Unit 03 Macromolecule Review
... choice of giving them butter, a piece of candy, a protein drink, water, or some cooked rice. Which would be the best thing to give them? Which would be the least effective? and why? 11. Besides storing extra energy, why are lipids so important for living things? 12. Why is the difference between a s ...
... choice of giving them butter, a piece of candy, a protein drink, water, or some cooked rice. Which would be the best thing to give them? Which would be the least effective? and why? 11. Besides storing extra energy, why are lipids so important for living things? 12. Why is the difference between a s ...
Isolation of proteins
... particularly basic and aromatic amino acids residues (hydrophilic arginine (ARG) and the hydrophobic phenylalanine (PHE), tryptophan (TRY), and proline (PRO) (aromatic amino acid residues). As the Coomassie preferentially binds to select amino acids and changes from a cationic (+) state to an anioni ...
... particularly basic and aromatic amino acids residues (hydrophilic arginine (ARG) and the hydrophobic phenylalanine (PHE), tryptophan (TRY), and proline (PRO) (aromatic amino acid residues). As the Coomassie preferentially binds to select amino acids and changes from a cationic (+) state to an anioni ...
Essential Biochemistry. 3rd Edition Brochure
... If you have a Marketing Code please enter it below: Marketing Code: Please note that by ordering from Research and Markets you are agreeing to our Terms and Conditions at ...
... If you have a Marketing Code please enter it below: Marketing Code: Please note that by ordering from Research and Markets you are agreeing to our Terms and Conditions at ...
ans - Gogarten Lab
... C. An exact function does not need to be hit upon, because natural selection can take a protein with limited function and make it better. D. Similar structures have similar function, so there are entire regions of protein space occupied by homologs that all function equally well, or nearly so. E ...
... C. An exact function does not need to be hit upon, because natural selection can take a protein with limited function and make it better. D. Similar structures have similar function, so there are entire regions of protein space occupied by homologs that all function equally well, or nearly so. E ...
Slide ()
... PTH effects on bone. PTH binds to osteoblast parathyroid hormone receptor 1 (PTHR1), stimulating the cell surface expression of RANKL, which binds to RANK, a cell surface protein on osteoclast precursors. Binding of RANKL to RANK activates osteoclast gene transcription and the differentiation into a ...
... PTH effects on bone. PTH binds to osteoblast parathyroid hormone receptor 1 (PTHR1), stimulating the cell surface expression of RANKL, which binds to RANK, a cell surface protein on osteoclast precursors. Binding of RANKL to RANK activates osteoclast gene transcription and the differentiation into a ...
File
... Fibrous protein (found in skin, tendons, bones, and muscles) does not dissolve in water (hydrophobic). Globular protein (found in enzymes, some hormones, and hemoglobin) can dissolve in water (hydrophilic). ...
... Fibrous protein (found in skin, tendons, bones, and muscles) does not dissolve in water (hydrophobic). Globular protein (found in enzymes, some hormones, and hemoglobin) can dissolve in water (hydrophilic). ...
Small GTPases
... RanGAP is in the cytoplasm RanGTP is converted here to RanGDP RanGEF is in the nucleus RanGDP is converted here to RanGTP transport from the cytoplasm to the nucleus: RanGTP in the nucleus binds the import complexes and releases the cargo transport from the nucleus to the cytoplasm: RanG ...
... RanGAP is in the cytoplasm RanGTP is converted here to RanGDP RanGEF is in the nucleus RanGDP is converted here to RanGTP transport from the cytoplasm to the nucleus: RanGTP in the nucleus binds the import complexes and releases the cargo transport from the nucleus to the cytoplasm: RanG ...
Ubiquitin-proteosome protein degradation ppt
... First, Ubiquitin is activated by forming a link to “enzyme 1” (E1). Then, ubiquitin is transferred to one of several types of “enzyme 2” (E2). Then, “enzyme 3” (E3) catalizes the transfer of ubiquitin from E2 to a Lys e-amino group of the “condemned” ...
... First, Ubiquitin is activated by forming a link to “enzyme 1” (E1). Then, ubiquitin is transferred to one of several types of “enzyme 2” (E2). Then, “enzyme 3” (E3) catalizes the transfer of ubiquitin from E2 to a Lys e-amino group of the “condemned” ...
Modification of Amino Acids
... Signal Sequences Target Proteins for Secretion Signal sequence at the amino-terminal end of membrane proteins or secretory proteins are recognized by factors and receptors that mediate transmembrane transport. Signal sequence is cleaved by signal peptidase. ...
... Signal Sequences Target Proteins for Secretion Signal sequence at the amino-terminal end of membrane proteins or secretory proteins are recognized by factors and receptors that mediate transmembrane transport. Signal sequence is cleaved by signal peptidase. ...
Predicting protein 3D structure from evolutionary sequence variation
... these inferred couplings is an excellent predictor of residue-residue proximity in folded structures. Indeed, the top-scoring residue couplings are sufficiently accurate and well-distributed to define the 3D protein fold with remarkable accuracy. We quantify this observation by computing, from seque ...
... these inferred couplings is an excellent predictor of residue-residue proximity in folded structures. Indeed, the top-scoring residue couplings are sufficiently accurate and well-distributed to define the 3D protein fold with remarkable accuracy. We quantify this observation by computing, from seque ...
With Light
... Excitation of the muscle spindle leads to muscle contraction through a reflex arc. Identify role that passive ionic currents play in this process. • Spindle is a sensory organ – stretch will cause local currents to flow and a depolarizing receptor potential to be generated. If large enough this wil ...
... Excitation of the muscle spindle leads to muscle contraction through a reflex arc. Identify role that passive ionic currents play in this process. • Spindle is a sensory organ – stretch will cause local currents to flow and a depolarizing receptor potential to be generated. If large enough this wil ...
Baker - International School of Crystallography
... ~60% of gene products have an inferred function (mostly by homology) ~25% are “conserved hypotheticals” ~15% are “unknowns” ~30% can be related to proteins of known 3D structure - but only ~25 TB protein structures Many metabolic pathways appear incomplete ...
... ~60% of gene products have an inferred function (mostly by homology) ~25% are “conserved hypotheticals” ~15% are “unknowns” ~30% can be related to proteins of known 3D structure - but only ~25 TB protein structures Many metabolic pathways appear incomplete ...
Uniform Isotope Labeling of Eukaryotic Proteins in Methylotrophic
... on hydrated LR proteoliposomes using 600 MHz and 800 MHz Bruker instruments, confirmed high structural homogeneity and purity of the sample, along with very low extent of glycosylation. Two-dimensional 13C-13C SPC-5326 and NCOCX correlation spectra (Figures 1 and 2) show many well-resolved resonance ...
... on hydrated LR proteoliposomes using 600 MHz and 800 MHz Bruker instruments, confirmed high structural homogeneity and purity of the sample, along with very low extent of glycosylation. Two-dimensional 13C-13C SPC-5326 and NCOCX correlation spectra (Figures 1 and 2) show many well-resolved resonance ...
general western blot troubleshooting tips
... Filter the secondary with a 0.2 µm filter to remove any aggregates. ...
... Filter the secondary with a 0.2 µm filter to remove any aggregates. ...
Chemical Signals in Animals
... • Discuss the sequence of events in a variety of second messenger systems in signal transduction • Describe examples of hormone interaction in the integration of complex animal processes (e.g. water balance, and insect development) • Explain the role of neurosecretory cells in the hypothalamus in th ...
... • Discuss the sequence of events in a variety of second messenger systems in signal transduction • Describe examples of hormone interaction in the integration of complex animal processes (e.g. water balance, and insect development) • Explain the role of neurosecretory cells in the hypothalamus in th ...
Study Guide-Carbon, monomers, polymers, amino acids, proteins
... h. You can also review the videos on these seven topics i. Review The formation of carbon-carbon bonds was an important event in chemical evolution activity j. Review Monomer & polymer activity k. Review SIMPLE MOLECULES AND ENERGY LEAD TO MIDSIZED BUILDING BLOCKS THAT LINKED TO FORM PROTEINS AND OT ...
... h. You can also review the videos on these seven topics i. Review The formation of carbon-carbon bonds was an important event in chemical evolution activity j. Review Monomer & polymer activity k. Review SIMPLE MOLECULES AND ENERGY LEAD TO MIDSIZED BUILDING BLOCKS THAT LINKED TO FORM PROTEINS AND OT ...
11-Cell Communications_1
... Certain mutations in the genes that produce these cause them to always be "on." In other cases, the genes are amplified. ...
... Certain mutations in the genes that produce these cause them to always be "on." In other cases, the genes are amplified. ...
PY460: Physiological Psychology
... Independence of chemistry of smell light - change in wave length, smell, completely different particles space- receptor take up space, more types more room needed. ...
... Independence of chemistry of smell light - change in wave length, smell, completely different particles space- receptor take up space, more types more room needed. ...
How to classify proteins on basis of structure?
... How to predict 3D structure from 1D sequence? How to determine function from structure? How to classify proteins on basis of structure? How to recognize 3D motifs and patterns? How to use bioinformatics databases to help in 3D structure determination? • How to predict which proteins will express wel ...
... How to predict 3D structure from 1D sequence? How to determine function from structure? How to classify proteins on basis of structure? How to recognize 3D motifs and patterns? How to use bioinformatics databases to help in 3D structure determination? • How to predict which proteins will express wel ...
Cyclic AMP and Hormone Action
... that work through the action of 3’-5’-cyclic AMP (cAMP) control enzymes by using ATP to phosphorylate serine and threonine groups on target enzymes. These so-called protein kinases represent a sequel of catalytic steps designed to amplify the action of the hormone. The key word here is “catalytic”, ...
... that work through the action of 3’-5’-cyclic AMP (cAMP) control enzymes by using ATP to phosphorylate serine and threonine groups on target enzymes. These so-called protein kinases represent a sequel of catalytic steps designed to amplify the action of the hormone. The key word here is “catalytic”, ...
Long term memory
... In the dark, the membrane potential of a rod cell is -30mV; rod cells constantly secrete neurotransmitters. A brief pulse of light causes a transient hyperpolarization of the rod cell membrane and decreases neurotransmitter release. Light triggered closing of sodium channels hyperpolarizes rod cells ...
... In the dark, the membrane potential of a rod cell is -30mV; rod cells constantly secrete neurotransmitters. A brief pulse of light causes a transient hyperpolarization of the rod cell membrane and decreases neurotransmitter release. Light triggered closing of sodium channels hyperpolarizes rod cells ...
Structural Genomics - University of Houston
... protein. If each residue is considered to have just 3 possible conformations the total number of conformations of the protein is 3100. Conformational changes occur on a time scale of 10-13 seconds i.e. the time required to sample all possible conformations would be 3100 x 10-13 seconds which is abou ...
... protein. If each residue is considered to have just 3 possible conformations the total number of conformations of the protein is 3100. Conformational changes occur on a time scale of 10-13 seconds i.e. the time required to sample all possible conformations would be 3100 x 10-13 seconds which is abou ...
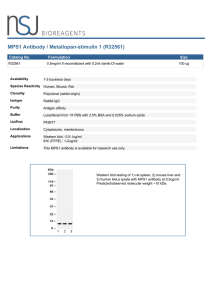
MPS1 Antibody / Metallopan-stimulin 1 (R32561)
... 40S ribosomal protein S27, also known as Metallopan-stimulin 1 or MPS-1, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RPS27 gene. Ribosomes, the organelles that catalyze protein synthesis, consist of a small 40S subunit and a large 60S subunit. Together these subunits are composed of 4 RNA species ...
... 40S ribosomal protein S27, also known as Metallopan-stimulin 1 or MPS-1, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RPS27 gene. Ribosomes, the organelles that catalyze protein synthesis, consist of a small 40S subunit and a large 60S subunit. Together these subunits are composed of 4 RNA species ...
G protein–coupled receptor

G protein–coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptor, and G protein–linked receptors (GPLR), constitute a large protein family of receptors that sense molecules outside the cell and activate inside signal transduction pathways and, ultimately, cellular responses. Coupling with G proteins, they are called seven-transmembrane receptors because they pass through the cell membrane seven times.G protein–coupled receptors are found only in eukaryotes, including yeast, choanoflagellates, and animals. The ligands that bind and activate these receptors include light-sensitive compounds, odors, pheromones, hormones, and neurotransmitters, and vary in size from small molecules to peptides to large proteins. G protein–coupled receptors are involved in many diseases, and are also the target of approximately 40% of all modern medicinal drugs. Two of the United States's top five selling drugs (Hydrocodone and Lisinopril) act by targeting a G protein–coupled receptor. The 2012 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Brian Kobilka and Robert Lefkowitz for their work that was ""crucial for understanding how G protein–coupled receptors function."". There have been at least seven other Nobel Prizes awarded for some aspect of G protein–mediated signaling.There are two principal signal transduction pathways involving the G protein–coupled receptors: the cAMP signal pathway and the phosphatidylinositol signal pathway. When a ligand binds to the GPCR it causes a conformational change in the GPCR, which allows it to act as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF). The GPCR can then activate an associated G protein by exchanging its bound GDP for a GTP. The G protein's α subunit, together with the bound GTP, can then dissociate from the β and γ subunits to further affect intracellular signaling proteins or target functional proteins directly depending on the α subunit type (Gαs, Gαi/o, Gαq/11, Gα12/13).