Chapter 11
... Catastrophism • Landscape developed by catastrophes • James Ussher, mid-1600s, concluded Earth was only a few thousand years old ...
... Catastrophism • Landscape developed by catastrophes • James Ussher, mid-1600s, concluded Earth was only a few thousand years old ...
Changes Within the Earth
... • Scientist Alfred Wegener created the theory of “Pangaea” started 180 million years ago. 1 land mass breaks off into the 7 current continents. • Scientists developed the theory of plate tectonics. These are plates of the earth’s crust that are constantly moving at a slow pace and creating pressure ...
... • Scientist Alfred Wegener created the theory of “Pangaea” started 180 million years ago. 1 land mass breaks off into the 7 current continents. • Scientists developed the theory of plate tectonics. These are plates of the earth’s crust that are constantly moving at a slow pace and creating pressure ...
study guide for module #6
... 13. What makes the rapid decay theory more scientifically valid than the dynamo theory? 14. Why is a catastrophe like Noah’s Flood an essential part of earth’s history if the rapid decay theory is true? 15. What two reasons make otherwise good scientists ignore the more scientifically valid rapid de ...
... 13. What makes the rapid decay theory more scientifically valid than the dynamo theory? 14. Why is a catastrophe like Noah’s Flood an essential part of earth’s history if the rapid decay theory is true? 15. What two reasons make otherwise good scientists ignore the more scientifically valid rapid de ...
Name____________________________
... 10. What is the longitude of the International Date Line (IDL)? __ __ __ 11. What are the two types of crust? _____________________ and _____________________ 12. One plate sliding down under another plate is called _______________________________ 13. What is the hottest region in the Earth? __ __ _ ...
... 10. What is the longitude of the International Date Line (IDL)? __ __ __ 11. What are the two types of crust? _____________________ and _____________________ 12. One plate sliding down under another plate is called _______________________________ 13. What is the hottest region in the Earth? __ __ _ ...
Study Notes: Chapter 27- Planets of the Solar System
... 2. About ____________ of all matter contained in the solar nebula now exists in the sun. 3. Small bodies that orbit planets are called ________________. 4. When early Earth’s atmosphere formed, _________________ and hydrogen gases were lost because Earth’s ______________ was too weak. 5. Copernicus ...
... 2. About ____________ of all matter contained in the solar nebula now exists in the sun. 3. Small bodies that orbit planets are called ________________. 4. When early Earth’s atmosphere formed, _________________ and hydrogen gases were lost because Earth’s ______________ was too weak. 5. Copernicus ...
(or the Earth) is the third planet from the Sun, and
... Solar System's four terrestrial planets. It is sometimes referred to as the wor ld, the Blue Planet,[21] or by its Latin name, Terra.[note 6] Earth formed approximately 4.54 billion years ago by accretion from the solar ne bula, and life appeared on its surface within one billion years.[22] The plan ...
... Solar System's four terrestrial planets. It is sometimes referred to as the wor ld, the Blue Planet,[21] or by its Latin name, Terra.[note 6] Earth formed approximately 4.54 billion years ago by accretion from the solar ne bula, and life appeared on its surface within one billion years.[22] The plan ...
What are the layers of the earth? Crust: Mantle: Outer Core: Inner
... Geologist -A scientist who studies Earth. Seismologist -A scientist who studies earthquakes Seismograph -A device that records the motion of Earth’s crust. Fault -A crack, break, or a defect in the earth’s crust Weathering -A slow process that uses temperature, gases, and water to break down rocks a ...
... Geologist -A scientist who studies Earth. Seismologist -A scientist who studies earthquakes Seismograph -A device that records the motion of Earth’s crust. Fault -A crack, break, or a defect in the earth’s crust Weathering -A slow process that uses temperature, gases, and water to break down rocks a ...
Section 7.3 Student note
... -crystal size depends on how slow it cooled -Intrusive igneous rocks formed well below the surface, ‘intruded into the rock’ -Extrusive rocks formed on the Earth’s surface (exited the Earth) -reach the surface through cracks in the crust/plates, or through erosion and uplift of layers of rock -figur ...
... -crystal size depends on how slow it cooled -Intrusive igneous rocks formed well below the surface, ‘intruded into the rock’ -Extrusive rocks formed on the Earth’s surface (exited the Earth) -reach the surface through cracks in the crust/plates, or through erosion and uplift of layers of rock -figur ...
Constructive and Destructive Forces Unit
... the process of replacing sand on a beach that was lost due to erosion and deposition ...
... the process of replacing sand on a beach that was lost due to erosion and deposition ...
Chapter 1 Study Guide
... Plates float on liquid rock in the _____________. What is the center of the solar system? Magma comes from what landform? About ____ percent of the earth’s surface is water. Australia- Is it in the N hemisphere or the S hemisphere? What are the layers of the earth from inside out? Define environment ...
... Plates float on liquid rock in the _____________. What is the center of the solar system? Magma comes from what landform? About ____ percent of the earth’s surface is water. Australia- Is it in the N hemisphere or the S hemisphere? What are the layers of the earth from inside out? Define environment ...
Inside The Earth Unit Test Study Guide
... 5) For each of Earth’s layers list the main elements that each is composed of. ...
... 5) For each of Earth’s layers list the main elements that each is composed of. ...
Earth Science Vocab
... Convection current- a circulation pattern in which material is heated and rises in one area, then cools and sinks in another area, flowing in a continuous loop ...
... Convection current- a circulation pattern in which material is heated and rises in one area, then cools and sinks in another area, flowing in a continuous loop ...
Drawing the Earth
... Directions: You will be creating a representation of the Earth, its layers (structural and compositional) and spheres. You have three (3) options: 1. Work with a group (3-4) and make a large poster 2. Work individually or with a partner and create a smaller drawing (8.5 x 11) 3. Create a layered “bo ...
... Directions: You will be creating a representation of the Earth, its layers (structural and compositional) and spheres. You have three (3) options: 1. Work with a group (3-4) and make a large poster 2. Work individually or with a partner and create a smaller drawing (8.5 x 11) 3. Create a layered “bo ...
Spheres of Earth - Red Hook Central Schools
... Atmosphere: Shell of gases that surrounds a planet, for example, Earth a. Earth’s atmosphere is unique because it contains oxygen b. Atmosphere = Air Lithosphere(also known as Geosphere): Solid portion of Earth below the atmosphere and the hydrosphere a. Includes: rocks, mountains and beaches ...
... Atmosphere: Shell of gases that surrounds a planet, for example, Earth a. Earth’s atmosphere is unique because it contains oxygen b. Atmosphere = Air Lithosphere(also known as Geosphere): Solid portion of Earth below the atmosphere and the hydrosphere a. Includes: rocks, mountains and beaches ...
The Rock Cycle Rock – a naturally occurring solid mixture of one or
... The Rock Cycle Rock – a naturally occurring solid mixture of one or more minerals or organic material Rock cycle – the continual process by which new rock forms from old rock material Erosion – the process by which wind, water, ice, or gravity moves soil and sediment from one location to another Dep ...
... The Rock Cycle Rock – a naturally occurring solid mixture of one or more minerals or organic material Rock cycle – the continual process by which new rock forms from old rock material Erosion – the process by which wind, water, ice, or gravity moves soil and sediment from one location to another Dep ...
Layers of the Earth Exit Slip Key
... 1. Imagine you could drill a hole all the way to the center of the Earth. Assuming that you drill the same speed the entire way, which layer would take the longest to drill through? a. Crust b. Mantle c. Outer core d. Inner core ...
... 1. Imagine you could drill a hole all the way to the center of the Earth. Assuming that you drill the same speed the entire way, which layer would take the longest to drill through? a. Crust b. Mantle c. Outer core d. Inner core ...
Ch 14 Notes - OCPS TeacherPress
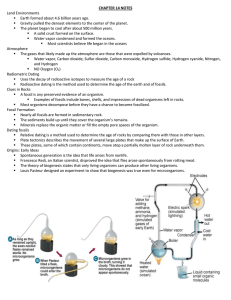
... Examples of fossils include bones, shells, and impressions of dead organisms left in rocks. Most organisms decompose before they have a chance to become fossilized. Fossil Formation Nearly all fossils are formed in sedimentary rock. The sediments build up until they cover the organism’s rema ...
... Examples of fossils include bones, shells, and impressions of dead organisms left in rocks. Most organisms decompose before they have a chance to become fossilized. Fossil Formation Nearly all fossils are formed in sedimentary rock. The sediments build up until they cover the organism’s rema ...
Changing Earth Study Guide My assessment is on What is the age
... What is the inner core of the Earth? ...
... What is the inner core of the Earth? ...
Age of the Earth

The age of the Earth is 4.54 ± 0.05 billion years (4.54 × 109 years ± 1%). This age is based on evidence from radiometric age dating of meteorite material and is consistent with the radiometric ages of the oldest-known terrestrial and lunar samples.Following the development of radiometric age dating in the early 20th century, measurements of lead in uranium-rich minerals showed that some were in excess of a billion years old.The oldest such minerals analyzed to date—small crystals of zircon from the Jack Hills of Western Australia—are at least 4.404 billion years old. Comparing the mass and luminosity of the Sun to those of other stars, it appears that the Solar System cannot be much older than those rocks. Calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions – the oldest known solid constituents within meteorites that are formed within the Solar System – are 4.567 billion years old, giving an age for the solar system and an upper limit for the age of Earth.It is hypothesised that the accretion of Earth began soon after the formation of the calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions and the meteorites. Because the exact amount of time this accretion process took is not yet known, and the predictions from different accretion models range from a few millions up to about 100 million years, the exact age of Earth is difficult to determine. It is also difficult to determine the exact age of the oldest rocks on Earth, exposed at the surface, as they are aggregates of minerals of possibly different ages.