Fluorescent Probe Studies of Proteins
... acid (ANS): Catalytic assays of phosphorylase kinase A number of fluorescent probes exhibit fluorescence char- ...
... acid (ANS): Catalytic assays of phosphorylase kinase A number of fluorescent probes exhibit fluorescence char- ...
Basic Science for Clinicians
... However, the molecular signaling role of AMP is dramatically extended by activation of the AMPK pathway. Because many more proteins are regulated by AMPK than contain specialized AMP-binding sites, the ability of AMP to signal energy compromise is greatly enhanced. AMPK is a protein kinase that has ...
... However, the molecular signaling role of AMP is dramatically extended by activation of the AMPK pathway. Because many more proteins are regulated by AMPK than contain specialized AMP-binding sites, the ability of AMP to signal energy compromise is greatly enhanced. AMPK is a protein kinase that has ...
WW Domains Provide a Platform for the
... during 25 min with a total run time of 45 min. Data were analyzed in batch using the Mascot search engine (57), and proteins were considered “hits” if two independent peptides or a single peptide with a Mascot score of 50 or higher was found. Protein hits were converted to gene identifiers (GeneIDs) ...
... during 25 min with a total run time of 45 min. Data were analyzed in batch using the Mascot search engine (57), and proteins were considered “hits” if two independent peptides or a single peptide with a Mascot score of 50 or higher was found. Protein hits were converted to gene identifiers (GeneIDs) ...
Isoniazid Drug Resistance: Computational
... the mycobacterial envelope, is activated by MnCl2 and the catalase– peroxidase KatG, possibly into an isonicotinoyl radical or anion, which then forms adduct in the presence of NADH/NADPH which inhibits different enzymes of MTB besides InhA (2-trans-enoyl-acyl carrier protein reductase) of MTB, thus ...
... the mycobacterial envelope, is activated by MnCl2 and the catalase– peroxidase KatG, possibly into an isonicotinoyl radical or anion, which then forms adduct in the presence of NADH/NADPH which inhibits different enzymes of MTB besides InhA (2-trans-enoyl-acyl carrier protein reductase) of MTB, thus ...
HIS-Select Nickel Affinity Gel (P6611) - Technical - Sigma
... The HIS-Select Nickel Affinity Gel is stored in 30% ethanol. The ethanol must be removed just prior to use. Thoroughly resuspend the affinity gel with gentle inversion and remove an appropriate aliquot for use. Take only the amount of affinity gel that is necessary for the purification to be done. T ...
... The HIS-Select Nickel Affinity Gel is stored in 30% ethanol. The ethanol must be removed just prior to use. Thoroughly resuspend the affinity gel with gentle inversion and remove an appropriate aliquot for use. Take only the amount of affinity gel that is necessary for the purification to be done. T ...
A domain-specific usherin/collagen IV interaction may be required
... fibronectin type III repeats. These domains, of approximately 100 amino acids, are shared with at least 45 different families of molecules ranging from cytokine receptors to cell surface binding proteins. Different type III domains may be almost completely dissimilar at the amino acid level and as m ...
... fibronectin type III repeats. These domains, of approximately 100 amino acids, are shared with at least 45 different families of molecules ranging from cytokine receptors to cell surface binding proteins. Different type III domains may be almost completely dissimilar at the amino acid level and as m ...
LNBI 9043 - Lupin Allergy: Uncovering Structural Features and
... The two major lupin storage proteins are α-conglutin (legumin-like or 11S globulin), and ß-conglutin (vicilin-like or 7S globulin). Vilicin proteins are characterized by two cupin (barrel-shaped) domains constituted by α-helices. Another family with a cupin-like structure, γ-conglutin (basic 7S-glob ...
... The two major lupin storage proteins are α-conglutin (legumin-like or 11S globulin), and ß-conglutin (vicilin-like or 7S globulin). Vilicin proteins are characterized by two cupin (barrel-shaped) domains constituted by α-helices. Another family with a cupin-like structure, γ-conglutin (basic 7S-glob ...
Mechanical stimuli of skeletal muscle: implications on mTOR/p70s6k
... The mTOR is a key signaling pathway in the diVerentiation process and control of cell size (Schmelzle and Hall 2000) activated by nutritional, chemical and mechanical stimuli (Reiling and Sabatini 2006). Studies in yeast have demonstrated that the target of rapamycin (TOR) performs two essential fun ...
... The mTOR is a key signaling pathway in the diVerentiation process and control of cell size (Schmelzle and Hall 2000) activated by nutritional, chemical and mechanical stimuli (Reiling and Sabatini 2006). Studies in yeast have demonstrated that the target of rapamycin (TOR) performs two essential fun ...
The Arf and Rab11 effector FIP3 acts synergistically with ASAP1 to
... contains only a portion of the Arf5/6 binding site (Inoue et al., 2008). This indicates that the Arf4 binding site on FIP3 is within amino acids 666–756, closer to the Rab11 binding site. We sought to determine whether ASAP1, in addition to recruiting Rab11a (Wang et al., 2012), specifically recruit ...
... contains only a portion of the Arf5/6 binding site (Inoue et al., 2008). This indicates that the Arf4 binding site on FIP3 is within amino acids 666–756, closer to the Rab11 binding site. We sought to determine whether ASAP1, in addition to recruiting Rab11a (Wang et al., 2012), specifically recruit ...
Metal ion reconstitution studies of yeast copper
... Yeast apo CuZnSOD has no tryptophan residues, one tyrosine residue, and one disulfide bond per subunit, resulting in a calculated ε280 of 3230 M –1 cm –1/dimer. Bovine apo CuZnSOD has identical numbers of tryptophan, tyrosine, and cystine residues [7], and therefore it is expected to have the same e ...
... Yeast apo CuZnSOD has no tryptophan residues, one tyrosine residue, and one disulfide bond per subunit, resulting in a calculated ε280 of 3230 M –1 cm –1/dimer. Bovine apo CuZnSOD has identical numbers of tryptophan, tyrosine, and cystine residues [7], and therefore it is expected to have the same e ...
The world of proteases Diversity and function
... Proteolytic enzyme An enzyme that degrades protein by hydrolysis of peptide bonds ...
... Proteolytic enzyme An enzyme that degrades protein by hydrolysis of peptide bonds ...
Collagen XV: Exploring Its Structure and Role within the Tumor
... restin peptide) retained the function (14, 20). Specifically, the ability of COLXV to enhance adherence of D98 AP2 cells to a collagen I substrate and to suppress the growth of tumors arising from the same cells in nude mice was not dependent on the restin fragment (14). The C-terminal domain contain ...
... restin peptide) retained the function (14, 20). Specifically, the ability of COLXV to enhance adherence of D98 AP2 cells to a collagen I substrate and to suppress the growth of tumors arising from the same cells in nude mice was not dependent on the restin fragment (14). The C-terminal domain contain ...
Chapter 33 Slides
... Protein Translocation An essential process for membrane proteins and secretory proteins • Such proteins are synthesized with a "leader peptide", aka a "signal sequence" of about 1626 amino acids • The signal sequence has a basic N-terminus, a central domain of 7-13 hydrophobic residues, and a nonhel ...
... Protein Translocation An essential process for membrane proteins and secretory proteins • Such proteins are synthesized with a "leader peptide", aka a "signal sequence" of about 1626 amino acids • The signal sequence has a basic N-terminus, a central domain of 7-13 hydrophobic residues, and a nonhel ...
Cloning and sequencing of a gene encoding acidophilic amylase
... conditions (data not shown). Therefore, the 160 kDa form was apparently not a disulphide-linkeddimer of the 90 kDa form. The amount of protein in the 90 kDa and 160 kDa bands was approximately the same, yet the starch-degrading activity of the 160 kDa protein was much higher (Fig. 1). Thus, the 160 ...
... conditions (data not shown). Therefore, the 160 kDa form was apparently not a disulphide-linkeddimer of the 90 kDa form. The amount of protein in the 90 kDa and 160 kDa bands was approximately the same, yet the starch-degrading activity of the 160 kDa protein was much higher (Fig. 1). Thus, the 160 ...
sequence-structure relationship - HAL
... it reduces the protein 3D complexity into one-dimensional string of characters. Based on this description, the local structure descriptions was extended to longer fragments, using an unsupervised clustering method called "Hybrid Protein Model" (HPM, (de Brevern and Hazout, 2001; de Brevern and Hazou ...
... it reduces the protein 3D complexity into one-dimensional string of characters. Based on this description, the local structure descriptions was extended to longer fragments, using an unsupervised clustering method called "Hybrid Protein Model" (HPM, (de Brevern and Hazout, 2001; de Brevern and Hazou ...
Mutational Analysis of Synaptobrevin Transmembrane Domain
... of recombinant synaptobrevin used different detergents for the extraction from the E. coli cell pellet (16, 18). To see if this difference could explain the different estimates of the magnitude of dimerization, we directly compared the effect that detergent had on the oligomerization state of the pu ...
... of recombinant synaptobrevin used different detergents for the extraction from the E. coli cell pellet (16, 18). To see if this difference could explain the different estimates of the magnitude of dimerization, we directly compared the effect that detergent had on the oligomerization state of the pu ...
CHEMICAL SYNTHESIS OF PROTEINS : A TOOL FOR PROTEIN
... functional features of the proteins refers to the modification of their chemical structure. In this regard, the chemical synthesis of proteins appears a key tool, as it allows the unlimited modification of a polypeptide chain with any kind and number of labels. The last decade has seen the introduct ...
... functional features of the proteins refers to the modification of their chemical structure. In this regard, the chemical synthesis of proteins appears a key tool, as it allows the unlimited modification of a polypeptide chain with any kind and number of labels. The last decade has seen the introduct ...
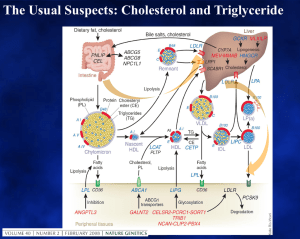
Masterclass 1
... • Most lipoproteins have TG and/or CE in their core • Hepatic Triglyceride rich lipoproteins are precursors of cholesterol-rich LDL • Cholesterol-ester transfer protein allows all triglyceride-rich lipoproteins to modify the composition of cholesterol-rich HDL and LDL. As a result, hypertriglycerida ...
... • Most lipoproteins have TG and/or CE in their core • Hepatic Triglyceride rich lipoproteins are precursors of cholesterol-rich LDL • Cholesterol-ester transfer protein allows all triglyceride-rich lipoproteins to modify the composition of cholesterol-rich HDL and LDL. As a result, hypertriglycerida ...
Multidrug resistance mediated by the ATP-binding
... Sequences were aligned along their entire length with MRP using CLUSTAL W(1.6) multiple sequence alignment. Sequence data were obtained using the following accession numbers: MRP, L05628/P33527; mrp, AF022908/1488428; MOAT, U49248/U63970; EBCR, 1430907/Z49144; C. elegans mrp1, U66260; C. elegans mrp ...
... Sequences were aligned along their entire length with MRP using CLUSTAL W(1.6) multiple sequence alignment. Sequence data were obtained using the following accession numbers: MRP, L05628/P33527; mrp, AF022908/1488428; MOAT, U49248/U63970; EBCR, 1430907/Z49144; C. elegans mrp1, U66260; C. elegans mrp ...
Some Structural and Kinetic Aspects of L
... N-terminal end of its subunit. Thus, the kinetic properties of types L and M1 are quite different: in the case of L-type affinity for substrate PEP is about 10 times less and affinity for inhibitor ATP is higher than these parameters of M1 type (Tanaka et al., 1967). The second substrate of PK react ...
... N-terminal end of its subunit. Thus, the kinetic properties of types L and M1 are quite different: in the case of L-type affinity for substrate PEP is about 10 times less and affinity for inhibitor ATP is higher than these parameters of M1 type (Tanaka et al., 1967). The second substrate of PK react ...
Tracing the Archaeal Origins of Eukaryotic Membrane
... evolved from a smaller set of primordial vesicle formation and fusion proteins that were present in early stages of eukaryogenesis. More recent phylogenetic studies have even yielded some insights into the proximal order of events immediately leading to the complexity seen in LECA (Elias et al. 2012 ...
... evolved from a smaller set of primordial vesicle formation and fusion proteins that were present in early stages of eukaryogenesis. More recent phylogenetic studies have even yielded some insights into the proximal order of events immediately leading to the complexity seen in LECA (Elias et al. 2012 ...
Microsoft Word
... for the apo form of human eIF4E by multidimensional NMR [47] and for the murine factor by hydrogendeuterium exchange combined with electrospray mass spectrometry [48]. The secondary elements were preserved in apo eIF4E while the loops exhibited mobility on the ns - ps time scale that became abrogat ...
... for the apo form of human eIF4E by multidimensional NMR [47] and for the murine factor by hydrogendeuterium exchange combined with electrospray mass spectrometry [48]. The secondary elements were preserved in apo eIF4E while the loops exhibited mobility on the ns - ps time scale that became abrogat ...
Solubility of recombinant Src homology 2 domains expressed in E
... by TANGO, we generated TFV → GYT and FV → YT mutants of the TSAd-90-188-PHRD and TSAd-90-188-PAAS constructs, and compared their expression to that of the ALX SH2 domain. These constructs were chosen, as they contained the shortest flanking sequences compared to the original TSAd 1-TD construct, and ...
... by TANGO, we generated TFV → GYT and FV → YT mutants of the TSAd-90-188-PHRD and TSAd-90-188-PAAS constructs, and compared their expression to that of the ALX SH2 domain. These constructs were chosen, as they contained the shortest flanking sequences compared to the original TSAd 1-TD construct, and ...
Supplementary Data - Institute of Cancer Research
... ΔLCE12 flies lacking the entire PGRP-LC locus, and ΔLCird7(1) flies with an insertion in exon 4 which consequently express only the rLC isoforms (Fig. 1c and Fig. 2c) 29, 30. Both mutants are unable to induce antibacterial peptide gene expression or survive Gram-negative infection (Fig. 2d, e), indi ...
... ΔLCE12 flies lacking the entire PGRP-LC locus, and ΔLCird7(1) flies with an insertion in exon 4 which consequently express only the rLC isoforms (Fig. 1c and Fig. 2c) 29, 30. Both mutants are unable to induce antibacterial peptide gene expression or survive Gram-negative infection (Fig. 2d, e), indi ...
Correlating ribosome function with high
... Translation of the genetic code into proteins is the second stage of protein biosynthesis. It is performed by a complex apparatus comprising ribosomes, mRNA, tRNAs and accessory protein factors. The ribosome (Box 1), a universal dynamic cellular ribonucleoprotein complex, is the key player in this p ...
... Translation of the genetic code into proteins is the second stage of protein biosynthesis. It is performed by a complex apparatus comprising ribosomes, mRNA, tRNAs and accessory protein factors. The ribosome (Box 1), a universal dynamic cellular ribonucleoprotein complex, is the key player in this p ...
G protein–coupled receptor

G protein–coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptor, and G protein–linked receptors (GPLR), constitute a large protein family of receptors that sense molecules outside the cell and activate inside signal transduction pathways and, ultimately, cellular responses. Coupling with G proteins, they are called seven-transmembrane receptors because they pass through the cell membrane seven times.G protein–coupled receptors are found only in eukaryotes, including yeast, choanoflagellates, and animals. The ligands that bind and activate these receptors include light-sensitive compounds, odors, pheromones, hormones, and neurotransmitters, and vary in size from small molecules to peptides to large proteins. G protein–coupled receptors are involved in many diseases, and are also the target of approximately 40% of all modern medicinal drugs. Two of the United States's top five selling drugs (Hydrocodone and Lisinopril) act by targeting a G protein–coupled receptor. The 2012 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Brian Kobilka and Robert Lefkowitz for their work that was ""crucial for understanding how G protein–coupled receptors function."". There have been at least seven other Nobel Prizes awarded for some aspect of G protein–mediated signaling.There are two principal signal transduction pathways involving the G protein–coupled receptors: the cAMP signal pathway and the phosphatidylinositol signal pathway. When a ligand binds to the GPCR it causes a conformational change in the GPCR, which allows it to act as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF). The GPCR can then activate an associated G protein by exchanging its bound GDP for a GTP. The G protein's α subunit, together with the bound GTP, can then dissociate from the β and γ subunits to further affect intracellular signaling proteins or target functional proteins directly depending on the α subunit type (Gαs, Gαi/o, Gαq/11, Gα12/13).