Test questions used for assessment
... a. is a complex protein network running through the cytosol b. functions in support, organization and movement of the cell c. is made up of microtubules, microfilaments, intermediate filaments and the microtrabecular lattice d. all of the above e. a and c 6. Which of the following are true? a. micro ...
... a. is a complex protein network running through the cytosol b. functions in support, organization and movement of the cell c. is made up of microtubules, microfilaments, intermediate filaments and the microtrabecular lattice d. all of the above e. a and c 6. Which of the following are true? a. micro ...
Chapter 7 Cell to Cell Interactions
... molecule that is made by the host as one of a multitude of responses to an outside signal molecule. It is called a ...
... molecule that is made by the host as one of a multitude of responses to an outside signal molecule. It is called a ...
ABSTRACT Mast cells are critical component of the immune system
... Mast cells are critical component of the immune system. In pathological situations, they are activated and are responsible for allergic reaction. Therefore, detail understanding of mast cell activation at molecular level is important for design of new therapies of allergic diseases. Principal transm ...
... Mast cells are critical component of the immune system. In pathological situations, they are activated and are responsible for allergic reaction. Therefore, detail understanding of mast cell activation at molecular level is important for design of new therapies of allergic diseases. Principal transm ...
Role of cystinosin in vesicular trafficking and membrane fusion
... structures and a diminution of the usual pattern of small discrete intracytoplasmic vesicles characteristic of lysosomes. The number of these structures was drastically decreased when cystinosin C-terminal tail, its 5th inter-TM loop, or both motifs were altered. The enlarged lysosomes are reminisce ...
... structures and a diminution of the usual pattern of small discrete intracytoplasmic vesicles characteristic of lysosomes. The number of these structures was drastically decreased when cystinosin C-terminal tail, its 5th inter-TM loop, or both motifs were altered. The enlarged lysosomes are reminisce ...
Mechanisms of Hormone Action: Steroid Receptors
... steroid receptors can exist in the cytoplasm, while occupied receptors act in the nucleus on target DNA. When bound to hormone, cytoplasmic receptors move into the nucleus. ...
... steroid receptors can exist in the cytoplasm, while occupied receptors act in the nucleus on target DNA. When bound to hormone, cytoplasmic receptors move into the nucleus. ...
STUDY PROBLEMS AND CALCULATIONS: UV/VIS
... Protein A: pI=6.5, Mw=20,000 Da; Protein B: pI=7.8, Mw=20,000 Da; Protein C: pI=6.5, Mw=83,000 Da 8. The following mixture of amino acids was separated by ion-exchange chromatography: Asp (pI=2.77), Cys (pI=4.60), and Phe (pI=5.48). The column was equilibrated with the buffer of pH=2 and eluted with ...
... Protein A: pI=6.5, Mw=20,000 Da; Protein B: pI=7.8, Mw=20,000 Da; Protein C: pI=6.5, Mw=83,000 Da 8. The following mixture of amino acids was separated by ion-exchange chromatography: Asp (pI=2.77), Cys (pI=4.60), and Phe (pI=5.48). The column was equilibrated with the buffer of pH=2 and eluted with ...
lec 010v2 cell communication
... a. Step 2 is transduction: converting the signal to a form that can bring about a specific cellular response. This can occur in a single step or in a sequence of steps called a signal transduction pathway. ...
... a. Step 2 is transduction: converting the signal to a form that can bring about a specific cellular response. This can occur in a single step or in a sequence of steps called a signal transduction pathway. ...
Vol. 147, No. 3, 1987 September 30, 1987 BIOCHEMICAL AND
... Ca~-/calmodulin dependent protein kinase exhibits, as side activity, PI kinase activity ; the specific lipid kinase activity a~sociated with the phosphorylase kinase preparations is about I nmol min-" mg-" [20,21S. In the experiments presented in this paper phosphorylase kinase has been used as exog ...
... Ca~-/calmodulin dependent protein kinase exhibits, as side activity, PI kinase activity ; the specific lipid kinase activity a~sociated with the phosphorylase kinase preparations is about I nmol min-" mg-" [20,21S. In the experiments presented in this paper phosphorylase kinase has been used as exog ...
Topic 21 - FSU Biology
... 2. peptide or protein hormones are lipid-insoluble; they cannot pass through the cell membrane; they interact with membrane-bound receptors. How can a few hormone molecules produce a large biological effect; the hormone signal is amplified by signal transduction pathways (fig. 11.5). G- proteins are ...
... 2. peptide or protein hormones are lipid-insoluble; they cannot pass through the cell membrane; they interact with membrane-bound receptors. How can a few hormone molecules produce a large biological effect; the hormone signal is amplified by signal transduction pathways (fig. 11.5). G- proteins are ...
Health Science 1110-2007 Module 3 Organic Chemistry Lab 3
... Carbs Question 1. The chemical compound that contains sugar and stores hereditary information is DNA, which we will study further in the next unit. Carbs Question 3. Admittedly, the wording on this question is a little “off”, but, what is the least "intrusive" change you can do to a sugar and still ...
... Carbs Question 1. The chemical compound that contains sugar and stores hereditary information is DNA, which we will study further in the next unit. Carbs Question 3. Admittedly, the wording on this question is a little “off”, but, what is the least "intrusive" change you can do to a sugar and still ...
New study illuminates ability of hot
... genetic information contained in the cell's DNA. This information is transferred via molecules known as messenger RNA, in a process called translation. The team was able to identify the exact part of the messenger RNA helix that the RbfA protein acts on during protein construction - it acts to ensur ...
... genetic information contained in the cell's DNA. This information is transferred via molecules known as messenger RNA, in a process called translation. The team was able to identify the exact part of the messenger RNA helix that the RbfA protein acts on during protein construction - it acts to ensur ...
Electrical Signaling-2
... the activity of adenylyl cyclase – 2 adenosine receptors inhibit adenylyl cyclase activity – 2 adenosine receptors increase adenylyl cyclase activity ...
... the activity of adenylyl cyclase – 2 adenosine receptors inhibit adenylyl cyclase activity – 2 adenosine receptors increase adenylyl cyclase activity ...
Unit 3. Basic of Biopolymers (3) Control of Protein Function
... compartment where it is needed, or when bound in a complex with other macromolecules that participate in its function. Localization Specification ...
... compartment where it is needed, or when bound in a complex with other macromolecules that participate in its function. Localization Specification ...
CHAPTER 5 THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF LARGE
... 16. Explain how a peptide bond forms between two amino acids. 17. Name the two ends of a protein and explain the reason for their names. 18. List and describe the four major components of an amino acid. Explain how amino acids may be grouped according to the physical and chemical properties of the R ...
... 16. Explain how a peptide bond forms between two amino acids. 17. Name the two ends of a protein and explain the reason for their names. 18. List and describe the four major components of an amino acid. Explain how amino acids may be grouped according to the physical and chemical properties of the R ...
Give a brief account of drug protein binding and outline its
... 1995b(13): Give a brief account of drug protein binding and outline its significance General: Drug protein binding refers to the interaction a drug has with proteins. - Can be intravascular, interstitial, or intracellular proteins o Plasma proteins binding is most significant - Interaction is usuall ...
... 1995b(13): Give a brief account of drug protein binding and outline its significance General: Drug protein binding refers to the interaction a drug has with proteins. - Can be intravascular, interstitial, or intracellular proteins o Plasma proteins binding is most significant - Interaction is usuall ...
lab.2 Precipitation of Proteins at isoelectric Point
... • There are many factors that contribute to protein solubility. • The most important determinant its electrostatic charge. • The solubility of proteins in aqueous buffers depends on the distribution of hydrophilic and hydrophobic amino acid residues on the protein’s surface. Proteins that have high ...
... • There are many factors that contribute to protein solubility. • The most important determinant its electrostatic charge. • The solubility of proteins in aqueous buffers depends on the distribution of hydrophilic and hydrophobic amino acid residues on the protein’s surface. Proteins that have high ...
Lecture 5
... So these immunoglobulins will ‘stick’ to the antigens against which they are raised in our fixed cells. But how do we see ...
... So these immunoglobulins will ‘stick’ to the antigens against which they are raised in our fixed cells. But how do we see ...
P N RANGARAJAN lecture 21
... -Hormone binding domains (HBD / LBD) in carboxyl terminus -DNA-binding domain (DBD) 5’ to ligand binding domain -A nonconserved hypervariable region, which may contribute to transcriptional activity of receptor ...
... -Hormone binding domains (HBD / LBD) in carboxyl terminus -DNA-binding domain (DBD) 5’ to ligand binding domain -A nonconserved hypervariable region, which may contribute to transcriptional activity of receptor ...
Lecture 3: Protein trafficking between cell compartments The cytosol
... 2. Conformational changes of SNAREs bring the membranes closer together….. ...
... 2. Conformational changes of SNAREs bring the membranes closer together….. ...
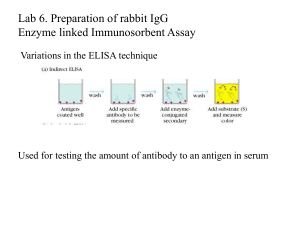
Enzyme-linked secondary antibodies
... The elution from the gel -use the lowest percentage of acrylamide that will allow resolution -high molecular weight proteins blot poorly Efficiency of binding to the membrane - nitrocellulose (not covalently bound) - Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) - Activated nylon ...
... The elution from the gel -use the lowest percentage of acrylamide that will allow resolution -high molecular weight proteins blot poorly Efficiency of binding to the membrane - nitrocellulose (not covalently bound) - Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) - Activated nylon ...
Protein Synthesis in a Eukaryotic Cell.
... Function of Structural Proteins For an HIV particle to recognize, attach, and infect a T-helper cell, the gp210 structure must be a precise shape and must exactly match its human cell membrane receptors ...
... Function of Structural Proteins For an HIV particle to recognize, attach, and infect a T-helper cell, the gp210 structure must be a precise shape and must exactly match its human cell membrane receptors ...
Glucose/Galactose Binding Protein (GGBP)
... differentiation, chromosomal segregation, and circadian rhythm. In humans, CK1s have been linked to neurodegenerative diseases and cancer. We are investigating regulation of CK1 activity by phosphorylation, using yeast CK1 protein kinases as models. We have previously identified phosphorylation site ...
... differentiation, chromosomal segregation, and circadian rhythm. In humans, CK1s have been linked to neurodegenerative diseases and cancer. We are investigating regulation of CK1 activity by phosphorylation, using yeast CK1 protein kinases as models. We have previously identified phosphorylation site ...
G protein–coupled receptor

G protein–coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptor, and G protein–linked receptors (GPLR), constitute a large protein family of receptors that sense molecules outside the cell and activate inside signal transduction pathways and, ultimately, cellular responses. Coupling with G proteins, they are called seven-transmembrane receptors because they pass through the cell membrane seven times.G protein–coupled receptors are found only in eukaryotes, including yeast, choanoflagellates, and animals. The ligands that bind and activate these receptors include light-sensitive compounds, odors, pheromones, hormones, and neurotransmitters, and vary in size from small molecules to peptides to large proteins. G protein–coupled receptors are involved in many diseases, and are also the target of approximately 40% of all modern medicinal drugs. Two of the United States's top five selling drugs (Hydrocodone and Lisinopril) act by targeting a G protein–coupled receptor. The 2012 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Brian Kobilka and Robert Lefkowitz for their work that was ""crucial for understanding how G protein–coupled receptors function."". There have been at least seven other Nobel Prizes awarded for some aspect of G protein–mediated signaling.There are two principal signal transduction pathways involving the G protein–coupled receptors: the cAMP signal pathway and the phosphatidylinositol signal pathway. When a ligand binds to the GPCR it causes a conformational change in the GPCR, which allows it to act as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF). The GPCR can then activate an associated G protein by exchanging its bound GDP for a GTP. The G protein's α subunit, together with the bound GTP, can then dissociate from the β and γ subunits to further affect intracellular signaling proteins or target functional proteins directly depending on the α subunit type (Gαs, Gαi/o, Gαq/11, Gα12/13).