Baclofen: Interaction with GABA Receptor Leading to CNS Depression
... receptor agonists, such as baclofen, are a common treatment for spasticity because they are effective in reducing muscle tone and, thus, muscle spasticity. The treatment for long term pain management following such traumas often includes opioid analgesic medications as well. Providers prescribing bo ...
... receptor agonists, such as baclofen, are a common treatment for spasticity because they are effective in reducing muscle tone and, thus, muscle spasticity. The treatment for long term pain management following such traumas often includes opioid analgesic medications as well. Providers prescribing bo ...
Chapter_Twenty_1_
... • The antihistamines are a family of drugs that counteract the effect of histamine because they are histamine receptor antagonists. • They competitively block the attachment of histamine to its receptors. Antihistamines have in common a disubstituted ethylamine side chain, usually with two N-methyl ...
... • The antihistamines are a family of drugs that counteract the effect of histamine because they are histamine receptor antagonists. • They competitively block the attachment of histamine to its receptors. Antihistamines have in common a disubstituted ethylamine side chain, usually with two N-methyl ...
Wheel Runnin Alters Serotonin (5-HT) Transporter, 5
... SEROTONIN 1A & 1B RECEPTORS (5-HT1A & 5-HT1B) Located on soma, dendrites and axon terminals Act as auto receptors that inhibit: ...
... SEROTONIN 1A & 1B RECEPTORS (5-HT1A & 5-HT1B) Located on soma, dendrites and axon terminals Act as auto receptors that inhibit: ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... specific enzyme (eg. adenylate cyclase or phospholipase C), which causes synthesis of second messenger ...
... specific enzyme (eg. adenylate cyclase or phospholipase C), which causes synthesis of second messenger ...
Drugs for Respiratory System
... Mechanism of Action: 1. Stabilizer of mass cell membrane: decrease the release of mediators from mast cells. 2. Inhibit the function of sensory nerve ending and neurogenic inflammation in airway. 3. Decrease bronchial hyperreactivity. ...
... Mechanism of Action: 1. Stabilizer of mass cell membrane: decrease the release of mediators from mast cells. 2. Inhibit the function of sensory nerve ending and neurogenic inflammation in airway. 3. Decrease bronchial hyperreactivity. ...
G protein
... • Cell-to-cell communication is essential for both multicellular and unicellular organisms • Biologists have discovered some universal mechanisms of cellular regulation • Cells most often communicate with each other via chemical signals • For example, the fight-or-flight response is triggered by a s ...
... • Cell-to-cell communication is essential for both multicellular and unicellular organisms • Biologists have discovered some universal mechanisms of cellular regulation • Cells most often communicate with each other via chemical signals • For example, the fight-or-flight response is triggered by a s ...
IN SILICO QUINAZOLINONES AS NMDA RECEPTOR INHIBITORS FOR ANTICONVULSANT ACTIVITY Research Article
... can precipitate convulsions in patients with seizure disorders. The compound is regarded as a NMDA receptor agonist. Clonic tonic seizures are elicited in mice which are antagonized by anticonvulsant drugs. Ten mice of either sex with a weight of 35 to 40 g were treated with test compound or the sta ...
... can precipitate convulsions in patients with seizure disorders. The compound is regarded as a NMDA receptor agonist. Clonic tonic seizures are elicited in mice which are antagonized by anticonvulsant drugs. Ten mice of either sex with a weight of 35 to 40 g were treated with test compound or the sta ...
CHEMICAL SENSES: SMELL AND TASTE _____ = Olfaction
... ______ of food is a composite of _____________ ________________. - when nose is congested by infection, food “tastes” different because the olfactory system is “blocked” In humans, the senses of taste and smell have lost important survival characteristics In many animal species, taste (especially of ...
... ______ of food is a composite of _____________ ________________. - when nose is congested by infection, food “tastes” different because the olfactory system is “blocked” In humans, the senses of taste and smell have lost important survival characteristics In many animal species, taste (especially of ...
Slide 1
... FIGURE 47.2 Model of short-term heterosynaptic facilitation of the sensorimotor connection that contributes to short-term sensitization in Aplysia. (A1) Sensitizing stimuli activate facilitatory interneurons (IN) that release modulatory transmitters, one of which is 5-HT. The modulator leads to an ...
... FIGURE 47.2 Model of short-term heterosynaptic facilitation of the sensorimotor connection that contributes to short-term sensitization in Aplysia. (A1) Sensitizing stimuli activate facilitatory interneurons (IN) that release modulatory transmitters, one of which is 5-HT. The modulator leads to an ...
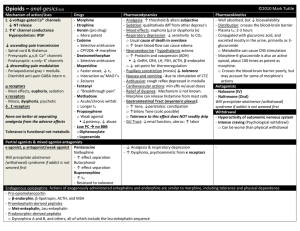
OPIOID ANALGESICS
... in the right hypochondrium, nausea, vomiting and temperature of 102 F. If hepatobiliary imaging reveals an obstructed cystic duct, which of the following agents would be the drug of choice for the treatment of this patient’s pain? ...
... in the right hypochondrium, nausea, vomiting and temperature of 102 F. If hepatobiliary imaging reveals an obstructed cystic duct, which of the following agents would be the drug of choice for the treatment of this patient’s pain? ...
*****************#***********#******|6******7#**8#**9
... • Antibodies against the a subunit of the nAChR • The ability of ACh to activate the nAChRs is blocked by the antibodies • As for many autoimmune diseases, stress can make the symptoms worse • Treatment is to potentiate cholinergic signaling and to remove the antibodies (blood dialysis) ...
... • Antibodies against the a subunit of the nAChR • The ability of ACh to activate the nAChRs is blocked by the antibodies • As for many autoimmune diseases, stress can make the symptoms worse • Treatment is to potentiate cholinergic signaling and to remove the antibodies (blood dialysis) ...
Health Canada - Isomer Design
... Canadian Status: JWH-175 and JWH-072 are not listed in the Schedules to the CDSA. JWH175 has been reported to bind to the CB1 cannabinoid receptor whereas JWH-072 has an affinity for both the CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors1. However, the efficacy of these two substances as cannabinoid receptor ag ...
... Canadian Status: JWH-175 and JWH-072 are not listed in the Schedules to the CDSA. JWH175 has been reported to bind to the CB1 cannabinoid receptor whereas JWH-072 has an affinity for both the CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors1. However, the efficacy of these two substances as cannabinoid receptor ag ...
Lecture 3 NS_2015
... Step 5: The transmitter is released into the extracellular space in quantized amounts and diffuses passively across the synaptic cleft (20-30 nm thick). Step 6: Some of the transmitter molecules bind to receptors in the postsynaptic membrane, and the activated receptors trigger some postsynaptic eve ...
... Step 5: The transmitter is released into the extracellular space in quantized amounts and diffuses passively across the synaptic cleft (20-30 nm thick). Step 6: Some of the transmitter molecules bind to receptors in the postsynaptic membrane, and the activated receptors trigger some postsynaptic eve ...
presentation
... SIMULATION RESULTS FOR NETWORK 2 NEURONS 7 AND 8 First, neurons 7 and 8 are unsynchronized, then we enable the astrocytes To inject slow inward currents EPSPs ...
... SIMULATION RESULTS FOR NETWORK 2 NEURONS 7 AND 8 First, neurons 7 and 8 are unsynchronized, then we enable the astrocytes To inject slow inward currents EPSPs ...
THE UNIVERSITY OF AUCKLAND
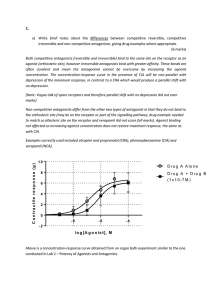
... a) Write brief notes about the differences between competitive reversible, competitive irreversible and non-competitive antagonism, giving drug examples where appropriate. (6 marks) Both competitive antagonists (reversible and irreversible) bind to the same site on the receptor as an agonist (orthos ...
... a) Write brief notes about the differences between competitive reversible, competitive irreversible and non-competitive antagonism, giving drug examples where appropriate. (6 marks) Both competitive antagonists (reversible and irreversible) bind to the same site on the receptor as an agonist (orthos ...
lec#37 by Dalin Mohammad corrected by Bayan
... be no action potential. So the receptor potential is usually like the cell body; it will give graded potential. And each receptor will have an ions’ type depending on the signal transfer. For the mechanical receptor it will be mechanical gated. For the chemical receptors they will be chemical gated. ...
... be no action potential. So the receptor potential is usually like the cell body; it will give graded potential. And each receptor will have an ions’ type depending on the signal transfer. For the mechanical receptor it will be mechanical gated. For the chemical receptors they will be chemical gated. ...
Uncaging Compunds: - Florida State University
... and dendrites overlap in the neuropil a synapse sometimes forms, and synaptic transmission occurs when APs reaches the synapse. – Action potentials invade the presynaptic terminal causing glutamate to be released and then to bind onto receptors on the postsynaptic spine. – 1:1 correspondence between ...
... and dendrites overlap in the neuropil a synapse sometimes forms, and synaptic transmission occurs when APs reaches the synapse. – Action potentials invade the presynaptic terminal causing glutamate to be released and then to bind onto receptors on the postsynaptic spine. – 1:1 correspondence between ...
20. Cell-to-Cell Signaling: Hormones and Receptors No cell lives in
... histamine (see Figure 21-28), that are derived from amino acids and function as hormones and neurotransmitters. Cell-Surface Receptors Belong to Four Major Classes G protein-coupled receptors (GPCR, see Figure 20-3a): Ligand binding activates a G protein, which in turn activates or inhibits an enzym ...
... histamine (see Figure 21-28), that are derived from amino acids and function as hormones and neurotransmitters. Cell-Surface Receptors Belong to Four Major Classes G protein-coupled receptors (GPCR, see Figure 20-3a): Ligand binding activates a G protein, which in turn activates or inhibits an enzym ...
N receptors
... N receptors : Ligand-gated Ion Channels • At the NMJ, N receptors pentameric with four types of subunits, two a subunits bind ACh for ligand gating • All other nAChRs, including those at the peripheral ganglia, ...
... N receptors : Ligand-gated Ion Channels • At the NMJ, N receptors pentameric with four types of subunits, two a subunits bind ACh for ligand gating • All other nAChRs, including those at the peripheral ganglia, ...
ADRENERGIC SYSTEM - LEC.2 2008
... circulation that will be prominent when B effect are abolished . labetalol ( alpha and beta block ) would be un alternative . 2- NOR- ADRENALINE : 1- it is one of the most commonly used adrenergic agonist drug in therapy .2- it is mainly alpha adrenoceptor agonist , but also affect Beta-1 . Pharmaco ...
... circulation that will be prominent when B effect are abolished . labetalol ( alpha and beta block ) would be un alternative . 2- NOR- ADRENALINE : 1- it is one of the most commonly used adrenergic agonist drug in therapy .2- it is mainly alpha adrenoceptor agonist , but also affect Beta-1 . Pharmaco ...
finding new tricks for old drugs: an efficient route
... class of compounds increased protein expression, a smaller subgroup was then screened in astrocytes and non-neuronal tissues expressing the GLT1 promoter. These studies allowed determination of the specificity and time-dependent effects of β-lactams on GLT1. To further elucidate the clinical potenti ...
... class of compounds increased protein expression, a smaller subgroup was then screened in astrocytes and non-neuronal tissues expressing the GLT1 promoter. These studies allowed determination of the specificity and time-dependent effects of β-lactams on GLT1. To further elucidate the clinical potenti ...
DOC - ADAM Interactive Anatomy
... Page 4. Neurotransmitters Can Act Directly on Chemically-gated Channels • Many receptors are physically part of an ion channel. • Binding neurotransmitter to a receptor on the postsynaptic cell causes a change in the shape of the receptor. • This can open, or in some cases close, the ion channel. • ...
... Page 4. Neurotransmitters Can Act Directly on Chemically-gated Channels • Many receptors are physically part of an ion channel. • Binding neurotransmitter to a receptor on the postsynaptic cell causes a change in the shape of the receptor. • This can open, or in some cases close, the ion channel. • ...
Opioids – anal-gesics (lol) ©2010 Mark Tuttle Mechanism of action
... Opioids – anal-gesics (lol) Mechanism of action/Uses 1. ↓voltage-gated Ca2+ channels ↓ NT release 2. ↑K+ channel conductance Hyperpolarizes: IPSP ...
... Opioids – anal-gesics (lol) Mechanism of action/Uses 1. ↓voltage-gated Ca2+ channels ↓ NT release 2. ↑K+ channel conductance Hyperpolarizes: IPSP ...
No Slide Title
... 2-adrenoceptor agonists (clonidine) NMDA receptor antagonists Selective serotonin reutake inhibitors Adenosine receptor agonists Valproic acid ...
... 2-adrenoceptor agonists (clonidine) NMDA receptor antagonists Selective serotonin reutake inhibitors Adenosine receptor agonists Valproic acid ...
NMDA receptor

The N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (also known as the NMDA receptor or NMDAR), is a glutamate receptor and ion channel protein found in nerve cells. It is activated when glutamate and glycine (or D-serine) bind to it, and when activated it allows positively charged ions to flow through the cell membrane. The NMDA receptor is very important for controlling synaptic plasticity and memory function.The NMDAR is a specific type of ionotropic glutamate receptor. The NMDA receptor is named this because the agonist molecule N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) binds selectively to it, and not to other glutamate receptors. Activation of NMDA receptors results in the opening of an ion channel that is nonselective to cations with a reversal potential near 0 mV. A property of the NMDA receptor is its voltage-dependent activation, a result of ion channel block by extracellular Mg2+ & Zn2+ ions. This allows the flow of Na+ and small amounts of Ca2+ ions into the cell and K+ out of the cell to be voltage-dependent.Calcium flux through NMDARs is thought to be critical in synaptic plasticity, a cellular mechanism for learning and memory. The NMDA receptor is distinct in two ways: first, it is both ligand-gated and voltage-dependent; second, it requires co-activation by two ligands: glutamate and either D-serine or glycine.The activity of the NMDA receptor is affected by many psychoactive drugs such as phencyclidine (PCP), alcohol (ethanol) and dextromethorphan (DXM). The anaesthetic effects of the drugs ketamine and nitrous oxide are partially because of their effects on NMDA receptor activity.