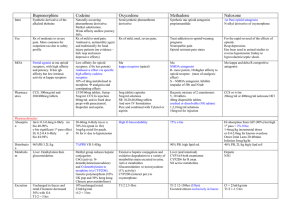
![Effect of arachidonic acid on specific binding of [3H]naloxone to](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/022505598_1-085ad7f0231ed6be49b2c9c96115ca73-300x300.png)
Effect of arachidonic acid on specific binding of [3H]naloxone to
... was significantly reduced by AA and the antagonist configuration of the opioid receptors were observed to be more susceptible to AA inhibition. The inhibitory effect of AA that was observed in our studies can not be explained simply by a negative feedback mechanism between the second messenger and t ...
... was significantly reduced by AA and the antagonist configuration of the opioid receptors were observed to be more susceptible to AA inhibition. The inhibitory effect of AA that was observed in our studies can not be explained simply by a negative feedback mechanism between the second messenger and t ...
11_Lecture_Presentation
... Concept 11.1: External signals are converted to responses within the cell • The yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, has two mating types, a and • Cells of different mating types locate each other via secreted factors specific to each type • A signal transduction pathway is a series of steps by which ...
... Concept 11.1: External signals are converted to responses within the cell • The yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, has two mating types, a and • Cells of different mating types locate each other via secreted factors specific to each type • A signal transduction pathway is a series of steps by which ...
Pharmacology 2004
... c. Nifedipine and verapamil have similar ability to relax vascular smooth muscle at therapeutic dosage d. Dihydropyridine type calcium channel blockers are less efficient than phenylalkylamine type blockers in their effect upon the SA node e. Benzothiazepine type calcium channel blockers decrease au ...
... c. Nifedipine and verapamil have similar ability to relax vascular smooth muscle at therapeutic dosage d. Dihydropyridine type calcium channel blockers are less efficient than phenylalkylamine type blockers in their effect upon the SA node e. Benzothiazepine type calcium channel blockers decrease au ...
Theodore-SSADH - SSADH Association
... high-affinity targets for GHB. The metabotropic GABAB receptors are activated by millimolar GHB. Elusive GHB high-affinity sites are activated by nM to mM GHB, consistent with normal endogenous concentrations. ...
... high-affinity targets for GHB. The metabotropic GABAB receptors are activated by millimolar GHB. Elusive GHB high-affinity sites are activated by nM to mM GHB, consistent with normal endogenous concentrations. ...
NV and antidiarrheal drugs
... 1) Phenothiazines (e.g.thiethylperazine; promethazine): vomiting caused by uremia, radiation, viral gastroenteritis; severe morning sickness of pregnancy. These drugs are only used in special cases due to their side effects profile. 2) Metoclopramide (PlasilR): It is a prokinetic agent and commonly ...
... 1) Phenothiazines (e.g.thiethylperazine; promethazine): vomiting caused by uremia, radiation, viral gastroenteritis; severe morning sickness of pregnancy. These drugs are only used in special cases due to their side effects profile. 2) Metoclopramide (PlasilR): It is a prokinetic agent and commonly ...
How do neurons communicate?
... ◦ the portion of the axon that is conveying information to the next neuron synapse or synaptic cleft ◦ the space between neurons where communication occurs postsynaptic membrane ◦ the portion of the neuron (usually dendrite) that receives information ...
... ◦ the portion of the axon that is conveying information to the next neuron synapse or synaptic cleft ◦ the space between neurons where communication occurs postsynaptic membrane ◦ the portion of the neuron (usually dendrite) that receives information ...
A4a - Viktor`s Notes for the Neurosurgery Resident
... relieves Mg2+ block in NMDA receptor channel, and Ca2+ enters neuron with Na+. – increase in cytoplasmic Ca2+ activates calmodulin (CaM), which in turn activates Ca2+/calmodulin kinase II (CaM kII). – CaM kII phosphorylates AMPA receptor (P), increasing its conductance + moves more AMPA receptors in ...
... relieves Mg2+ block in NMDA receptor channel, and Ca2+ enters neuron with Na+. – increase in cytoplasmic Ca2+ activates calmodulin (CaM), which in turn activates Ca2+/calmodulin kinase II (CaM kII). – CaM kII phosphorylates AMPA receptor (P), increasing its conductance + moves more AMPA receptors in ...
buprenorphine oxycodone table
... Antitussive, antimotility agent and traditionally for head injury patients (no evidence – lack resp and neuro depressive effects) ...
... Antitussive, antimotility agent and traditionally for head injury patients (no evidence – lack resp and neuro depressive effects) ...
Parkinson`s Disease
... preventing the loss of neurons. Memantine acts by physically blocking the NMDA receptor associated ion channel, but at therapeutic doses, only a fraction of these channels are actually blocked. This partial blockade may allow memantine to limit Ca2+ influx into the neuron such that toxic intracellul ...
... preventing the loss of neurons. Memantine acts by physically blocking the NMDA receptor associated ion channel, but at therapeutic doses, only a fraction of these channels are actually blocked. This partial blockade may allow memantine to limit Ca2+ influx into the neuron such that toxic intracellul ...
P2 Receptor Antagonist Trinitrophenyl-Adenosine
... involves a pronounced reduction in intracellular oxygen and glucose, which leads to rapid cell death associated with Ca2⫹, Na⫹, K⫹, and Cl⫺ deregulation. In particular, the increase of Ca2⫹ influx can directly control the activation of proteolytic enzymes and apoptotic genes and the production of re ...
... involves a pronounced reduction in intracellular oxygen and glucose, which leads to rapid cell death associated with Ca2⫹, Na⫹, K⫹, and Cl⫺ deregulation. In particular, the increase of Ca2⫹ influx can directly control the activation of proteolytic enzymes and apoptotic genes and the production of re ...
Pharm - 11-30
... a. Muscarinic receptors are found in the large bronchioles, beta 2 receptors are found in the small bronchioles b.Muscarinic receptors are found in the large bronchioles, beta 2 receptors are found in the large bronchioles c. Muscarinic receptors are found in the small bronchioles, beta 2 receptors ...
... a. Muscarinic receptors are found in the large bronchioles, beta 2 receptors are found in the small bronchioles b.Muscarinic receptors are found in the large bronchioles, beta 2 receptors are found in the large bronchioles c. Muscarinic receptors are found in the small bronchioles, beta 2 receptors ...
Steroid hormone receptor homologs in development
... proach, the receptor was shown to bind retinoic acid with high affinity (Brand et al. 1988; Benbrook et al. 1988). The structure of the two receptors are very similar (90% in the ligand-binding domain), but the B form of the receptor transactivates at a slightly lower concentration of RA (Brand et a ...
... proach, the receptor was shown to bind retinoic acid with high affinity (Brand et al. 1988; Benbrook et al. 1988). The structure of the two receptors are very similar (90% in the ligand-binding domain), but the B form of the receptor transactivates at a slightly lower concentration of RA (Brand et a ...
Gene Section FGFR1 (Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 1) in Oncology and Haematology
... protein core; tyrosine kinase receptor; contains four major domains: an extracellular domain with 2 or 3 Iglike loops, a transmembrane domain and an intracellular domain, a juxtamembrane domain, and an intracellular domain composed of the tyrosine kinase domain (two kinase domains interrupted by a s ...
... protein core; tyrosine kinase receptor; contains four major domains: an extracellular domain with 2 or 3 Iglike loops, a transmembrane domain and an intracellular domain, a juxtamembrane domain, and an intracellular domain composed of the tyrosine kinase domain (two kinase domains interrupted by a s ...
Appetitive Instrumental Learning Requires Coincident Activation of
... control rats from experiment 3 (f). Infusion sites for all animals receiving the combined low doses of AP-5 (0.5 nmol) and SCH-23390 (0.15 nmol) in experiment 3 (⽧) are also plotted. The shaded regions represent the areas containing all infusion sites from all experiments. From Paxinos and Watson (1 ...
... control rats from experiment 3 (f). Infusion sites for all animals receiving the combined low doses of AP-5 (0.5 nmol) and SCH-23390 (0.15 nmol) in experiment 3 (⽧) are also plotted. The shaded regions represent the areas containing all infusion sites from all experiments. From Paxinos and Watson (1 ...
File
... Where are they located? The receptor cells are ________________ neurons with hairlike ________________ covering the dendrites. These project into the ____________________cavity. Nerve pathways: When olfactory receptors are stimulated, their fibers synapse with neurons in the ______________ _______ l ...
... Where are they located? The receptor cells are ________________ neurons with hairlike ________________ covering the dendrites. These project into the ____________________cavity. Nerve pathways: When olfactory receptors are stimulated, their fibers synapse with neurons in the ______________ _______ l ...
The G protein pathway in neuroscience
... and we are still describing a set of mechanisms that manipulate impulse frequencies in individual neurons. ...
... and we are still describing a set of mechanisms that manipulate impulse frequencies in individual neurons. ...
Analgesics Power Point - IHMC Public Cmaps (3)
... • Methadone has advantages of being more orally effective and of lasting longer than morphine or heroin ...
... • Methadone has advantages of being more orally effective and of lasting longer than morphine or heroin ...
FUN2: 11:00-12:00 Scribe: Taylor Nelson Wednesday, December
... i. The use of the term indirect is the same as the use for the term Cholinergic stimulus ii. These compounds produce their effects by releasing NE from the nerve terminals iii. They do not inhibit an enzyme iv. The best example, with a major indirect mechanism of action is amphetamine and its variou ...
... i. The use of the term indirect is the same as the use for the term Cholinergic stimulus ii. These compounds produce their effects by releasing NE from the nerve terminals iii. They do not inhibit an enzyme iv. The best example, with a major indirect mechanism of action is amphetamine and its variou ...
Neurochemistry of Dementias
... Many drug development programmes target GABA and glutamate Benzodiazepines positively modulate GABAA and increase chloride ...
... Many drug development programmes target GABA and glutamate Benzodiazepines positively modulate GABAA and increase chloride ...
OPIOID ANALGESICS
... • Methadone has advantages of being more orally effective and of lasting longer than morphine or heroin ...
... • Methadone has advantages of being more orally effective and of lasting longer than morphine or heroin ...
Final Exam - Psychology
... A. SSRIs are more effective at relieving depression B. SSRIs have less serious side effects C. Drug companies more aggressively advertise for the use of SSRIs D. SSRIs produce beneficial effects more rapidly E. all of the above are true ______(1 point) Which of the following is not a side effect tha ...
... A. SSRIs are more effective at relieving depression B. SSRIs have less serious side effects C. Drug companies more aggressively advertise for the use of SSRIs D. SSRIs produce beneficial effects more rapidly E. all of the above are true ______(1 point) Which of the following is not a side effect tha ...
Cross-Talk among RORal and the Rev-erb Family
... hormone receptors (1 l-l 3). These receptors comprise a superfamily of transcription factors that initiate nuclear responses to steroids, retinoids, vitamin DI, and thyroid hormone (14). An increasing number of proteins that possess sequence similarity and functional homology with members of the nuc ...
... hormone receptors (1 l-l 3). These receptors comprise a superfamily of transcription factors that initiate nuclear responses to steroids, retinoids, vitamin DI, and thyroid hormone (14). An increasing number of proteins that possess sequence similarity and functional homology with members of the nuc ...
NMDA receptor

The N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (also known as the NMDA receptor or NMDAR), is a glutamate receptor and ion channel protein found in nerve cells. It is activated when glutamate and glycine (or D-serine) bind to it, and when activated it allows positively charged ions to flow through the cell membrane. The NMDA receptor is very important for controlling synaptic plasticity and memory function.The NMDAR is a specific type of ionotropic glutamate receptor. The NMDA receptor is named this because the agonist molecule N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) binds selectively to it, and not to other glutamate receptors. Activation of NMDA receptors results in the opening of an ion channel that is nonselective to cations with a reversal potential near 0 mV. A property of the NMDA receptor is its voltage-dependent activation, a result of ion channel block by extracellular Mg2+ & Zn2+ ions. This allows the flow of Na+ and small amounts of Ca2+ ions into the cell and K+ out of the cell to be voltage-dependent.Calcium flux through NMDARs is thought to be critical in synaptic plasticity, a cellular mechanism for learning and memory. The NMDA receptor is distinct in two ways: first, it is both ligand-gated and voltage-dependent; second, it requires co-activation by two ligands: glutamate and either D-serine or glycine.The activity of the NMDA receptor is affected by many psychoactive drugs such as phencyclidine (PCP), alcohol (ethanol) and dextromethorphan (DXM). The anaesthetic effects of the drugs ketamine and nitrous oxide are partially because of their effects on NMDA receptor activity.