Supplementary Information (docx 4776K)
... Mn(III) was also monitored during Mn(II) oxidation by the co-culture of strain Arthrobacter and strain Sphingopyxis. Ligand-binding complex P2O74- (PP) was selected to complex Mn(III) by forming stable Mn(III)-PP complex, which has max absorbance at 258 nm (ε = 6,750 M-1). The co-culture was first c ...
... Mn(III) was also monitored during Mn(II) oxidation by the co-culture of strain Arthrobacter and strain Sphingopyxis. Ligand-binding complex P2O74- (PP) was selected to complex Mn(III) by forming stable Mn(III)-PP complex, which has max absorbance at 258 nm (ε = 6,750 M-1). The co-culture was first c ...
Structure, function and mechanism of G
... • Alfred Wittinghofer Vetter and Wittinghofer „The Guanine nucleotide binding switch in three dimensions.“ Science (2001) Bos, Rehmann, Wittinghofer „GEFs and GAPs critical elements in the control of G-Proteins.“ Cell (2007) A. Wittinghofer, H. Waldmann. „Ras - A molecular switch involved in tumor ...
... • Alfred Wittinghofer Vetter and Wittinghofer „The Guanine nucleotide binding switch in three dimensions.“ Science (2001) Bos, Rehmann, Wittinghofer „GEFs and GAPs critical elements in the control of G-Proteins.“ Cell (2007) A. Wittinghofer, H. Waldmann. „Ras - A molecular switch involved in tumor ...
CH - TeacherWeb
... Each channel is specific to an ion and the direction they move is determined by either their concentration or voltage across the membrane. Facilitated Diffusion – has substances going from an area of High concentration to an area of Low concentration, but requires a CARRIER. These carriers are spec ...
... Each channel is specific to an ion and the direction they move is determined by either their concentration or voltage across the membrane. Facilitated Diffusion – has substances going from an area of High concentration to an area of Low concentration, but requires a CARRIER. These carriers are spec ...
proteome
... Needed- Software that will describe a o 1 sequence that will generate a o particular 3 sequence. ...
... Needed- Software that will describe a o 1 sequence that will generate a o particular 3 sequence. ...
Protein Sequence WKS - Kenton County Schools
... ☺ To take a DNA sequence and make a specific amino acid sequence through the processes of transcription and translation ☺ Use the amino acid sequence to identify the protein that it codes for. Materials: ☺ DNA sequence ☺ mRNA cards ☺ amino acid cards ☺ amino acid wheel ☺ ribosome unit ☺ fasteners Pr ...
... ☺ To take a DNA sequence and make a specific amino acid sequence through the processes of transcription and translation ☺ Use the amino acid sequence to identify the protein that it codes for. Materials: ☺ DNA sequence ☺ mRNA cards ☺ amino acid cards ☺ amino acid wheel ☺ ribosome unit ☺ fasteners Pr ...
Protein Physics
... backbone amino and carbonyl groups and those in the next turn of the helix • The R-groups protrude out from the helix • Proline tends to interrupt an alpha-helix ...
... backbone amino and carbonyl groups and those in the next turn of the helix • The R-groups protrude out from the helix • Proline tends to interrupt an alpha-helix ...
Lecture (12)
... Although free energies for receptor-ligand binding reactions are generally determined experimentally (through KD), it is possible to computationally estimate the changes in free energy that accompany point mutations in one of the amino acids in the ligand. This approach can be used to design a new a ...
... Although free energies for receptor-ligand binding reactions are generally determined experimentally (through KD), it is possible to computationally estimate the changes in free energy that accompany point mutations in one of the amino acids in the ligand. This approach can be used to design a new a ...
Insulin-like Growth Factor-I (IGF-I) (Human) Cat. No. HEGFP
... The Insulin-like Growth factors (IGFs) are mitogenic polypeptide growth factors that stimulate the proliferation and survival of various cell types including muscle, bone, and cartilage tissue in vitro. The liver predominantly produces iGFs, although a variety of tissues produce the IGFs at distinct ...
... The Insulin-like Growth factors (IGFs) are mitogenic polypeptide growth factors that stimulate the proliferation and survival of various cell types including muscle, bone, and cartilage tissue in vitro. The liver predominantly produces iGFs, although a variety of tissues produce the IGFs at distinct ...
Prokaryotic Cells, Eukaryotic cells and HIV: Structures, Transcription
... and 10 disulfide bonds are formed. Without these changes the protein does not function properly and can aggregate. The Golgi apparatus Vesicles from the ER are targeted to the Golgi by proteins that coat the vesicles. Exactly which proteins when is not key, but here is an image showing that process. ...
... and 10 disulfide bonds are formed. Without these changes the protein does not function properly and can aggregate. The Golgi apparatus Vesicles from the ER are targeted to the Golgi by proteins that coat the vesicles. Exactly which proteins when is not key, but here is an image showing that process. ...
A new blueprint for plant pathogen resistance
... should consider whether it may be premature to declare the problem completely solved. Sheen and colleagues have seen pathogen resistance only in leaves upon transient overexpression of the active MAPKKK, MAPKKs and WRKY genes. A previous report showed that overexpression of active MAPKK in tobacco l ...
... should consider whether it may be premature to declare the problem completely solved. Sheen and colleagues have seen pathogen resistance only in leaves upon transient overexpression of the active MAPKKK, MAPKKs and WRKY genes. A previous report showed that overexpression of active MAPKK in tobacco l ...
What Triggers Inflammation?
... Direct injury on Activation of inflammatory cascades Subcellular signal activation DNA or proteins ...
... Direct injury on Activation of inflammatory cascades Subcellular signal activation DNA or proteins ...
Chapter 1
... Amino Acids only 20 types of amino acids are used for protein synthesis in biological systems. ...
... Amino Acids only 20 types of amino acids are used for protein synthesis in biological systems. ...
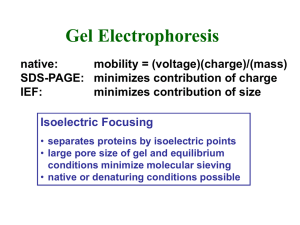
lab2 precipitation of casein at isoelectric point
... • There are many factors that contribute to protein solubility. • The most important determinant its electrostatic charge. • The solubility of proteins in aqueous buffers depends on the distribution of hydrophilic and hydrophobic amino acid residues on the protein’s surface. Proteins that have high ...
... • There are many factors that contribute to protein solubility. • The most important determinant its electrostatic charge. • The solubility of proteins in aqueous buffers depends on the distribution of hydrophilic and hydrophobic amino acid residues on the protein’s surface. Proteins that have high ...
1.4+ billion cows X 200 liters of methane per day = > 7 million tons of
... Why are proteins not completely flexible? Why are proteins not completely stiff? ...
... Why are proteins not completely flexible? Why are proteins not completely stiff? ...
Integral proteins
... or isoprenoid lipid anchors into raft domains. • Integral proteins may concentrate in raft domains via interactions with raft lipids or with other raft proteins. • Some raft domains contain derivatives of phosphatidylinositol that bind signal proteins with pleckstrin homology domains. Integral prote ...
... or isoprenoid lipid anchors into raft domains. • Integral proteins may concentrate in raft domains via interactions with raft lipids or with other raft proteins. • Some raft domains contain derivatives of phosphatidylinositol that bind signal proteins with pleckstrin homology domains. Integral prote ...
No Slide Title
... • filmless autoradiography • screens contain 'storage-phosphors' • traps the energy of radioactive emissions • sensitive to both b-particles and g-rays • efficiency ~100% for particle striking screen ...
... • filmless autoradiography • screens contain 'storage-phosphors' • traps the energy of radioactive emissions • sensitive to both b-particles and g-rays • efficiency ~100% for particle striking screen ...
Types of Receptors
... peripheral nervous system. The classification of receptors into types can be based on three different criteria: structure of the receptors, location of the receptors relative to the stimuli they sense, and by the types of stimuli to which they respond. Regardless of type, the function of these recep ...
... peripheral nervous system. The classification of receptors into types can be based on three different criteria: structure of the receptors, location of the receptors relative to the stimuli they sense, and by the types of stimuli to which they respond. Regardless of type, the function of these recep ...
PROTEIN APPLICATIONS IN BIOTECHNOLOGY
... BIO 251 – PROTEIN APPLICATIONS IN BIOTECHNOLOGY (4 CR.) Course Description Prepares students to understand protein structure and function and teaches the laboratory skills needed to successfully work with proteins. Focuses on levels of protein structure and protein function. Includes common laborato ...
... BIO 251 – PROTEIN APPLICATIONS IN BIOTECHNOLOGY (4 CR.) Course Description Prepares students to understand protein structure and function and teaches the laboratory skills needed to successfully work with proteins. Focuses on levels of protein structure and protein function. Includes common laborato ...
PowerPoint-presentatie
... Assessment of the pipeline's performance Coverage: up to 42%, 22% and 42%, respectively for the human, yeast and Arabidopsis subsets. ...
... Assessment of the pipeline's performance Coverage: up to 42%, 22% and 42%, respectively for the human, yeast and Arabidopsis subsets. ...
Document
... Hydrolysis of GTP provides energy to drive some reactions. mRNA, rRNA, and tRNA are involved. ...
... Hydrolysis of GTP provides energy to drive some reactions. mRNA, rRNA, and tRNA are involved. ...
receptors and ion channels - The Company of Biologists
... Throughout this symposium a unifying idea is the interactions of receptors and ion channels and the modifiability of this connection. In recent years our knowledge of the different types of second messengers turned on by receptor activation and of their effects on the conductances of ion channels ha ...
... Throughout this symposium a unifying idea is the interactions of receptors and ion channels and the modifiability of this connection. In recent years our knowledge of the different types of second messengers turned on by receptor activation and of their effects on the conductances of ion channels ha ...
GABRA1 (gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor. alpha 1
... seizures (several per day) and bilateral, synchronous, symmetric 3-Hz spike waves on EEG. During adolescence, tonic-clonic and myoclonic seizures develop. Absence seizures may either remit or persist into adulthood. Similarity: Belongs to the ligand-gated ionic channel (TC 1.A.9) family [view classi ...
... seizures (several per day) and bilateral, synchronous, symmetric 3-Hz spike waves on EEG. During adolescence, tonic-clonic and myoclonic seizures develop. Absence seizures may either remit or persist into adulthood. Similarity: Belongs to the ligand-gated ionic channel (TC 1.A.9) family [view classi ...
Transport Unit Study Guide
... transport, endocytosis, and exocytosis and give examples Be able to predict the effect of a hypotonic, isotonic or hypertonic solution on a cell Be able to discuss how the plasma membrane helps a cell maintain homeostasis Dialysis tubing lab/demonstration – be able to explain which molecules diffuse ...
... transport, endocytosis, and exocytosis and give examples Be able to predict the effect of a hypotonic, isotonic or hypertonic solution on a cell Be able to discuss how the plasma membrane helps a cell maintain homeostasis Dialysis tubing lab/demonstration – be able to explain which molecules diffuse ...
G protein–coupled receptor

G protein–coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptor, and G protein–linked receptors (GPLR), constitute a large protein family of receptors that sense molecules outside the cell and activate inside signal transduction pathways and, ultimately, cellular responses. Coupling with G proteins, they are called seven-transmembrane receptors because they pass through the cell membrane seven times.G protein–coupled receptors are found only in eukaryotes, including yeast, choanoflagellates, and animals. The ligands that bind and activate these receptors include light-sensitive compounds, odors, pheromones, hormones, and neurotransmitters, and vary in size from small molecules to peptides to large proteins. G protein–coupled receptors are involved in many diseases, and are also the target of approximately 40% of all modern medicinal drugs. Two of the United States's top five selling drugs (Hydrocodone and Lisinopril) act by targeting a G protein–coupled receptor. The 2012 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Brian Kobilka and Robert Lefkowitz for their work that was ""crucial for understanding how G protein–coupled receptors function."". There have been at least seven other Nobel Prizes awarded for some aspect of G protein–mediated signaling.There are two principal signal transduction pathways involving the G protein–coupled receptors: the cAMP signal pathway and the phosphatidylinositol signal pathway. When a ligand binds to the GPCR it causes a conformational change in the GPCR, which allows it to act as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF). The GPCR can then activate an associated G protein by exchanging its bound GDP for a GTP. The G protein's α subunit, together with the bound GTP, can then dissociate from the β and γ subunits to further affect intracellular signaling proteins or target functional proteins directly depending on the α subunit type (Gαs, Gαi/o, Gαq/11, Gα12/13).