
Science Review: Land Formations (Rocks, Minerals, Soil, etc
... Deposition- putting new sediments in place Forms: beaches Dunes Deltas Example: A friend lives on Marblehead Neck and has a private beach at the water line. After a storm, the sand is not there! It is all rocks! It has been washed away- this is erosion. That sand was swept over and dumped by the wat ...
... Deposition- putting new sediments in place Forms: beaches Dunes Deltas Example: A friend lives on Marblehead Neck and has a private beach at the water line. After a storm, the sand is not there! It is all rocks! It has been washed away- this is erosion. That sand was swept over and dumped by the wat ...
Powerpoint 1
... A. A rainstorm washes away soil from a garden. B. A sudden flood transports pebbles into a river. C. A landslide moves rocks down the side of a mountain. D. A constant crashing of waves on a rock slowly breaks it ...
... A. A rainstorm washes away soil from a garden. B. A sudden flood transports pebbles into a river. C. A landslide moves rocks down the side of a mountain. D. A constant crashing of waves on a rock slowly breaks it ...
10457761045776LP 10 ES 09
... 1. Explain how heat is transferred 2. Identify what causes convection currents inside the Earth. 3. Describe convection currents in the mantle. Pg 132 Section 2 “Convection in the Mantle” I. Types of Heat Transfer a. Radiation b. Conduction c. Convection Assignment—Vocab for chapter 5 pg 156 ...
... 1. Explain how heat is transferred 2. Identify what causes convection currents inside the Earth. 3. Describe convection currents in the mantle. Pg 132 Section 2 “Convection in the Mantle” I. Types of Heat Transfer a. Radiation b. Conduction c. Convection Assignment—Vocab for chapter 5 pg 156 ...
Review Unit 1 - Effingham County Schools
... #57. Since there are no rock layers that have fossils of both dinosaur and horse remains scientists know that dinosaurs and horses did not exist in the same geological eras. ...
... #57. Since there are no rock layers that have fossils of both dinosaur and horse remains scientists know that dinosaurs and horses did not exist in the same geological eras. ...
File
... 2) ____________ mountains: When plates collide, rocks can fold if they are hot enough to act like bendable plastic. 3) ______________________ mountains: Sometimes the rocks in Earth’s crust are too brittle to fold, and they instead break, forming a fault. Fault blocks can tilt or slide down. 4) Moun ...
... 2) ____________ mountains: When plates collide, rocks can fold if they are hot enough to act like bendable plastic. 3) ______________________ mountains: Sometimes the rocks in Earth’s crust are too brittle to fold, and they instead break, forming a fault. Fault blocks can tilt or slide down. 4) Moun ...
Outline General Geology 2011
... THE HASHEMITE UNIVERSITY Faculty of Natural Resources and Environment Department of Earth Sciences and Environment ...
... THE HASHEMITE UNIVERSITY Faculty of Natural Resources and Environment Department of Earth Sciences and Environment ...
Types of Fossils - Parkway C-2
... The lower the sediment layer is, the older the fossils of the layer will be.- Law of Superposition As time elapses, more and more sediment layers form to create the layers of sedimentary rocks. ...
... The lower the sediment layer is, the older the fossils of the layer will be.- Law of Superposition As time elapses, more and more sediment layers form to create the layers of sedimentary rocks. ...
Earth`s Interior Information- Core-Innermost layer Inner Core
... Asthenosphere-Not liquid, but there is melted rock, carries the lithosphere, moves slowly Lithosphere-broken into giant plates that fit around the globe like puzzle pieces. The pieces move a little bit each year. They slide on a somewhat liquid asthenosphere Crust-Layer of rock that forms Earth’s ou ...
... Asthenosphere-Not liquid, but there is melted rock, carries the lithosphere, moves slowly Lithosphere-broken into giant plates that fit around the globe like puzzle pieces. The pieces move a little bit each year. They slide on a somewhat liquid asthenosphere Crust-Layer of rock that forms Earth’s ou ...
Geology 208 History of Earth System Midterm Topics 1 Topics
... Principles of relative age dating and block diagram The nature of unconformities – what is implied Fossil succession and extinction events Biostratigraphy o Defining geologic time systems o Problems o Biomarkers don’t parallel formation boundaries Magnetostratigraphy o DRM o TRM – Correlat ...
... Principles of relative age dating and block diagram The nature of unconformities – what is implied Fossil succession and extinction events Biostratigraphy o Defining geologic time systems o Problems o Biomarkers don’t parallel formation boundaries Magnetostratigraphy o DRM o TRM – Correlat ...
Inside the Earth - ReedEarthScience
... • We are not sure? Why? – Extreme conditions inside Earth • Temperature rises – Why? Heat left over from formation of planet and radioactive substances inside Earth’s interior releasing energy ...
... • We are not sure? Why? – Extreme conditions inside Earth • Temperature rises – Why? Heat left over from formation of planet and radioactive substances inside Earth’s interior releasing energy ...
Earth Science
... Crust-outer layer of rock Lithosphere-shell formed from Earth’s solid upper mantle and crust Mantle-thick layer of Earth’s structure just below the crust Plate Tectonics-giant plates of rock ...
... Crust-outer layer of rock Lithosphere-shell formed from Earth’s solid upper mantle and crust Mantle-thick layer of Earth’s structure just below the crust Plate Tectonics-giant plates of rock ...
Plate tectonics Hydrosphere Magma Fault Outer Core Seismograph
... Scientific theory that Earth’s crust is made of moving plates ...
... Scientific theory that Earth’s crust is made of moving plates ...
Layer Depth (km) Rigidity
... • Acid rain: from acid gases in atmosphere • Reaction with surface rocks to form dissolved products and sediments • Little change in oceans through time: -- Salinity and area remained ~ constant -- depth and volume increased a little ...
... • Acid rain: from acid gases in atmosphere • Reaction with surface rocks to form dissolved products and sediments • Little change in oceans through time: -- Salinity and area remained ~ constant -- depth and volume increased a little ...
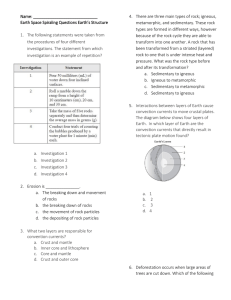
Name: Earth Space Spiraling Questions Earth`s Structure 1. The
... correctly describes a scientific law? a. A scientific law is not accepted to be true and universal b. A scientific law is complex and needs to be tested multiple times. c. A scientific law is simple and describes an action or set of actions. ...
... correctly describes a scientific law? a. A scientific law is not accepted to be true and universal b. A scientific law is complex and needs to be tested multiple times. c. A scientific law is simple and describes an action or set of actions. ...
File
... 4. The hot softer part of M___________ that the L_______________ sits on top of is called the A_______________. 5. Materials that are L__________ D_______________ rise to Earth’s surface. 6. Materials that are M__________ D_______________ sink toward Earth’s center. 7. Earth’s core has two parts, th ...
... 4. The hot softer part of M___________ that the L_______________ sits on top of is called the A_______________. 5. Materials that are L__________ D_______________ rise to Earth’s surface. 6. Materials that are M__________ D_______________ sink toward Earth’s center. 7. Earth’s core has two parts, th ...
What creates Earth`s Magnetic Field?
... in your hand or touch, hear with your ears or see with your own eyes. ...
... in your hand or touch, hear with your ears or see with your own eyes. ...
Half life - schoolphysics
... radiation is 10 Bq and the original reading of the Geiger counter is 170 Bq what is the reading after: (a) 20 hours (b) 25 hours (c) 30 hours 11. A sample of radon gas leaks into, a school laboratory! If the safety regulations require that the activity has fallen to 10-6 of the original value how lo ...
... radiation is 10 Bq and the original reading of the Geiger counter is 170 Bq what is the reading after: (a) 20 hours (b) 25 hours (c) 30 hours 11. A sample of radon gas leaks into, a school laboratory! If the safety regulations require that the activity has fallen to 10-6 of the original value how lo ...
Age of the Earth

The age of the Earth is 4.54 ± 0.05 billion years (4.54 × 109 years ± 1%). This age is based on evidence from radiometric age dating of meteorite material and is consistent with the radiometric ages of the oldest-known terrestrial and lunar samples.Following the development of radiometric age dating in the early 20th century, measurements of lead in uranium-rich minerals showed that some were in excess of a billion years old.The oldest such minerals analyzed to date—small crystals of zircon from the Jack Hills of Western Australia—are at least 4.404 billion years old. Comparing the mass and luminosity of the Sun to those of other stars, it appears that the Solar System cannot be much older than those rocks. Calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions – the oldest known solid constituents within meteorites that are formed within the Solar System – are 4.567 billion years old, giving an age for the solar system and an upper limit for the age of Earth.It is hypothesised that the accretion of Earth began soon after the formation of the calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions and the meteorites. Because the exact amount of time this accretion process took is not yet known, and the predictions from different accretion models range from a few millions up to about 100 million years, the exact age of Earth is difficult to determine. It is also difficult to determine the exact age of the oldest rocks on Earth, exposed at the surface, as they are aggregates of minerals of possibly different ages.





















![c1b revision sheet 1[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/016683336_1-baea0f7acdab057d50ded8ac95b62330-300x300.png)