Correlating Rock Layers
... • 2. Sedimentary Rocks – rocks formed from sediments (minerals, sand, small pieces of plant/ organic matter) that are deposited over time (usually as layers, called strata). The sediments in these rocks are compressed for long periods of time before they become solid layers of rock. • Sediments for ...
... • 2. Sedimentary Rocks – rocks formed from sediments (minerals, sand, small pieces of plant/ organic matter) that are deposited over time (usually as layers, called strata). The sediments in these rocks are compressed for long periods of time before they become solid layers of rock. • Sediments for ...
Rheology Thoughts
... Rheology: Where geophysicists, tectonicists and structural geologists collide! This session is aimed at folks who teach students in geophysics class and have a need to engage or infuse one or more of the course topics with an understanding of the processes behind the mathematical descriptions of mat ...
... Rheology: Where geophysicists, tectonicists and structural geologists collide! This session is aimed at folks who teach students in geophysics class and have a need to engage or infuse one or more of the course topics with an understanding of the processes behind the mathematical descriptions of mat ...
The Rock cycle
... small, they settle out slowly. In fact, shale formations can take about 5 million years to form. ...
... small, they settle out slowly. In fact, shale formations can take about 5 million years to form. ...
G2S15Lesson1 Introd
... Some rocks are between these two extremes and include less quartz and more amphibole. These rocks include Diorite and Andesite Some igneous rocks are very mafic and we call them “ultramafic”. Our one example is the rock Peridotite. We divide igneous rocks into two general categories: 1. Plutonic or ...
... Some rocks are between these two extremes and include less quartz and more amphibole. These rocks include Diorite and Andesite Some igneous rocks are very mafic and we call them “ultramafic”. Our one example is the rock Peridotite. We divide igneous rocks into two general categories: 1. Plutonic or ...
Mineral - Weebly
... 3. A specific mineral, no matter where found on Earth, will always contain the same chemicals in the same ratio: Quartz: I part Silicon / 2 parts Oxygen 4. An element is comprised of a single atom and therefore a pure substance 5. Some minerals appear in nature as an element and not a compound: such ...
... 3. A specific mineral, no matter where found on Earth, will always contain the same chemicals in the same ratio: Quartz: I part Silicon / 2 parts Oxygen 4. An element is comprised of a single atom and therefore a pure substance 5. Some minerals appear in nature as an element and not a compound: such ...
Plate Tectonics, Tectonic Plates Information, Facts, News, Photos
... pushes apart two or more plates. Mountains and volcanoes rise along the seam. The process renews the ocean floor and widens the giant basins. A single mid-ocean ridge system connects the world's oceans, making the ridge the longest mountain range in the world. On land, giant troughs such as the Grea ...
... pushes apart two or more plates. Mountains and volcanoes rise along the seam. The process renews the ocean floor and widens the giant basins. A single mid-ocean ridge system connects the world's oceans, making the ridge the longest mountain range in the world. On land, giant troughs such as the Grea ...
Determining Earth`s Interior Structure
... During the last century, there were a total of about 1 million recorded fatalities, or about 10,000 per year. This is much less than the number of coal-related deaths from mining and transportation accidents, black lung disease, and other diseases. ...
... During the last century, there were a total of about 1 million recorded fatalities, or about 10,000 per year. This is much less than the number of coal-related deaths from mining and transportation accidents, black lung disease, and other diseases. ...
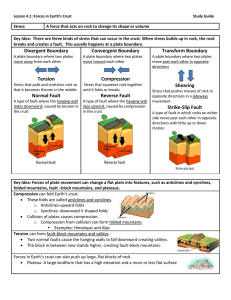
Chapter 4 lesson 1
... Two normal faults cause the hanging walls to fall downward creating valleys. The block in between now stands higher, creating fault-block mountains. Forces in Earth’s crust can also push up large, flat blocks of rock. Plateau- A large landform that has a high elevation and a more or less flat ...
... Two normal faults cause the hanging walls to fall downward creating valleys. The block in between now stands higher, creating fault-block mountains. Forces in Earth’s crust can also push up large, flat blocks of rock. Plateau- A large landform that has a high elevation and a more or less flat ...
Plate Tectonics Review Worksheet
... 1. Continental Drift: A theory proposed by Alfred Wegner that said all continents were once joined 300 million years ago in a single land mass called Pangaea. Over time the continents moved to their present day locations. 2. What are four pieces of evidence for continental drift? Fossils, puzzle fit ...
... 1. Continental Drift: A theory proposed by Alfred Wegner that said all continents were once joined 300 million years ago in a single land mass called Pangaea. Over time the continents moved to their present day locations. 2. What are four pieces of evidence for continental drift? Fossils, puzzle fit ...
1 Inside the Earth - Middletown Public Schools
... How do scientists know things about the deepest parts of the Earth? No one has ever been to these places. Scientists have never even drilled through the crust, which is only a thin layer on the surface of the Earth. So how do we know so much about the mantle and the core? Much of what scientists kno ...
... How do scientists know things about the deepest parts of the Earth? No one has ever been to these places. Scientists have never even drilled through the crust, which is only a thin layer on the surface of the Earth. So how do we know so much about the mantle and the core? Much of what scientists kno ...
Earth is made of materials with different DENSITIES The 4 layers of
... thinned valley floor sinks BELOW SEA LEVEL & water from nearby oceans or rivers may fill the valley and form a LAKE or SEAS. 8. A HOT SPOT can provide a fixed point for measuring the speed & direction of plate movements because it generally stays in one place where the magma rises in a plume from th ...
... thinned valley floor sinks BELOW SEA LEVEL & water from nearby oceans or rivers may fill the valley and form a LAKE or SEAS. 8. A HOT SPOT can provide a fixed point for measuring the speed & direction of plate movements because it generally stays in one place where the magma rises in a plume from th ...
Plate Tectonics
... the mid-Atlantic Ocean to the northern top of Japan. The Cocos Plate covers a small area in the Pacific Ocean just west of Central America. • These plates are not anchored in place but slide over a hot and bendable layer of the mantle. ...
... the mid-Atlantic Ocean to the northern top of Japan. The Cocos Plate covers a small area in the Pacific Ocean just west of Central America. • These plates are not anchored in place but slide over a hot and bendable layer of the mantle. ...
Origin and Formation of Earth Homework Sheet 1 Due
... 2. Draw a labelled diagram of the Earth’s inner structure. Be sure to label each of the internal layers (use inner core, outer core, mantle, crust).Indicate the relative thickness of each layer with measurements. ...
... 2. Draw a labelled diagram of the Earth’s inner structure. Be sure to label each of the internal layers (use inner core, outer core, mantle, crust).Indicate the relative thickness of each layer with measurements. ...
Warm-Up - mssarnelli
... is the former “supercontinent” called? Why is it called Pangaea? The idea that the continents had slowly moved is called…? Who was the scientist that proposed the idea of both Pangaea & Continental Drift? Why didn’t people believe him? What did he use as evidence to prove his theory? Wha ...
... is the former “supercontinent” called? Why is it called Pangaea? The idea that the continents had slowly moved is called…? Who was the scientist that proposed the idea of both Pangaea & Continental Drift? Why didn’t people believe him? What did he use as evidence to prove his theory? Wha ...
ISN- Insert Plate Tectonics for Cornell Notes
... Earth’s lithosphere is broken into sections separated by cracks in Earth’s crust, or faults. They fit closely together and carry the continents, or parts of the ocean floor, or both. In the mid-1960s, geologists combined what they knew about seafloor spreading, Earth’s plates, and plate motion into ...
... Earth’s lithosphere is broken into sections separated by cracks in Earth’s crust, or faults. They fit closely together and carry the continents, or parts of the ocean floor, or both. In the mid-1960s, geologists combined what they knew about seafloor spreading, Earth’s plates, and plate motion into ...
Chapter 21 Notes - Valdosta State University
... Similar fossils have been found in South America and Africa. Other fossils have been found in South America, Africa, India, Australia, and Antarctica. A certain species of garden snail is found only in the western part of Europe and the eastern part of North America. All of these organisms would hav ...
... Similar fossils have been found in South America and Africa. Other fossils have been found in South America, Africa, India, Australia, and Antarctica. A certain species of garden snail is found only in the western part of Europe and the eastern part of North America. All of these organisms would hav ...
8.4 Plate Movement and Continental Growth
... continuously until they reached today’s configuration. ...
... continuously until they reached today’s configuration. ...
Midterm Exam
... Because they float on the oceans Because they float on Earth’s liquid mantle Because of “trench-pull” and “ridge-push forces” ...
... Because they float on the oceans Because they float on Earth’s liquid mantle Because of “trench-pull” and “ridge-push forces” ...
Minerals and Rocks
... A long period of weathering Glacial activity A fine-grained igneous rock was probably formed by Wind erosion Weathering and erosion Extreme pressure Great heat and pressure that did not produce melting Rapid cooling of molten material Burial and cementation of sediment ...
... A long period of weathering Glacial activity A fine-grained igneous rock was probably formed by Wind erosion Weathering and erosion Extreme pressure Great heat and pressure that did not produce melting Rapid cooling of molten material Burial and cementation of sediment ...
geologic time, concepts, and principles
... Gould argued that Hutton's interpretation of uniformitarianism actually included a cyclical series of events in which all of Earth history was repeated with "repair" of the earlier age, much as many primal societies view time as a cyclical, rather than linear, phenomenon. Furthermore, the rates of g ...
... Gould argued that Hutton's interpretation of uniformitarianism actually included a cyclical series of events in which all of Earth history was repeated with "repair" of the earlier age, much as many primal societies view time as a cyclical, rather than linear, phenomenon. Furthermore, the rates of g ...
File
... o When water reacts with carbon dioxide gas in the air or soil, carbonic acid forms. (Found in soft drinks) o Carbonic acid dissolves calcite, the main mineral in limestone. This forms caves. o Feldspar, found in granite, is weathered to form Kaolinite clay in soils. ...
... o When water reacts with carbon dioxide gas in the air or soil, carbonic acid forms. (Found in soft drinks) o Carbonic acid dissolves calcite, the main mineral in limestone. This forms caves. o Feldspar, found in granite, is weathered to form Kaolinite clay in soils. ...
• Internal Structure of Earth and Plate Tectonics • Chapter 2 The
... Understanding Plate Tectonics helped to clear up two geological problems: How did fossils of the same animals and plants end up in both South America and Africa Evidence of ancient glaciation on several continents with inferred directions of ice flow were the same as if there was only one cont ...
... Understanding Plate Tectonics helped to clear up two geological problems: How did fossils of the same animals and plants end up in both South America and Africa Evidence of ancient glaciation on several continents with inferred directions of ice flow were the same as if there was only one cont ...
Age of the Earth

The age of the Earth is 4.54 ± 0.05 billion years (4.54 × 109 years ± 1%). This age is based on evidence from radiometric age dating of meteorite material and is consistent with the radiometric ages of the oldest-known terrestrial and lunar samples.Following the development of radiometric age dating in the early 20th century, measurements of lead in uranium-rich minerals showed that some were in excess of a billion years old.The oldest such minerals analyzed to date—small crystals of zircon from the Jack Hills of Western Australia—are at least 4.404 billion years old. Comparing the mass and luminosity of the Sun to those of other stars, it appears that the Solar System cannot be much older than those rocks. Calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions – the oldest known solid constituents within meteorites that are formed within the Solar System – are 4.567 billion years old, giving an age for the solar system and an upper limit for the age of Earth.It is hypothesised that the accretion of Earth began soon after the formation of the calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions and the meteorites. Because the exact amount of time this accretion process took is not yet known, and the predictions from different accretion models range from a few millions up to about 100 million years, the exact age of Earth is difficult to determine. It is also difficult to determine the exact age of the oldest rocks on Earth, exposed at the surface, as they are aggregates of minerals of possibly different ages.