *Semantic memory * Episodic memory * Skill memory ...
File
... oligodendrocyte forms myelin sheaths for several (3–50) nerve fibers. The axolemma shows a thickening where the cell membrane of the oligodendrocyte comes into contact with it. This limits the diffusion of materials into the periaxonal space between the axon and the myelin sheath ...
... oligodendrocyte forms myelin sheaths for several (3–50) nerve fibers. The axolemma shows a thickening where the cell membrane of the oligodendrocyte comes into contact with it. This limits the diffusion of materials into the periaxonal space between the axon and the myelin sheath ...
Ch. 12 – Nerve Cells
... 4. signal travels from dendrite cell body axon 5. K+ channels then open behind the action potential allowing K+ out to re-polarize the cell 6. action potential reaches end of axon stimulating neurotransmitter to be released to next neuron OR an effector (muscle, gland, etc.) ...
... 4. signal travels from dendrite cell body axon 5. K+ channels then open behind the action potential allowing K+ out to re-polarize the cell 6. action potential reaches end of axon stimulating neurotransmitter to be released to next neuron OR an effector (muscle, gland, etc.) ...
kumc 05 nervous system review student
... information to the cell body. Usually several to many. Relatively short. Often branched. Have receptors for neurotransmitters. Conduct local potentials. ...
... information to the cell body. Usually several to many. Relatively short. Often branched. Have receptors for neurotransmitters. Conduct local potentials. ...
CHAPTER 10
... If the stimulus is strong enough to cause a response in the neuron, it responds _______________________. A greater intensity of stimulation produces more impulses per second; not a _______________________ impulse. For a very short time following passage of a nerve impulse, a threshold stimulus will ...
... If the stimulus is strong enough to cause a response in the neuron, it responds _______________________. A greater intensity of stimulation produces more impulses per second; not a _______________________ impulse. For a very short time following passage of a nerve impulse, a threshold stimulus will ...
eprint_2_23793_166
... and transmit information to and from other neurons, muscle cells, or glands. 2) Composed of a cell body, dendrites, axon and its terminal arborization, and synapses. B. Glial cells (neuroglia) (supporting cells): 1) Provide metabolic and structural support for neurons, insulation (myelin sheath), ho ...
... and transmit information to and from other neurons, muscle cells, or glands. 2) Composed of a cell body, dendrites, axon and its terminal arborization, and synapses. B. Glial cells (neuroglia) (supporting cells): 1) Provide metabolic and structural support for neurons, insulation (myelin sheath), ho ...
Biol 155 Human Physiology - University of British Columbia
... making the inside positive. The Na+ channels close at the same time the V-G K+ channels open. When this happens, there is a rush of K+ out of the cell, making the inside more negative. ...
... making the inside positive. The Na+ channels close at the same time the V-G K+ channels open. When this happens, there is a rush of K+ out of the cell, making the inside more negative. ...
Nervous System Functions
... The gated channels for Ca2+ respond to the action potential by opening up. In turn, the Ca2+ enters the cell and triggers the release of neurotransmitters. The neurotransmitter crosses the synapse and binds with protein receptors on the next neuron membrane. Neurotransmitters degrade or are re ...
... The gated channels for Ca2+ respond to the action potential by opening up. In turn, the Ca2+ enters the cell and triggers the release of neurotransmitters. The neurotransmitter crosses the synapse and binds with protein receptors on the next neuron membrane. Neurotransmitters degrade or are re ...
file - Athens Academy
... allow the current to flow easily between the extracellular fluid and the axon. allow action potentials to develop. allow for saltatory conduction of the action potential. All of these are true of nodes of Ranvier. ...
... allow the current to flow easily between the extracellular fluid and the axon. allow action potentials to develop. allow for saltatory conduction of the action potential. All of these are true of nodes of Ranvier. ...
ANATOMICAL ORGANIZATION of the NERVOUS SYSTEM
... Branches off the cell body that carry information to the cell body. Usually several to many. Relatively short. Often branched. Have receptors for neurotransmitters. Conduct local potentials. ...
... Branches off the cell body that carry information to the cell body. Usually several to many. Relatively short. Often branched. Have receptors for neurotransmitters. Conduct local potentials. ...
The Nervous System - biology-rocks
... Occurs when there is a intense stimulus that reach the threshold value ALL-OR-NONE (yes-impulse or none at all) ...
... Occurs when there is a intense stimulus that reach the threshold value ALL-OR-NONE (yes-impulse or none at all) ...
File
... – 1. Sensory: carry impulses from sense organs to the brain – 2. Motor: carry impulses from the brain to ...
... – 1. Sensory: carry impulses from sense organs to the brain – 2. Motor: carry impulses from the brain to ...
PsychSim 5 neural messages
... This activity explains the way that neurons communicate with each other. Neuron Parts Match the part of the neuron identified with its description: o ___ Axon ...
... This activity explains the way that neurons communicate with each other. Neuron Parts Match the part of the neuron identified with its description: o ___ Axon ...
NMSI - 1 Intro to the Nervous System
... reading the question and ending with marking an answer. a. interneurons motor neurons sensory neurons effectors b. effectors sensory neurons interneurons motor neurons c. sensory neurons interneurons motor neurons effectors d. interneurons sensory neurons motor neurons effect ...
... reading the question and ending with marking an answer. a. interneurons motor neurons sensory neurons effectors b. effectors sensory neurons interneurons motor neurons c. sensory neurons interneurons motor neurons effectors d. interneurons sensory neurons motor neurons effect ...
Nerve Tissue - Coach Frei Science
... 23. ____ A neuron that conducts impulses away from the brain and the spinal cord to the muscles or glands. 24. ____ Some change that occurs within or outside the body, that cause signals to be sent via the nervous System, for example: a change in temperature. 25. ____ A neuron that conducts impulses ...
... 23. ____ A neuron that conducts impulses away from the brain and the spinal cord to the muscles or glands. 24. ____ Some change that occurs within or outside the body, that cause signals to be sent via the nervous System, for example: a change in temperature. 25. ____ A neuron that conducts impulses ...
PsychSim - Stamford High School
... This activity explains the way that neurons communicate with each other. Neuron Parts Match ...
... This activity explains the way that neurons communicate with each other. Neuron Parts Match ...
Node of Ranvier

The nodes of Ranvier also known as myelin sheath gaps, are the gaps (approximately 1 micrometer in length) formed between the myelin sheaths generated by different cells. A myelin sheath is a many-layered coating, largely composed of a fatty substance called myelin, that wraps around the axon of a neuron and very efficiently insulates it. At nodes of Ranvier, the axonal membrane is uninsulated and, therefore, capable of generating electrical activity.