Earth,Notes,RevQs,Ch1
... history of Earth. Acceptance of the uniformitarian concept logically forces one to accept a very old age for Earth and a very long geologic time. 5. The currently accepted age of the Earth is 4.5 to 4.6 billion years, based on meticulous experimental measurements of lead isotopes on meteoritic and t ...
... history of Earth. Acceptance of the uniformitarian concept logically forces one to accept a very old age for Earth and a very long geologic time. 5. The currently accepted age of the Earth is 4.5 to 4.6 billion years, based on meticulous experimental measurements of lead isotopes on meteoritic and t ...
Unit 1B Natural hazards
... margin is a conservative margin, as crust is neither made nor destroyed. 3. If the plates are moving towards each other, then one of 2 things can happen a) One plate moves under the other. This is a destructive margin (as some crust is reabsorbed into the mantle and destroyed) b) If two plates appro ...
... margin is a conservative margin, as crust is neither made nor destroyed. 3. If the plates are moving towards each other, then one of 2 things can happen a) One plate moves under the other. This is a destructive margin (as some crust is reabsorbed into the mantle and destroyed) b) If two plates appro ...
ppt file - Angelfire
... Big bang theory •There was a big bang some 15 billion years ago, when the size of the universe was zero and the temperature was infinite. The universe then started expanding at near light speed. •At about 10,000 years after the Big Bang, the temperature had fallen to such an extent that the energy ...
... Big bang theory •There was a big bang some 15 billion years ago, when the size of the universe was zero and the temperature was infinite. The universe then started expanding at near light speed. •At about 10,000 years after the Big Bang, the temperature had fallen to such an extent that the energy ...
Heat Budget and Climate Change
... wind patterns shift in the Pacific Ocean pushing warmer water off of the west coast of South America – known for its cooler water. This influx of warm water can lead to a rise in temperature, air convection and precipitation for various locations around the Earth. The heat budget of the planet will ...
... wind patterns shift in the Pacific Ocean pushing warmer water off of the west coast of South America – known for its cooler water. This influx of warm water can lead to a rise in temperature, air convection and precipitation for various locations around the Earth. The heat budget of the planet will ...
Intro2-3
... expands as it freezes, and breaks the rocks. Rocks eventually break down into smaller pieces called sediment. Flowing water moves sediment to form new landforms, such as river deltas. Another force that wears down landforms is erosion. Erosion takes place when sediment is moved by ice, water, and wi ...
... expands as it freezes, and breaks the rocks. Rocks eventually break down into smaller pieces called sediment. Flowing water moves sediment to form new landforms, such as river deltas. Another force that wears down landforms is erosion. Erosion takes place when sediment is moved by ice, water, and wi ...
Earth Layers Creative Writing
... • Starred items like this ***** are great things you included and that I liked in your work! Yeah! • Circled items with comments are areas that points were deducted and the reasons why ...
... • Starred items like this ***** are great things you included and that I liked in your work! Yeah! • Circled items with comments are areas that points were deducted and the reasons why ...
The Fossil Record and Evolution
... Problem exists that new cosmogenic isotopes are always being created. Not constant number like non-cosmogenic isotopes. Also dealing with very small amounts of daughter isotopes. May be lost due to erosion. ...
... Problem exists that new cosmogenic isotopes are always being created. Not constant number like non-cosmogenic isotopes. Also dealing with very small amounts of daughter isotopes. May be lost due to erosion. ...
Study guide: exam #1
... Advise: review notes; read book; and answer the appropriate questions in the back of each chapter. Exam will consist of 45 multiple choice questions. Figure numbers are taken from the 7th edition. ...
... Advise: review notes; read book; and answer the appropriate questions in the back of each chapter. Exam will consist of 45 multiple choice questions. Figure numbers are taken from the 7th edition. ...
Section 19.2
... 19.2 Movement of continents The surface of Earth is broken into many pieces like a giant jigsaw puzzle. Plate tectonics describes how these pieces move on Earth’s surface. ...
... 19.2 Movement of continents The surface of Earth is broken into many pieces like a giant jigsaw puzzle. Plate tectonics describes how these pieces move on Earth’s surface. ...
Final S2 ES Option one
... 8. State the principle of uniformitariansim. Explain how the law of superposition can be used to determine the relative age of rocks. Compare three types of unconformities. Apply the law of crosscutting relationships to determine the relative age of rocks (show and explain examples.) Summarize the l ...
... 8. State the principle of uniformitariansim. Explain how the law of superposition can be used to determine the relative age of rocks. Compare three types of unconformities. Apply the law of crosscutting relationships to determine the relative age of rocks (show and explain examples.) Summarize the l ...
Name:
... However, people thought Wegner’s idea was too radical and did not believe him until further research was conducted. Evidence of continental drift collected from the sea floor and through the explanation of convection currents finally convinced people that continental drift did occur. Evidence from t ...
... However, people thought Wegner’s idea was too radical and did not believe him until further research was conducted. Evidence of continental drift collected from the sea floor and through the explanation of convection currents finally convinced people that continental drift did occur. Evidence from t ...
8H - UCC Revision
... There have been many different theories about how the rocks of the Earth were formed. A scientific theory is an idea that can explain many different observations, and it can make predictions that can be tested. Creationism says that the Earth was formed in a few days by a divine being. Different rel ...
... There have been many different theories about how the rocks of the Earth were formed. A scientific theory is an idea that can explain many different observations, and it can make predictions that can be tested. Creationism says that the Earth was formed in a few days by a divine being. Different rel ...
Layers of the Earth
... The top layers of the mantle are hot enough to be plastic or semi-liquid, which allows it to… FLOW ...
... The top layers of the mantle are hot enough to be plastic or semi-liquid, which allows it to… FLOW ...
Plate Tectonics - Noadswood Science
... People once thought that the oceans and the continents were formed by shrinkage from when the Earth cooled down after being formed. Alfred Wegener proposed something different. People didn’t believe him because he couldn’t prove it, so he had to find some evidence: ...
... People once thought that the oceans and the continents were formed by shrinkage from when the Earth cooled down after being formed. Alfred Wegener proposed something different. People didn’t believe him because he couldn’t prove it, so he had to find some evidence: ...
Plate Tectonics Study Guide
... of the plate with it as it sinks into the mantle 7. Where are the convection currents located that move Earth’s plates? The Athenosphere 8. What is a convection current? the movement of heat energy throughout a fluid caused by differences in temp/density 9. What happens to convection currents when t ...
... of the plate with it as it sinks into the mantle 7. Where are the convection currents located that move Earth’s plates? The Athenosphere 8. What is a convection current? the movement of heat energy throughout a fluid caused by differences in temp/density 9. What happens to convection currents when t ...
Unit Test Study Guide: The Restless Earth and Volcanoes
... 11. The landforms that we call volcanoes are created by __________________VOLs1 12. Where are volcanoes most likely to form? V__________________OLs3 13. What would you expect to see during a non-explosive eruption? VO__________________Ls1 14. Molten rock deep underground often gathers in a V________ ...
... 11. The landforms that we call volcanoes are created by __________________VOLs1 12. Where are volcanoes most likely to form? V__________________OLs3 13. What would you expect to see during a non-explosive eruption? VO__________________Ls1 14. Molten rock deep underground often gathers in a V________ ...
Plate Tectonics and the Changing Earth NO PICS
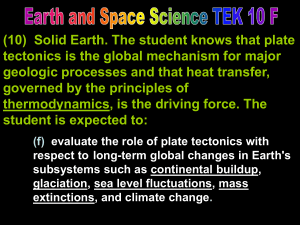
... (10) Solid Earth. The student knows that plate tectonics is the global mechanism for major geologic processes and that heat transfer, governed by the principles of thermodynamics, is the driving force. The student is expected to: (f) evaluate the role of plate tectonics with respect to long-term glo ...
... (10) Solid Earth. The student knows that plate tectonics is the global mechanism for major geologic processes and that heat transfer, governed by the principles of thermodynamics, is the driving force. The student is expected to: (f) evaluate the role of plate tectonics with respect to long-term glo ...
The Theory of Plate Tectonics Homework
... Answer the following questions on a separate sheet of paper. 4. Describe what happens when (a) two plates carrying oceanic crust collide, (b) two plates carrying continental crust collide, and (c) a plate carrying oceanic crust collides with a plate carrying continental crust. 5. Explain what force ...
... Answer the following questions on a separate sheet of paper. 4. Describe what happens when (a) two plates carrying oceanic crust collide, (b) two plates carrying continental crust collide, and (c) a plate carrying oceanic crust collides with a plate carrying continental crust. 5. Explain what force ...
SCIENCE IN THE NEWS | Plate Tectonics
... California is called the San Andreas Fault. It is along or near this fault line that most of California’s earthquakes take place, as the two tectonic plates move in different directions. ...
... California is called the San Andreas Fault. It is along or near this fault line that most of California’s earthquakes take place, as the two tectonic plates move in different directions. ...
Lesson Plan - ScienceA2Z.com
... from what were formerly sediments), and extrusive igneous rocks (e.g., lavas, volcanic ash, and other formerly molten rocks extruded onto the Earth's surface). The layers of rock are known as "strata", and the study of their succession is known as "stratigraphy". Fundamental to stratigraphy are a se ...
... from what were formerly sediments), and extrusive igneous rocks (e.g., lavas, volcanic ash, and other formerly molten rocks extruded onto the Earth's surface). The layers of rock are known as "strata", and the study of their succession is known as "stratigraphy". Fundamental to stratigraphy are a se ...
Section 1: Earth: A Unique Planet
... from Earth’s center. Weight and Location • Because the distance between Earth’s surface and its center is greater at the equator than at the poles, the weight of an object at the equator is about 0.3% less than its weight at the North Pole. ...
... from Earth’s center. Weight and Location • Because the distance between Earth’s surface and its center is greater at the equator than at the poles, the weight of an object at the equator is about 0.3% less than its weight at the North Pole. ...
File - Sturgeon City
... The inner core is made up of iron and nickel just like the outer core. However, since it is so deep within the earth it is under immense pressure. Even though it is just as hot as the outer core, the pressure causes the iron an nickel to remain solid. The inner core is the hottest part of the earth ...
... The inner core is made up of iron and nickel just like the outer core. However, since it is so deep within the earth it is under immense pressure. Even though it is just as hot as the outer core, the pressure causes the iron an nickel to remain solid. The inner core is the hottest part of the earth ...
Age of the Earth

The age of the Earth is 4.54 ± 0.05 billion years (4.54 × 109 years ± 1%). This age is based on evidence from radiometric age dating of meteorite material and is consistent with the radiometric ages of the oldest-known terrestrial and lunar samples.Following the development of radiometric age dating in the early 20th century, measurements of lead in uranium-rich minerals showed that some were in excess of a billion years old.The oldest such minerals analyzed to date—small crystals of zircon from the Jack Hills of Western Australia—are at least 4.404 billion years old. Comparing the mass and luminosity of the Sun to those of other stars, it appears that the Solar System cannot be much older than those rocks. Calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions – the oldest known solid constituents within meteorites that are formed within the Solar System – are 4.567 billion years old, giving an age for the solar system and an upper limit for the age of Earth.It is hypothesised that the accretion of Earth began soon after the formation of the calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions and the meteorites. Because the exact amount of time this accretion process took is not yet known, and the predictions from different accretion models range from a few millions up to about 100 million years, the exact age of Earth is difficult to determine. It is also difficult to determine the exact age of the oldest rocks on Earth, exposed at the surface, as they are aggregates of minerals of possibly different ages.