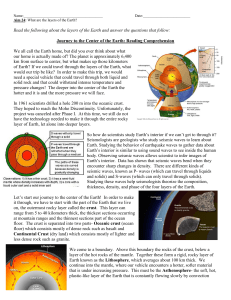
7.3 Landforms are the result of the interaction of constructive and
... constantly changing result of dynamic processes and forces at work inside the Earth. 2. Earth is formed of three basic layers, with the densest being the iron and nickel core. The middle layer, the mantle, of the Earth is composed of mostly light elements such as silicon, oxygen and magnesium and is ...
... constantly changing result of dynamic processes and forces at work inside the Earth. 2. Earth is formed of three basic layers, with the densest being the iron and nickel core. The middle layer, the mantle, of the Earth is composed of mostly light elements such as silicon, oxygen and magnesium and is ...
Evidence for a Plate Tectonics Debate - IG
... Although our planet Earth has been around for more than four billion years, in our vision it would never be the same after 1912. In that year, Alfred Wegener, a German astronomer and meteorologist, often on scientific expeditions to Greenland, first proposed that the continents had drifted apart fro ...
... Although our planet Earth has been around for more than four billion years, in our vision it would never be the same after 1912. In that year, Alfred Wegener, a German astronomer and meteorologist, often on scientific expeditions to Greenland, first proposed that the continents had drifted apart fro ...
Scientists who aided theory of Evolution PPT
... more offspring than can survive because populations increase faster than earth can support This would mean that natural selection would be “the survival of the fittest” because there were not enough resources for every organism to survive. ...
... more offspring than can survive because populations increase faster than earth can support This would mean that natural selection would be “the survival of the fittest” because there were not enough resources for every organism to survive. ...
Plate Tectonics
... Difficult to fathom as our life spans only 80 Simplified history of Earth – Waugh pg. 9 Oldest rocks are ~ 4 billion years old Found in the Northwest Territories ...
... Difficult to fathom as our life spans only 80 Simplified history of Earth – Waugh pg. 9 Oldest rocks are ~ 4 billion years old Found in the Northwest Territories ...
OUR PLANET
... the crust: Is the earth skin- like the peel of an orange. Beneath the crust is a thick layer, called the mantle, made of mostly solid rock which subjected to enough heat and pressure. • The Earth crust is cracked into huge pieces that fit together like a giant puzzle. These pieces are called plates ...
... the crust: Is the earth skin- like the peel of an orange. Beneath the crust is a thick layer, called the mantle, made of mostly solid rock which subjected to enough heat and pressure. • The Earth crust is cracked into huge pieces that fit together like a giant puzzle. These pieces are called plates ...
Read the following about the layers of the Earth and answer the
... need a special vehicle that could travel through both liquid and solid rock and that could withstand intense temperature and pressure changes! The deeper into the center of the Earth the hotter and it is and the more pressure we will face. In 1961 scientists drilled a hole 200 m into the oceanic cru ...
... need a special vehicle that could travel through both liquid and solid rock and that could withstand intense temperature and pressure changes! The deeper into the center of the Earth the hotter and it is and the more pressure we will face. In 1961 scientists drilled a hole 200 m into the oceanic cru ...
Earth System - Rock Cycle
... Name:___________________ Date:____________________ Class:___________________ ...
... Name:___________________ Date:____________________ Class:___________________ ...
General Geology
... the rocks and minerals which compose it, the processes which are constantly changing it, the concepts of relative and absolute time, the risks associated with geologic hazards, and the role of geology in shaping man’s environment. The course presents the tools, methods and approach employed by pract ...
... the rocks and minerals which compose it, the processes which are constantly changing it, the concepts of relative and absolute time, the risks associated with geologic hazards, and the role of geology in shaping man’s environment. The course presents the tools, methods and approach employed by pract ...
Plate Tectonics
... Cocos and Nazca plates: only oceanic crust North plate: continental and oceanic crust ...
... Cocos and Nazca plates: only oceanic crust North plate: continental and oceanic crust ...
Introduction to geology
... Geology is the science that try an understanding of the planet Earth 1. Physical geology - examines the materials composing Earth and seeks to understand the many processes that operate beneath and upon its surface 2. Historical geology - seeks an understanding of the origin of Earth and its develop ...
... Geology is the science that try an understanding of the planet Earth 1. Physical geology - examines the materials composing Earth and seeks to understand the many processes that operate beneath and upon its surface 2. Historical geology - seeks an understanding of the origin of Earth and its develop ...
Chapter 2 Presentation
... Glaciers are large bodies of ice that move across the Earth’s surface, changing the landscape as they flow. ...
... Glaciers are large bodies of ice that move across the Earth’s surface, changing the landscape as they flow. ...
The Theory of Continental Drift (Now Plate Tectonics)
... - __________ plates move about 10 cm/year - _________________ plates about 2 cm/year - It is believed that the plate movements have carried ______________ across the earth. - It is believed that about 250 million years ago there was one large continent called _____________. - Gradually due to tecton ...
... - __________ plates move about 10 cm/year - _________________ plates about 2 cm/year - It is believed that the plate movements have carried ______________ across the earth. - It is believed that about 250 million years ago there was one large continent called _____________. - Gradually due to tecton ...
Ch. 2 Earth`s Water Lesson ppt
... • Almost all of the hydrosphere is saltwater found in oceans, seas, and some lakes. • The amount of water on Earth never changes, but it is constantly moving through the processes of evaporation, condensation, and precipitation. • Evaporation is when the sun’s energy causes water to change into vapo ...
... • Almost all of the hydrosphere is saltwater found in oceans, seas, and some lakes. • The amount of water on Earth never changes, but it is constantly moving through the processes of evaporation, condensation, and precipitation. • Evaporation is when the sun’s energy causes water to change into vapo ...
plate tectonic review
... I’m am the term that is used to describe when one plate sinks below another. ...
... I’m am the term that is used to describe when one plate sinks below another. ...
Lecture 2 Notes: Origin and Age of the Earth
... 3. Now we have all the elements, but how do we parse them up into sun, planets, moons, etc.? The starting point was a haze of very diffuse matter produced by the above processes. How do we know? The abundance of elements in the Sun and in one of the most primitive (i.e. least changed) meteorite clas ...
... 3. Now we have all the elements, but how do we parse them up into sun, planets, moons, etc.? The starting point was a haze of very diffuse matter produced by the above processes. How do we know? The abundance of elements in the Sun and in one of the most primitive (i.e. least changed) meteorite clas ...
learning targets for
... How do engineers make a building safe? Research and build a model of a home/building that uses earthquake prevention mechanisms. Include a description of the techniques. What are the major factors that determine the intensity of ground shaking from an earthquake? Create ground scenarios, have a cont ...
... How do engineers make a building safe? Research and build a model of a home/building that uses earthquake prevention mechanisms. Include a description of the techniques. What are the major factors that determine the intensity of ground shaking from an earthquake? Create ground scenarios, have a cont ...
Unit 1
... Create a 4x4 chart using the physical systems we just discussed in class First row should include the names of the systems Rows 2-4 should include one characteristic about the systems above Atmosphere ...
... Create a 4x4 chart using the physical systems we just discussed in class First row should include the names of the systems Rows 2-4 should include one characteristic about the systems above Atmosphere ...
Z SR Midterm Test Review
... Describe the movement of the continents from the landmass Pangaea, to their present location today, and how they may be situated in the future. ______________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ...
... Describe the movement of the continents from the landmass Pangaea, to their present location today, and how they may be situated in the future. ______________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ...
Purpose, Standards and Prelesson
... Science. The APES course is one that consist of cross curriculum subjects including Earth Science Biology, Chemistry Economics, and Math. The focus with this trip is to review basic earth science concepts that answer the questions: How has the Earth evolved?* What major geologic processes occur ...
... Science. The APES course is one that consist of cross curriculum subjects including Earth Science Biology, Chemistry Economics, and Math. The focus with this trip is to review basic earth science concepts that answer the questions: How has the Earth evolved?* What major geologic processes occur ...
Homework01h - Kean University
... 2. What happens to the volume and density of any substance when it is heated? 3. If a low density ("light") substance is surrounded by high density ("heavy") materials, which moves to the lower level? 4. What happens to the volume and density of any substance when it is cooled? 5. What is convection ...
... 2. What happens to the volume and density of any substance when it is heated? 3. If a low density ("light") substance is surrounded by high density ("heavy") materials, which moves to the lower level? 4. What happens to the volume and density of any substance when it is cooled? 5. What is convection ...
Age of the Earth

The age of the Earth is 4.54 ± 0.05 billion years (4.54 × 109 years ± 1%). This age is based on evidence from radiometric age dating of meteorite material and is consistent with the radiometric ages of the oldest-known terrestrial and lunar samples.Following the development of radiometric age dating in the early 20th century, measurements of lead in uranium-rich minerals showed that some were in excess of a billion years old.The oldest such minerals analyzed to date—small crystals of zircon from the Jack Hills of Western Australia—are at least 4.404 billion years old. Comparing the mass and luminosity of the Sun to those of other stars, it appears that the Solar System cannot be much older than those rocks. Calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions – the oldest known solid constituents within meteorites that are formed within the Solar System – are 4.567 billion years old, giving an age for the solar system and an upper limit for the age of Earth.It is hypothesised that the accretion of Earth began soon after the formation of the calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions and the meteorites. Because the exact amount of time this accretion process took is not yet known, and the predictions from different accretion models range from a few millions up to about 100 million years, the exact age of Earth is difficult to determine. It is also difficult to determine the exact age of the oldest rocks on Earth, exposed at the surface, as they are aggregates of minerals of possibly different ages.