February 2015
... calculator, which will be provided by the teacher in charge. The PARCC will be given in two parts. The PBA or performance based assessment is the one scheduled for March. There is also an EOY, end of the year assessment, scheduled for May. ...
... calculator, which will be provided by the teacher in charge. The PARCC will be given in two parts. The PBA or performance based assessment is the one scheduled for March. There is also an EOY, end of the year assessment, scheduled for May. ...
Document
... Earth, and how do we know all of this “stuff” without having been there? The center of the Earth is too hot and too high of a pressure. We know about the inside of the Earth because of Seismological Studies. 41. Why is it so hot in the middle of the Earth? Left over heat from the formation of the so ...
... Earth, and how do we know all of this “stuff” without having been there? The center of the Earth is too hot and too high of a pressure. We know about the inside of the Earth because of Seismological Studies. 41. Why is it so hot in the middle of the Earth? Left over heat from the formation of the so ...
SIXTH GRADE EARTH SCIENCE THEME
... e. Construct appropriate graphs from data. Develop qualitative statements about the relationships between variables. f. Communicate the steps and results of an experiment using written reports and verbal presentations. g. Recognize changes in natural phenomena over time. h. Practice safety procedure ...
... e. Construct appropriate graphs from data. Develop qualitative statements about the relationships between variables. f. Communicate the steps and results of an experiment using written reports and verbal presentations. g. Recognize changes in natural phenomena over time. h. Practice safety procedure ...
GEOSPHERE The geosphere is the Earth itself, the rocks, minerals
... GEOSPHERE The geosphere is the Earth itself, the rocks, minerals, and landforms of the surface as well as its interior. Below the crust, which varies from about 5 km beneath the ocean floor to up to 70 km below the land surface, temperatures are high enough for deformation and a paste-like flow. At ...
... GEOSPHERE The geosphere is the Earth itself, the rocks, minerals, and landforms of the surface as well as its interior. Below the crust, which varies from about 5 km beneath the ocean floor to up to 70 km below the land surface, temperatures are high enough for deformation and a paste-like flow. At ...
Plate tectonics assessment
... These partially melted rocks are called magma. Temperatures here are around 5,000°C. The crust is the _______________ layer of the Earth and is made up of solid rock. The crust is the outer layer of the Earth. The Earth's crust is broken up into pieces called ______________, which move or 'float' up ...
... These partially melted rocks are called magma. Temperatures here are around 5,000°C. The crust is the _______________ layer of the Earth and is made up of solid rock. The crust is the outer layer of the Earth. The Earth's crust is broken up into pieces called ______________, which move or 'float' up ...
Chapter 5 Section 1
... and the asthenosphere? 3. How do temperature and pressure change as you go deeper into the Earth? 4. How are oceanic and continental crusts alike and different? 5. Place these terms in correct order so they begin at Earth’s surface and move toward the center: inner core, asthenosphere, crust, lithos ...
... and the asthenosphere? 3. How do temperature and pressure change as you go deeper into the Earth? 4. How are oceanic and continental crusts alike and different? 5. Place these terms in correct order so they begin at Earth’s surface and move toward the center: inner core, asthenosphere, crust, lithos ...
The Archean: 4.6
... generate the present ocean waters (and this assumes no contribution from degassing, which has occurred). Considering that comet/meteor impacts have been 2000x times greater in the Archean, delivery of water to Earth is reasonable. ...
... generate the present ocean waters (and this assumes no contribution from degassing, which has occurred). Considering that comet/meteor impacts have been 2000x times greater in the Archean, delivery of water to Earth is reasonable. ...
Alfred Wegener - Colts Neck Township Schools
... •Paleoclimate –Evidence of Ice Sheets were found covering parts of S. America, Africa, India, and Australia –Coral reefs found in Northern Canada –Coal formation in North America ...
... •Paleoclimate –Evidence of Ice Sheets were found covering parts of S. America, Africa, India, and Australia –Coral reefs found in Northern Canada –Coal formation in North America ...
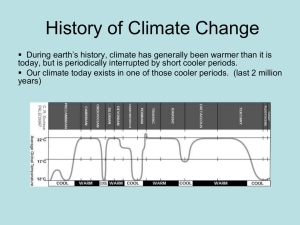
History of Climate Change
... History of Climate Change During earth’s history, climate has generally been warmer than it is today, but is periodically interrupted by short cooler periods. Our climate today exists in one of those cooler periods. (last 2 million years) ...
... History of Climate Change During earth’s history, climate has generally been warmer than it is today, but is periodically interrupted by short cooler periods. Our climate today exists in one of those cooler periods. (last 2 million years) ...
welcome to gg 101 physical geology
... But geologists face the special challenge of not being able to do experiments in the sense that chemists and physicists do. ...
... But geologists face the special challenge of not being able to do experiments in the sense that chemists and physicists do. ...
10-25 miles
... degrees F to 9000 degrees F 11. Made of Nickel and Iron 12. This liquid core produces a magnetic field that helps protect earth from coronal mass ejections (CME’s) produced by the sun. ...
... degrees F to 9000 degrees F 11. Made of Nickel and Iron 12. This liquid core produces a magnetic field that helps protect earth from coronal mass ejections (CME’s) produced by the sun. ...
Practice01 e - Kean University
... 3. Convection cells in the mantle are principally responsible for plate movements. Oceanic plates are pulled apart at the _____- ______ ridges, and are recycled into the mantle at ____________ zones. 4. Under the lithosphere is the ___________, a zone of heat softened rock located in the upper mantl ...
... 3. Convection cells in the mantle are principally responsible for plate movements. Oceanic plates are pulled apart at the _____- ______ ridges, and are recycled into the mantle at ____________ zones. 4. Under the lithosphere is the ___________, a zone of heat softened rock located in the upper mantl ...
Science Ch 5 webnotes
... Seismometer: instrument that detects and measures waves produced by earthquakes Primary (P) waves: fastest; pass through solid and liquid layers; move back and forth Secondary(S) waves: half as fast; only through solid layers; move up and down Surface (L) waves: slowest like ripples on a pond; on Ea ...
... Seismometer: instrument that detects and measures waves produced by earthquakes Primary (P) waves: fastest; pass through solid and liquid layers; move back and forth Secondary(S) waves: half as fast; only through solid layers; move up and down Surface (L) waves: slowest like ripples on a pond; on Ea ...
Layers of the Earth Lyrics and Diagram
... Throw your hands up for the layers of the earth Throw ‘em up for what's below the surface Throw your hands up, and let's discuss The inner core, outer core, mantle, and crust Verse I The layer we’ll discuss first Is the central inner core, in the center of the earth A solid ball buried below the dir ...
... Throw your hands up for the layers of the earth Throw ‘em up for what's below the surface Throw your hands up, and let's discuss The inner core, outer core, mantle, and crust Verse I The layer we’ll discuss first Is the central inner core, in the center of the earth A solid ball buried below the dir ...
Plate Tectonics
... Heat is transferred in the mantle through radiation, conduction, and convection. Radiation is the transfer of heat through empty space. Conduction is heat transfer by direct contact of particles of matter. Convection is heat transfer by the movement of heated liquid. ...
... Heat is transferred in the mantle through radiation, conduction, and convection. Radiation is the transfer of heat through empty space. Conduction is heat transfer by direct contact of particles of matter. Convection is heat transfer by the movement of heated liquid. ...
Outer Core
... How do we know for sure what’s under us??? How can we know what each part is made from if we haven’t been there? Scientists use vibrations called Seismic Waves created during earthquakes to determine thickness and composition. Waves move through solid and liquid material at different speeds. ...
... How do we know for sure what’s under us??? How can we know what each part is made from if we haven’t been there? Scientists use vibrations called Seismic Waves created during earthquakes to determine thickness and composition. Waves move through solid and liquid material at different speeds. ...
Context Clues3 - Arizonans for Children
... Directions: Read the paragraphs below. After each paragraph you will be asked to find the definitions, or meanings of the underlined, bold words in the sentence. Use the context clues you have learned about to find the definitions of the words. Underline the context clue in the sentence you find the ...
... Directions: Read the paragraphs below. After each paragraph you will be asked to find the definitions, or meanings of the underlined, bold words in the sentence. Use the context clues you have learned about to find the definitions of the words. Underline the context clue in the sentence you find the ...
Component 4: Chemistry Oils, Earth and Atmosphere – Word Bank
... relatively quickly, by biological means, into the raw materials of nature and disappear into the nvironment. Incineration - this is a process of burning rubbish. It can be useful for getting rid of waste material, but it can often produce toxic gases or greenhouse gases. Landfill sites - these are s ...
... relatively quickly, by biological means, into the raw materials of nature and disappear into the nvironment. Incineration - this is a process of burning rubbish. It can be useful for getting rid of waste material, but it can often produce toxic gases or greenhouse gases. Landfill sites - these are s ...
g. What do fossils show -evidence of the changing surface and
... S6E5. Students will investigate the scientific view of how the earth’s surface is formed. a. Earth’s crust, mantle, and core including temperature, density, and composition. 1. Holes drilled several kilometers into Earth’s crust provide direct evidence about Earth’s interior in the form of a. seismi ...
... S6E5. Students will investigate the scientific view of how the earth’s surface is formed. a. Earth’s crust, mantle, and core including temperature, density, and composition. 1. Holes drilled several kilometers into Earth’s crust provide direct evidence about Earth’s interior in the form of a. seismi ...
The History of Life
... – Older fossils will be in the bottom layers – More recent fossils will be in the upper layers ...
... – Older fossils will be in the bottom layers – More recent fossils will be in the upper layers ...
Age of the Earth

The age of the Earth is 4.54 ± 0.05 billion years (4.54 × 109 years ± 1%). This age is based on evidence from radiometric age dating of meteorite material and is consistent with the radiometric ages of the oldest-known terrestrial and lunar samples.Following the development of radiometric age dating in the early 20th century, measurements of lead in uranium-rich minerals showed that some were in excess of a billion years old.The oldest such minerals analyzed to date—small crystals of zircon from the Jack Hills of Western Australia—are at least 4.404 billion years old. Comparing the mass and luminosity of the Sun to those of other stars, it appears that the Solar System cannot be much older than those rocks. Calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions – the oldest known solid constituents within meteorites that are formed within the Solar System – are 4.567 billion years old, giving an age for the solar system and an upper limit for the age of Earth.It is hypothesised that the accretion of Earth began soon after the formation of the calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions and the meteorites. Because the exact amount of time this accretion process took is not yet known, and the predictions from different accretion models range from a few millions up to about 100 million years, the exact age of Earth is difficult to determine. It is also difficult to determine the exact age of the oldest rocks on Earth, exposed at the surface, as they are aggregates of minerals of possibly different ages.