Single TMS Receptors
... The most familiar 1-TMS receptor is the insulin receptor. Insulin is the polypeptide hormone that signals a high blood glucose concentration. Insulin promotes the transport of glucose into the liver, muscle and adipose tissue. Insulin promotes the storage of glucose as glycogen in the liver and the ...
... The most familiar 1-TMS receptor is the insulin receptor. Insulin is the polypeptide hormone that signals a high blood glucose concentration. Insulin promotes the transport of glucose into the liver, muscle and adipose tissue. Insulin promotes the storage of glucose as glycogen in the liver and the ...
Cell Communication
... continually remove phosphate groups from target proteins Stopped by endocytosis of receptors and their bound extracellular signals ...
... continually remove phosphate groups from target proteins Stopped by endocytosis of receptors and their bound extracellular signals ...
7.5 Proteins – summary of mark schemes
... B. long and narrow / long strands C. support / structural functions D. (mostly) insoluble in water vs. ...
... B. long and narrow / long strands C. support / structural functions D. (mostly) insoluble in water vs. ...
Typical Signal Transduction Pathway
... c. Signals released by one cell type can travel long distances to target cells of another cell types. 1. Endocrine signals are produced by endocrine cells that release signaling molecules, which are specific and can travel long distances through the blood to reach all parts of the body. ...
... c. Signals released by one cell type can travel long distances to target cells of another cell types. 1. Endocrine signals are produced by endocrine cells that release signaling molecules, which are specific and can travel long distances through the blood to reach all parts of the body. ...
Flexible Multi-scale Fitting of Atomic Structures into Low
... Used NMA to fit high resolution xtal structures to low resolution EM maps. Mostly concerned with conformational change. Also employed flexible fitting method with Calpha only claiming this allowed larger systems to be computationally tractable. Show that this method works better than Situs package o ...
... Used NMA to fit high resolution xtal structures to low resolution EM maps. Mostly concerned with conformational change. Also employed flexible fitting method with Calpha only claiming this allowed larger systems to be computationally tractable. Show that this method works better than Situs package o ...
Bacillus subtilis
... Escherichia coli is grown in a medium containing a mixture of glucose and lactose. During the first few hours the bacteria divide exponentially, using the glucose as the carbon and energy source. When the glucose is used up there is a brief lag period while the lac genes are switched on before the b ...
... Escherichia coli is grown in a medium containing a mixture of glucose and lactose. During the first few hours the bacteria divide exponentially, using the glucose as the carbon and energy source. When the glucose is used up there is a brief lag period while the lac genes are switched on before the b ...
Anti-Adenosine A3 Receptor antibody - Cytoplasmic domain ab140700
... Our Abpromise to you: Quality guaranteed and expert technical support Replacement or refund for products not performing as stated on the datasheet Valid for 12 months from date of delivery Response to your inquiry within 24 hours We provide support in Chinese, English, French, German, Japanese and S ...
... Our Abpromise to you: Quality guaranteed and expert technical support Replacement or refund for products not performing as stated on the datasheet Valid for 12 months from date of delivery Response to your inquiry within 24 hours We provide support in Chinese, English, French, German, Japanese and S ...
Ass4 - The University of Sydney
... Lead to inhibition of export of proteins from the nucleus Lead to the inhibition of protein kinase C because of increased levels of intra-cellular Ca 2+ Lead to production of both phosphotyrosine and phosphoserinemodified proteins Have no effect in cells which do not express the NFKB transcription f ...
... Lead to inhibition of export of proteins from the nucleus Lead to the inhibition of protein kinase C because of increased levels of intra-cellular Ca 2+ Lead to production of both phosphotyrosine and phosphoserinemodified proteins Have no effect in cells which do not express the NFKB transcription f ...
File
... The receptor proteins for steroid hormones are transcription factors. Only once the hormone signal has bound to the receptor can the transcription factor bind to gene regulatory sequences of DNA for transcription to occur. ...
... The receptor proteins for steroid hormones are transcription factors. Only once the hormone signal has bound to the receptor can the transcription factor bind to gene regulatory sequences of DNA for transcription to occur. ...
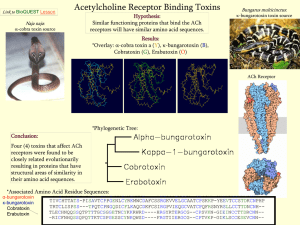
Cytokine receptors and signal transduction
... Immunoglobulin superfamily (IgSF) The immunoglobulin superfamily (IgSF) - a large group of cell surface and soluble proteins that are involved in the recognition, binding, or adhesion processes of cells. ...
... Immunoglobulin superfamily (IgSF) The immunoglobulin superfamily (IgSF) - a large group of cell surface and soluble proteins that are involved in the recognition, binding, or adhesion processes of cells. ...
Extracellular Regulation of the Cell Cycle by Signal Transduction
... Damaged mitochondria leak mitochondria proteins into cytoplasm. Ex: cytochrome c binds to Apaf (Apoptosis Pathway Activating Factor) Apaf-cytochrome c activates initiator caspase ...
... Damaged mitochondria leak mitochondria proteins into cytoplasm. Ex: cytochrome c binds to Apaf (Apoptosis Pathway Activating Factor) Apaf-cytochrome c activates initiator caspase ...
9/18 - MIT
... Structures of MAP kinase in its inactive, unphosphorylated form and active, phosphorylated form Phosphorylation of MAP kinase by MEK at tyrosine 185 (pY185) and threonine 183 ...
... Structures of MAP kinase in its inactive, unphosphorylated form and active, phosphorylated form Phosphorylation of MAP kinase by MEK at tyrosine 185 (pY185) and threonine 183 ...
Slide ()
... transcriptional modulators vorinostat (targeting histone deacetylase), azacytidine derivatives (targeting DNA methyltransferase), or retinoid receptor Source: PRINCIPLES OF CANCER TREATMENT, Harrison's Hematology and Oncology, 2e modulators all-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA) or bexarotene. Cytokine rece ...
... transcriptional modulators vorinostat (targeting histone deacetylase), azacytidine derivatives (targeting DNA methyltransferase), or retinoid receptor Source: PRINCIPLES OF CANCER TREATMENT, Harrison's Hematology and Oncology, 2e modulators all-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA) or bexarotene. Cytokine rece ...
Protein Targeting
... Lysosomal Targeting Man-6 P is the marker, added in cis golgi Added by 2 step enzyme catalysed reaction ...
... Lysosomal Targeting Man-6 P is the marker, added in cis golgi Added by 2 step enzyme catalysed reaction ...
G-Protein-Coupled Receptors
... Cell communication systems based on surface receptors have 3 components: (1) Extracellular signal molecules (2) Surface receptors that receive signals (3) Internal response pathways triggered when receptors bind a signal ...
... Cell communication systems based on surface receptors have 3 components: (1) Extracellular signal molecules (2) Surface receptors that receive signals (3) Internal response pathways triggered when receptors bind a signal ...
Effects of activation of opiate receptors and drugs acting on them
... Effects of activation of opiate receptors and drugs acting on them Aron Takacs ...
... Effects of activation of opiate receptors and drugs acting on them Aron Takacs ...
G protein–coupled receptors
... A common way to translate a signal to a biologic effect inside cells is by way of nucleotide regulatory proteins (G proteins) that bind GTP. GTP is the guanosine analog of ATP . When the signal reaches a G protein, the protein exchanges GDP for GTP. The GTP-protein complex brings about the effect. T ...
... A common way to translate a signal to a biologic effect inside cells is by way of nucleotide regulatory proteins (G proteins) that bind GTP. GTP is the guanosine analog of ATP . When the signal reaches a G protein, the protein exchanges GDP for GTP. The GTP-protein complex brings about the effect. T ...
Outline Section 4
... b. Convergent, or redundant, cross-talk for essential responses occurs when two or more ligands can produce the same target mechanism 3. Multiple target mechanism pathways and divergent crosstalk a. Divergent cross-talk for complex, integrated responses where a single ligand can activate two or mor ...
... b. Convergent, or redundant, cross-talk for essential responses occurs when two or more ligands can produce the same target mechanism 3. Multiple target mechanism pathways and divergent crosstalk a. Divergent cross-talk for complex, integrated responses where a single ligand can activate two or mor ...
GPCRs10
... Heterotrimeric guanine nucleotide–binding protein (G protein)–coupled receptors constitute the largest family of eukaryotic signal transduction proteins that communicate across the membrane. We report the crystal structure of a human β2-adrenergic receptor–T4 lysozyme fusion protein bound to the par ...
... Heterotrimeric guanine nucleotide–binding protein (G protein)–coupled receptors constitute the largest family of eukaryotic signal transduction proteins that communicate across the membrane. We report the crystal structure of a human β2-adrenergic receptor–T4 lysozyme fusion protein bound to the par ...
Getting things where they need to go: Protein Targeting
... Sorting places proteins in membrane and in lumen of organelles ...
... Sorting places proteins in membrane and in lumen of organelles ...
Metal Regulation and Signalling - Zn Proteins
... Structural Zn proteins have different functions, but all create interfaces for macromolecular interactions: protein-protein, protein-DNA, protein-RNA, protein-polysaccharides. No Zn binding motifs found in the e. coli genome, in contrast to an abundance of motifs in eukaryotic cells. Speculation tha ...
... Structural Zn proteins have different functions, but all create interfaces for macromolecular interactions: protein-protein, protein-DNA, protein-RNA, protein-polysaccharides. No Zn binding motifs found in the e. coli genome, in contrast to an abundance of motifs in eukaryotic cells. Speculation tha ...
G protein–coupled receptor

G protein–coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptor, and G protein–linked receptors (GPLR), constitute a large protein family of receptors that sense molecules outside the cell and activate inside signal transduction pathways and, ultimately, cellular responses. Coupling with G proteins, they are called seven-transmembrane receptors because they pass through the cell membrane seven times.G protein–coupled receptors are found only in eukaryotes, including yeast, choanoflagellates, and animals. The ligands that bind and activate these receptors include light-sensitive compounds, odors, pheromones, hormones, and neurotransmitters, and vary in size from small molecules to peptides to large proteins. G protein–coupled receptors are involved in many diseases, and are also the target of approximately 40% of all modern medicinal drugs. Two of the United States's top five selling drugs (Hydrocodone and Lisinopril) act by targeting a G protein–coupled receptor. The 2012 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Brian Kobilka and Robert Lefkowitz for their work that was ""crucial for understanding how G protein–coupled receptors function."". There have been at least seven other Nobel Prizes awarded for some aspect of G protein–mediated signaling.There are two principal signal transduction pathways involving the G protein–coupled receptors: the cAMP signal pathway and the phosphatidylinositol signal pathway. When a ligand binds to the GPCR it causes a conformational change in the GPCR, which allows it to act as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF). The GPCR can then activate an associated G protein by exchanging its bound GDP for a GTP. The G protein's α subunit, together with the bound GTP, can then dissociate from the β and γ subunits to further affect intracellular signaling proteins or target functional proteins directly depending on the α subunit type (Gαs, Gαi/o, Gαq/11, Gα12/13).