Chapter 06 - Neurotransmitter Systems
... Binding of the neurotransmitter to the receptor protein ...
... Binding of the neurotransmitter to the receptor protein ...
Getting things where they need to go: Protein Targeting
... Hypotheses for molecular basis of bipolar disorder •Suggest problem lies in protein targeting Proteins made in cytosol (cytosolic and membrane ones) Sorting places proteins in membrane and in lumen of organelles ‘Routing’ controlled by the presence or absence of targeting Information in the primary ...
... Hypotheses for molecular basis of bipolar disorder •Suggest problem lies in protein targeting Proteins made in cytosol (cytosolic and membrane ones) Sorting places proteins in membrane and in lumen of organelles ‘Routing’ controlled by the presence or absence of targeting Information in the primary ...
Chem*3560 Lecture 33: Membrane receptors and signalling
... Complex organisms indicate developmental or metabolic states by release of signalling molecules or hormones from one tissue to stimulate a response in another tissue. Some of these signalling molecules are relatively nonpolar and can pass through the bilayer. Steroids like estradiol or testosterone ...
... Complex organisms indicate developmental or metabolic states by release of signalling molecules or hormones from one tissue to stimulate a response in another tissue. Some of these signalling molecules are relatively nonpolar and can pass through the bilayer. Steroids like estradiol or testosterone ...
Old exams 1. Which one of these answers best describes a
... 94.Receptors can be located in the nucleus 95.Receptor molecules can contain zinc finger motifs in their structure 96.Adaptation of the receptor might include removal of the receptor from the cell membrane 97.Multiple steps in signaling cascades allow for the amplification of the signal 98.The endog ...
... 94.Receptors can be located in the nucleus 95.Receptor molecules can contain zinc finger motifs in their structure 96.Adaptation of the receptor might include removal of the receptor from the cell membrane 97.Multiple steps in signaling cascades allow for the amplification of the signal 98.The endog ...
No Slide Title
... How can thyroid hormone cause different responses in different parts of the body? Ligand needs to bind with receptor Different cells make different receptors Same receptor/ligand complex may trigger different response in a different cell type Differences between binding specificity and effector spec ...
... How can thyroid hormone cause different responses in different parts of the body? Ligand needs to bind with receptor Different cells make different receptors Same receptor/ligand complex may trigger different response in a different cell type Differences between binding specificity and effector spec ...
Anti-MC5 Receptor antibody - Extracellular domain ab188932
... The application notes include recommended starting dilutions; optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user. ...
... The application notes include recommended starting dilutions; optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user. ...
邵吉民_Signaling_and_diseases
... Activates IR -subunit PTK activity -subunit phosphorylates Tyr residues on cytoplasmic domains as well as downstream substrates (IRS) ...
... Activates IR -subunit PTK activity -subunit phosphorylates Tyr residues on cytoplasmic domains as well as downstream substrates (IRS) ...
Why Do Cells Communicate? Regulation • Cells need to control
... • An elaborate ex of cell signaling that causes controlled cell suicide • During this process the cell is dismantled and digested through many CS pathways to protect neighboring cells from damage • Triggered by signals that activate a cascade of suicide proteins in cells • In vertebrates, this is a ...
... • An elaborate ex of cell signaling that causes controlled cell suicide • During this process the cell is dismantled and digested through many CS pathways to protect neighboring cells from damage • Triggered by signals that activate a cascade of suicide proteins in cells • In vertebrates, this is a ...
Membrane Proteins Integral membrane proteins often contain
... Integral membrane proteins often contain helical segments of appropriate length to span the lipid bilayer. In a protein that has a single segment that spans the membrane, the helix usually only contains hydrophobic residues and is called a single-span membrane protein. In transmembrane proteins with ...
... Integral membrane proteins often contain helical segments of appropriate length to span the lipid bilayer. In a protein that has a single segment that spans the membrane, the helix usually only contains hydrophobic residues and is called a single-span membrane protein. In transmembrane proteins with ...
Analytical Sciences, Poster AS-101 Kinetics and identification of non
... kinase 8 (MAPK8) and green fluorescent protein (GFP). Most of these proteins fulfill important functions within cellular processes. RPS6KA2 was recently identified as a potential drug target and seems to be suitable for the development of novel inhibitors for pancreatic cancer therapy. K-Ras works a ...
... kinase 8 (MAPK8) and green fluorescent protein (GFP). Most of these proteins fulfill important functions within cellular processes. RPS6KA2 was recently identified as a potential drug target and seems to be suitable for the development of novel inhibitors for pancreatic cancer therapy. K-Ras works a ...
Contents: The Journal of Cell Biology
... of placental alkaline phosphatase: a single amino acid change converts a phosphatidylinositol-glycan-anchored protein to a secreted protein. ...
... of placental alkaline phosphatase: a single amino acid change converts a phosphatidylinositol-glycan-anchored protein to a secreted protein. ...
幻灯片 1
... astonishing variety of extracellular stimuli—light, proteins, peptides, small molecules, hormones, and ions. Once activated, GPCRs trigger a cascade of responses inside the cell, primarily through interactions with their G protein partners. ...
... astonishing variety of extracellular stimuli—light, proteins, peptides, small molecules, hormones, and ions. Once activated, GPCRs trigger a cascade of responses inside the cell, primarily through interactions with their G protein partners. ...
HERE - Oregon State University
... inducing β-cell proliferation 2. Using the figure above: a. What is the effect of a drug which inhibits cyclin D1 (labeled as A)? Inhibiting cyclin D1 will prevent the induction of β-cell proliferation b. What is the effect of a drug which activates adenylyl cyclase (labeled as B)? A drug which acti ...
... inducing β-cell proliferation 2. Using the figure above: a. What is the effect of a drug which inhibits cyclin D1 (labeled as A)? Inhibiting cyclin D1 will prevent the induction of β-cell proliferation b. What is the effect of a drug which activates adenylyl cyclase (labeled as B)? A drug which acti ...
Hepatocyte growth factor receptor B-2837-3_2
... (e.g. heat the reagent to 95 °C for 5 minutes, then cool to assay temperature). The product is shipped frozen. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. For long term use, aliquotting is recommended to avoid freeze‐thaw cycles. 2 years from date of receipt at ‐ ...
... (e.g. heat the reagent to 95 °C for 5 minutes, then cool to assay temperature). The product is shipped frozen. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. For long term use, aliquotting is recommended to avoid freeze‐thaw cycles. 2 years from date of receipt at ‐ ...
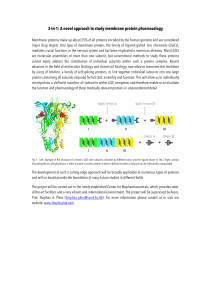
3-in-1: A novel approach to study membrane protein pharmacology
... 3-in-1: A novel approach to study membrane protein pharmacology Membrane proteins make up about 25% of all proteins encoded by the human genome and are considered major drug targets. One type of membrane protein, the family of ligand-gated ion channels (LGICs), mediates crucial functions in the nerv ...
... 3-in-1: A novel approach to study membrane protein pharmacology Membrane proteins make up about 25% of all proteins encoded by the human genome and are considered major drug targets. One type of membrane protein, the family of ligand-gated ion channels (LGICs), mediates crucial functions in the nerv ...
SOMAmer® anti-Interleukin-6 receptor subunit alpha
... The product is shipped frozen. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. For long term use, aliquotting is recommended to avoid freeze-thaw cycles. 2 years from date of receipt at -20 °C to -70 °C, as supplied 3 months at 4 °C ...
... The product is shipped frozen. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. For long term use, aliquotting is recommended to avoid freeze-thaw cycles. 2 years from date of receipt at -20 °C to -70 °C, as supplied 3 months at 4 °C ...
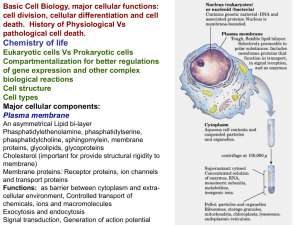
Getting things where they need to go: Protein Targeting
... What kind of energy is needed? Main Classes: Passive versus Active Transport Going with or against the flow Types of active transport: Coupled– ex. symports or antiports ...
... What kind of energy is needed? Main Classes: Passive versus Active Transport Going with or against the flow Types of active transport: Coupled– ex. symports or antiports ...
Enzyme Catalysis
... produce glycogen, a storage form of glucose. • End result – high blood [glucose] leads to glycogen synthesis ...
... produce glycogen, a storage form of glucose. • End result – high blood [glucose] leads to glycogen synthesis ...
03 Endocrine and Cell Communication Hormonal Communication PPT
... c. Signals released by one cell type can travel long distances to target cells of another cell types. 1. Endocrine signals are produced by endocrine cells that release signaling molecules, which are specific and can travel long distances through the blood to reach all parts of the body. ...
... c. Signals released by one cell type can travel long distances to target cells of another cell types. 1. Endocrine signals are produced by endocrine cells that release signaling molecules, which are specific and can travel long distances through the blood to reach all parts of the body. ...
lecture-2-hhd - WordPress.com
... The amino-terminus: In most cases, this region is involved in activating or stimulating transcription by interacting with other components of the transcriptional machinery. The sequence is highly variable among different receptors. DNA binding domain: Amino acids in this region are responsible for b ...
... The amino-terminus: In most cases, this region is involved in activating or stimulating transcription by interacting with other components of the transcriptional machinery. The sequence is highly variable among different receptors. DNA binding domain: Amino acids in this region are responsible for b ...
Endo part 3
... c. Signals released by one cell type can travel long distances to target cells of another cell types. 1. Endocrine signals are produced by endocrine cells that release signaling molecules, which are specific and can travel long distances through the blood to reach all parts of the body. ...
... c. Signals released by one cell type can travel long distances to target cells of another cell types. 1. Endocrine signals are produced by endocrine cells that release signaling molecules, which are specific and can travel long distances through the blood to reach all parts of the body. ...
G protein–coupled receptor

G protein–coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptor, and G protein–linked receptors (GPLR), constitute a large protein family of receptors that sense molecules outside the cell and activate inside signal transduction pathways and, ultimately, cellular responses. Coupling with G proteins, they are called seven-transmembrane receptors because they pass through the cell membrane seven times.G protein–coupled receptors are found only in eukaryotes, including yeast, choanoflagellates, and animals. The ligands that bind and activate these receptors include light-sensitive compounds, odors, pheromones, hormones, and neurotransmitters, and vary in size from small molecules to peptides to large proteins. G protein–coupled receptors are involved in many diseases, and are also the target of approximately 40% of all modern medicinal drugs. Two of the United States's top five selling drugs (Hydrocodone and Lisinopril) act by targeting a G protein–coupled receptor. The 2012 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Brian Kobilka and Robert Lefkowitz for their work that was ""crucial for understanding how G protein–coupled receptors function."". There have been at least seven other Nobel Prizes awarded for some aspect of G protein–mediated signaling.There are two principal signal transduction pathways involving the G protein–coupled receptors: the cAMP signal pathway and the phosphatidylinositol signal pathway. When a ligand binds to the GPCR it causes a conformational change in the GPCR, which allows it to act as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF). The GPCR can then activate an associated G protein by exchanging its bound GDP for a GTP. The G protein's α subunit, together with the bound GTP, can then dissociate from the β and γ subunits to further affect intracellular signaling proteins or target functional proteins directly depending on the α subunit type (Gαs, Gαi/o, Gαq/11, Gα12/13).