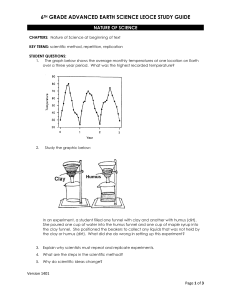
Metamorphic Rock Metamorphic rocks have been changed over
... Metamorphic rocks can be formed by pressure deep under the Earth's surface, from the extreme heat caused by magma or by the intense collisions and friction of tectonic plates. Uplift and erosion help bring metamorphic rock to the Earth's surface. Examples of metamorphic rocks include anthracite, qua ...
... Metamorphic rocks can be formed by pressure deep under the Earth's surface, from the extreme heat caused by magma or by the intense collisions and friction of tectonic plates. Uplift and erosion help bring metamorphic rock to the Earth's surface. Examples of metamorphic rocks include anthracite, qua ...
Unit 6: Sedimentary Rocks
... Rock particles in flowing water settle out and layers form. The layers of sediment become covered by other layers.The upper layers press down on the lower layers.The weight of accumulated particles, along with mineral-laden water, cements everything together. After thousands of years, layers of sedi ...
... Rock particles in flowing water settle out and layers form. The layers of sediment become covered by other layers.The upper layers press down on the lower layers.The weight of accumulated particles, along with mineral-laden water, cements everything together. After thousands of years, layers of sedi ...
Plate Tectonics Crossword
... Alfred _______ is credited with developing the theory of continental drift. ...
... Alfred _______ is credited with developing the theory of continental drift. ...
6TH GRADE ADVANCED EARTH SCIENCE LEOCE STUDY GUIDE
... 6. Explain the Sun’s role in the water cycle. 7. Explain the effects of ocean currents on climate. 8. How are deep ocean currents formed? 9. What effect does Earth’s rotation have on global wind patterns? 10. What affects the salinity of the ocean? 11. What factors influence ocean surface temperatur ...
... 6. Explain the Sun’s role in the water cycle. 7. Explain the effects of ocean currents on climate. 8. How are deep ocean currents formed? 9. What effect does Earth’s rotation have on global wind patterns? 10. What affects the salinity of the ocean? 11. What factors influence ocean surface temperatur ...
Table of Contents - Carson
... The historian Will Durant used to say “Civilization exists by geologic consent, subject to change without notice.” This observation was inspired, in part, by volcanic eruptions that not only kill people close to them, but may affect climate on a worldwide scale for many years, as did the eruption of ...
... The historian Will Durant used to say “Civilization exists by geologic consent, subject to change without notice.” This observation was inspired, in part, by volcanic eruptions that not only kill people close to them, but may affect climate on a worldwide scale for many years, as did the eruption of ...
The Precambrian: Hadean, Archean and Proterozoic
... acid (HCl), which was the source of the chloride in sea salt (mostly NaCl). • The volatiles were probably released early in the Earth's history, when it melted and segregated into the core, mantle, and crust. This segregation occurred because of differences in density, the crust being the "lightest" ...
... acid (HCl), which was the source of the chloride in sea salt (mostly NaCl). • The volatiles were probably released early in the Earth's history, when it melted and segregated into the core, mantle, and crust. This segregation occurred because of differences in density, the crust being the "lightest" ...
Continental Crust
... • The Earth’s crust is divided into 12 major plates which are moved in various directions. • This plate motion causes them to collide, pull apart, or scrape against each other. • Each type of interaction causes a characteristic set of Earth structures or “tectonic” features. • The word, tectonic, re ...
... • The Earth’s crust is divided into 12 major plates which are moved in various directions. • This plate motion causes them to collide, pull apart, or scrape against each other. • Each type of interaction causes a characteristic set of Earth structures or “tectonic” features. • The word, tectonic, re ...
Plate Tectonics
... Plate Tectonics Liz LaRosa for use with my 5th Grade Science Class http://www.middleschoolscience.com 2009 ...
... Plate Tectonics Liz LaRosa for use with my 5th Grade Science Class http://www.middleschoolscience.com 2009 ...
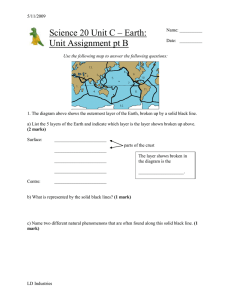
Unit C UA pt B - LD Industries
... ________ - relating to waves that travel through Earth as a result of explosions or earthquakes ________ - a large concentration of petroleum confined between layers of impermeable shale ________ - an instrument that records seismic waves ________ - a submerged ridge of rock, sand, or coral that ris ...
... ________ - relating to waves that travel through Earth as a result of explosions or earthquakes ________ - a large concentration of petroleum confined between layers of impermeable shale ________ - an instrument that records seismic waves ________ - a submerged ridge of rock, sand, or coral that ris ...
stress A force that acts on rock to change its shape or volume
... according to their intensity and how much damage they cause at a particular place. ...
... according to their intensity and how much damage they cause at a particular place. ...
Closer to Poles (c)
... Temperature Changes with Latitude Solar energy does not hit earth uniformly ...
... Temperature Changes with Latitude Solar energy does not hit earth uniformly ...
Layers of the earth new
... • Solid sphere composed mostly of iron • It is believed to be as hot as 6,650°C (12,000°F) • Heat in the core is probably generated by the radioactive decay of uranium and other elements • It is solid because of the pressure from the outer core, mantle, and crust compressing it tremendously ...
... • Solid sphere composed mostly of iron • It is believed to be as hot as 6,650°C (12,000°F) • Heat in the core is probably generated by the radioactive decay of uranium and other elements • It is solid because of the pressure from the outer core, mantle, and crust compressing it tremendously ...
GEOS 101 The Dynamic Earth Fall 2011
... Phone: 724‐357‐2611 Office Hours: Mon 3:30‐4:30, Tues 9:00‐11:00, Fri 10:00‐12:00, or by appointment The Course From volcanic eruptions and catastrophic earthquakes to the slow drift of continents and the passage of ice ages, Earth processes have shaped the history of life and altered the devel ...
... Phone: 724‐357‐2611 Office Hours: Mon 3:30‐4:30, Tues 9:00‐11:00, Fri 10:00‐12:00, or by appointment The Course From volcanic eruptions and catastrophic earthquakes to the slow drift of continents and the passage of ice ages, Earth processes have shaped the history of life and altered the devel ...
Earth’s Sub-Surface Processes
... CRUST: outer surface; can be oceanic or continental LITHOSPHERE: rigid interior of crust ...
... CRUST: outer surface; can be oceanic or continental LITHOSPHERE: rigid interior of crust ...
Worlds in Eruption – Volcanoes
... Erupting moons To the surprise of many scientists, the spacecraft armada has revealed that volcanism is not confined to the rocky planets of the inner Solar System. One of the highlights of the Voyager missions to Jupiter in 1979 and 1980 was the discovery of active volcanism on its moon Io. Naviga ...
... Erupting moons To the surprise of many scientists, the spacecraft armada has revealed that volcanism is not confined to the rocky planets of the inner Solar System. One of the highlights of the Voyager missions to Jupiter in 1979 and 1980 was the discovery of active volcanism on its moon Io. Naviga ...
What do Earth`s layers consist of?
... • Hess’ idea of sea floor spreading caused scientists to revisit Wegener’s idea of continental drift! ...
... • Hess’ idea of sea floor spreading caused scientists to revisit Wegener’s idea of continental drift! ...
Earth`s Structure
... 19. In California, there is a transform boundary between the North American Plate and what other plate? ...
... 19. In California, there is a transform boundary between the North American Plate and what other plate? ...
WGCh2Notetaking
... plunges below another. The rocky plate melts as it dives downward into the hot mantle. b. Volcanoes also arise in various hot spots, where deep within the Earth the temperature is hotter than normal. The __________________________________________ were formed by this type of volcanic activity. c. Mol ...
... plunges below another. The rocky plate melts as it dives downward into the hot mantle. b. Volcanoes also arise in various hot spots, where deep within the Earth the temperature is hotter than normal. The __________________________________________ were formed by this type of volcanic activity. c. Mol ...
Fact Sheet - SharpSchool
... sea floor, which were very similar to the ones that existed on land. Scientists identified a mountain ridge that stretched from north to south along the middle of the ocean ad they called this ridge the Mid-Atlantic Ocean Ridge. Magnetometers: The Magnetometer helped because a magnetometer is not ...
... sea floor, which were very similar to the ones that existed on land. Scientists identified a mountain ridge that stretched from north to south along the middle of the ocean ad they called this ridge the Mid-Atlantic Ocean Ridge. Magnetometers: The Magnetometer helped because a magnetometer is not ...
Layers of the Earth Model and Story Project
... The Descriptions Key must be an attached piece of the Project that includes a full description of the 4 main layers of the Earth. This can be a cardboard chart, index cards, Ribbon attached to the model, or some other creative idea for describing each layer. A plain paper key will not be acceptable. ...
... The Descriptions Key must be an attached piece of the Project that includes a full description of the 4 main layers of the Earth. This can be a cardboard chart, index cards, Ribbon attached to the model, or some other creative idea for describing each layer. A plain paper key will not be acceptable. ...
Constructive and Destructive Forces Study Guide
... FILL IN THE BLANKS TO THE STUDY GUIDE- Make flashcards to help you study! I. Earth’s layers: The crust and mantle are divided into sections called plates, which “float” on the softer rock of the ___________. These plate movements cause many changes in Earth’s surface. Crust – surface layer of the ...
... FILL IN THE BLANKS TO THE STUDY GUIDE- Make flashcards to help you study! I. Earth’s layers: The crust and mantle are divided into sections called plates, which “float” on the softer rock of the ___________. These plate movements cause many changes in Earth’s surface. Crust – surface layer of the ...
Age of the Earth

The age of the Earth is 4.54 ± 0.05 billion years (4.54 × 109 years ± 1%). This age is based on evidence from radiometric age dating of meteorite material and is consistent with the radiometric ages of the oldest-known terrestrial and lunar samples.Following the development of radiometric age dating in the early 20th century, measurements of lead in uranium-rich minerals showed that some were in excess of a billion years old.The oldest such minerals analyzed to date—small crystals of zircon from the Jack Hills of Western Australia—are at least 4.404 billion years old. Comparing the mass and luminosity of the Sun to those of other stars, it appears that the Solar System cannot be much older than those rocks. Calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions – the oldest known solid constituents within meteorites that are formed within the Solar System – are 4.567 billion years old, giving an age for the solar system and an upper limit for the age of Earth.It is hypothesised that the accretion of Earth began soon after the formation of the calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions and the meteorites. Because the exact amount of time this accretion process took is not yet known, and the predictions from different accretion models range from a few millions up to about 100 million years, the exact age of Earth is difficult to determine. It is also difficult to determine the exact age of the oldest rocks on Earth, exposed at the surface, as they are aggregates of minerals of possibly different ages.