Function of BMPs and BMP Antagonists in Adult Bone
... Endogenous BMP expression appears during cell differentiation from mesenchymal cells to osteoblasts. After differentiation, cells express alkaline phosphatase and osteoblast markers, such as collagen type I, bone sialoprotein (BSP), osterix, and osteocalcin. In the late stage cells deposit minerals ...
... Endogenous BMP expression appears during cell differentiation from mesenchymal cells to osteoblasts. After differentiation, cells express alkaline phosphatase and osteoblast markers, such as collagen type I, bone sialoprotein (BSP), osterix, and osteocalcin. In the late stage cells deposit minerals ...
Sphingolipid homeostasis in the web of metabolic routes
... [33,34]. When SL levels drop, TORC2 is activated and Ypk1p is phosphorylated, which in turn phosphorylates Orm proteins that are inactivated, allowing the increase in SPT activity. The PP2A phosphatase is a candidate to counteract Ypk1p in controlling the Orm phosphorylation state [35]. Alternativel ...
... [33,34]. When SL levels drop, TORC2 is activated and Ypk1p is phosphorylated, which in turn phosphorylates Orm proteins that are inactivated, allowing the increase in SPT activity. The PP2A phosphatase is a candidate to counteract Ypk1p in controlling the Orm phosphorylation state [35]. Alternativel ...
ENS’06 FUSION PHAGE AS A BIOSELECTIVE NANOMATERIAL: EVOLUTION OF THE CONCEPT
... anti-cancer drugs has been proven over the past decade both in pharmaceutical research and clinical setting. Examples of a successful realization of this concept are listed in numerous reviews, for example [34-37]. In particular, it is commonly accepted that selectivity of drug delivery systems can ...
... anti-cancer drugs has been proven over the past decade both in pharmaceutical research and clinical setting. Examples of a successful realization of this concept are listed in numerous reviews, for example [34-37]. In particular, it is commonly accepted that selectivity of drug delivery systems can ...
How proteins produce cellular membrane curvature
... physics and mathematics is to understand the evolutionary, developmental and functional rationale for these shapes, as well as the mechanisms that are used by cells to produce them. Each shape evolved for specific physiological reasons1–3. Cells without internal membranes, such as prokaryotic cells ...
... physics and mathematics is to understand the evolutionary, developmental and functional rationale for these shapes, as well as the mechanisms that are used by cells to produce them. Each shape evolved for specific physiological reasons1–3. Cells without internal membranes, such as prokaryotic cells ...
Cardiolipin-Mediated Mitochondrial Dynamics and
... 3C). Interestingly, two separate regions at the N terminus seemed to contain mitochondrial targeting signals. Signal 1 (amino acids ...
... 3C). Interestingly, two separate regions at the N terminus seemed to contain mitochondrial targeting signals. Signal 1 (amino acids ...
Chapter 6 General discussion
... tTG and the UPR Our data, in combination with recent data from others, strongly support the notion that tTG is associated with the ER in various cell-types throughout the body (Piacentini et al., 2014). The physiological function of tTG expression at the ER is at present poorly characterized, but se ...
... tTG and the UPR Our data, in combination with recent data from others, strongly support the notion that tTG is associated with the ER in various cell-types throughout the body (Piacentini et al., 2014). The physiological function of tTG expression at the ER is at present poorly characterized, but se ...
Biomarkery a mechanismy toxicity
... (effects at relatively high concentrations, depends on Kow) 2) Besides the nonpolar narcosis, more polar compounds may affect also „nonspecifically“ affect membrane proteins (polar narcosis) (effects at lower concentrations than expected from Kow, molecular mechanisms not fully clear) 3) Further, so ...
... (effects at relatively high concentrations, depends on Kow) 2) Besides the nonpolar narcosis, more polar compounds may affect also „nonspecifically“ affect membrane proteins (polar narcosis) (effects at lower concentrations than expected from Kow, molecular mechanisms not fully clear) 3) Further, so ...
Defining the Schistosoma haematobium kinome enables the
... focused on protein kinases13,14, because they are involved in signalling cascades of essential regulatory and developmental processes15–17, particular kinase groups have relatively conserved structures18, and also because drugs targeting these enzymes in humans have shown particular potential for th ...
... focused on protein kinases13,14, because they are involved in signalling cascades of essential regulatory and developmental processes15–17, particular kinase groups have relatively conserved structures18, and also because drugs targeting these enzymes in humans have shown particular potential for th ...
Theory and practice of size exclusion chromatography for
... http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2014.04.011 0731-7085/© 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved. ...
... http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2014.04.011 0731-7085/© 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved. ...
Engineering subunit association of multisubunit proteins
... could be reduced significantly by deleting a loop from G113 through W120 that should have no apparent contact with biotin in a dimeric molecule. The resulting protein, containing both the H127D mutation and the loop deletion, formed a soluble dimeric streptavidin in the presence of biotin. There are ...
... could be reduced significantly by deleting a loop from G113 through W120 that should have no apparent contact with biotin in a dimeric molecule. The resulting protein, containing both the H127D mutation and the loop deletion, formed a soluble dimeric streptavidin in the presence of biotin. There are ...
Processing of the Presequence of the Schizosaccharomyces pombe
... sufficient by itself for sequential two-step processing. To test whether S. pombe mitochondria contain any MPP and MIP activity, we imported S. cerevisiae iron-sulfur protein, which is normally processed by MPP and MIP in S. cerevisiae mitochondria, into S. pombe mitochondria (Fig. 3C). At first gla ...
... sufficient by itself for sequential two-step processing. To test whether S. pombe mitochondria contain any MPP and MIP activity, we imported S. cerevisiae iron-sulfur protein, which is normally processed by MPP and MIP in S. cerevisiae mitochondria, into S. pombe mitochondria (Fig. 3C). At first gla ...
Protein structural class prediction using predicted secondary
... This thesis explores machine learning models based on various feature sets to solve the protein structural class prediction problem which is a significant classification problem in bioinformatics. Knowledge of protein structural classes contributes to an understanding of protein folding patterns, an ...
... This thesis explores machine learning models based on various feature sets to solve the protein structural class prediction problem which is a significant classification problem in bioinformatics. Knowledge of protein structural classes contributes to an understanding of protein folding patterns, an ...
Heriditary Platelet Function Defects
... Composed of cross-linked actin filaments coating the inner surface of the lipid bilayer Regulates the shape of the resting platelet Interacts with transmembrane receptors Platelet activation, intracellular protein phosphorylation cascade and subsequent contraction leads to extrusion of platele ...
... Composed of cross-linked actin filaments coating the inner surface of the lipid bilayer Regulates the shape of the resting platelet Interacts with transmembrane receptors Platelet activation, intracellular protein phosphorylation cascade and subsequent contraction leads to extrusion of platele ...
Cell-Free Synthesis for Analyzing the Membrane
... membrane-translocation processes. Since secretory as well as transmembrane proteins were found to use the same translocation machinery in the ER membrane (7– 9), the lysate system proved suitable to study both types of proteins. Early experiments suggested that the oligomerization of membrane protei ...
... membrane-translocation processes. Since secretory as well as transmembrane proteins were found to use the same translocation machinery in the ER membrane (7– 9), the lysate system proved suitable to study both types of proteins. Early experiments suggested that the oligomerization of membrane protei ...
bio98a_l10
... 2. Covalent modification • group addition - often reversible, ie phosphorylation allosteric* = allo (other); steric (shape, object) ...
... 2. Covalent modification • group addition - often reversible, ie phosphorylation allosteric* = allo (other); steric (shape, object) ...
How to move an amphipathic molecule across a lipid
... 2HYD structure of Dawson and Locher [46] suggests that the coupling helices contained within the long intracellular loops linking TM helices interact with the NBD of the opposite subunit in an arrangement termed ‘domain swapping’ [47]. Interestingly, ABCD proteins have a significant number of conser ...
... 2HYD structure of Dawson and Locher [46] suggests that the coupling helices contained within the long intracellular loops linking TM helices interact with the NBD of the opposite subunit in an arrangement termed ‘domain swapping’ [47]. Interestingly, ABCD proteins have a significant number of conser ...
Proteomics of
... sperm coating proteins. It is interesting that the heparin-binding activity of aggregated forms of proteins from boar seminal plasma corresponds to the activity of isolated monomers with only one exception: heterodimer PSPI/PSP-II spermadhesin, which displays carbohydrate binding activity linked to ...
... sperm coating proteins. It is interesting that the heparin-binding activity of aggregated forms of proteins from boar seminal plasma corresponds to the activity of isolated monomers with only one exception: heterodimer PSPI/PSP-II spermadhesin, which displays carbohydrate binding activity linked to ...
Structural Basis for Bivalent Smac-Mimetics Recognition in the IAP
... zinc-finger motif and are generally composed of five α-helices and a three-stranded β-sheet. Some IAPs, like cIAP1 and cIAP2, contain also a caspaseassociated recruitment domain (CARD) located between the BIR3 domain and the C-terminal RING domain.11 cIAP1 and 2 are crucial regulators of receptor-me ...
... zinc-finger motif and are generally composed of five α-helices and a three-stranded β-sheet. Some IAPs, like cIAP1 and cIAP2, contain also a caspaseassociated recruitment domain (CARD) located between the BIR3 domain and the C-terminal RING domain.11 cIAP1 and 2 are crucial regulators of receptor-me ...
Capacitation-associated Changes in Protein
... ABSTRACT : The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of Ca2+, HCO3- and BSA on the in vitro capacitation-associated protein tyrosine phosphorylation, hyperactivation and acrosome reaction in guinea pig sperm. Caudal epididymal sperm were incubated in four different groups: modified TALP (Tyr ...
... ABSTRACT : The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of Ca2+, HCO3- and BSA on the in vitro capacitation-associated protein tyrosine phosphorylation, hyperactivation and acrosome reaction in guinea pig sperm. Caudal epididymal sperm were incubated in four different groups: modified TALP (Tyr ...
Mercury, Cadmium, and Arsenite Enhance Heat Shock Protein
... Fig. 1. A: Dose-dependent changes in de novo stress protein synthesis induced in chick embryos exposed to metals. Representative SDSPAGE (12.5% minigels) profiles of 35S-methionine-labeled chick embryonic proteins 2 h after exposure to 0 (Con), 3, 10, 30, or 100 nmol/ embryo of arsenite (As), cadmiu ...
... Fig. 1. A: Dose-dependent changes in de novo stress protein synthesis induced in chick embryos exposed to metals. Representative SDSPAGE (12.5% minigels) profiles of 35S-methionine-labeled chick embryonic proteins 2 h after exposure to 0 (Con), 3, 10, 30, or 100 nmol/ embryo of arsenite (As), cadmiu ...
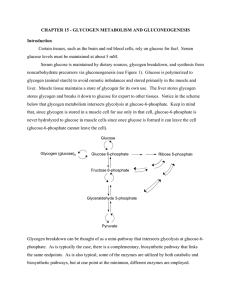
CHAPTER 15 - GLYCOGEN METABOLISM AND
... below in Figure 15-19. This kinase exerts its effect on PP1, which binds to the glycogen particle via its G subunit. Insulin will be secreted from the pancreas when the energy demands of the cell have been met. Until that point, PP1 must remain inactive. Inactivation of PP1 occurs as a result of the ...
... below in Figure 15-19. This kinase exerts its effect on PP1, which binds to the glycogen particle via its G subunit. Insulin will be secreted from the pancreas when the energy demands of the cell have been met. Until that point, PP1 must remain inactive. Inactivation of PP1 occurs as a result of the ...
Free amino acids and proteins dynamics in somatic embryogenesis
... African pearwood (Baillonella toxisperma Pierre) is one of the biggest trees of the Central Africa rainforest. It offers number of uses but the species is classified as vulnerable. This study is conducted in view of its domestication via somatic embryogenesis. Here we analyzed the variations of free ...
... African pearwood (Baillonella toxisperma Pierre) is one of the biggest trees of the Central Africa rainforest. It offers number of uses but the species is classified as vulnerable. This study is conducted in view of its domestication via somatic embryogenesis. Here we analyzed the variations of free ...
Malonate decarboxylase of Pseudomonas putida is composed of
... four subunits K (MdcA), L (MdcD), Q (MdcE), and N (MdcC) lacking MdcH [6]. There are several discrepancies between Pseudomonas enzyme and Klebsiella enzyme in point of the subunit composition and the necessity of the O subunit. The O subunit was susceptible to dissociation from the intact malonate d ...
... four subunits K (MdcA), L (MdcD), Q (MdcE), and N (MdcC) lacking MdcH [6]. There are several discrepancies between Pseudomonas enzyme and Klebsiella enzyme in point of the subunit composition and the necessity of the O subunit. The O subunit was susceptible to dissociation from the intact malonate d ...
Fluorescent Probe Studies of Proteins
... acid (ANS): Catalytic assays of phosphorylase kinase A number of fluorescent probes exhibit fluorescence char- ...
... acid (ANS): Catalytic assays of phosphorylase kinase A number of fluorescent probes exhibit fluorescence char- ...
G protein–coupled receptor

G protein–coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptor, and G protein–linked receptors (GPLR), constitute a large protein family of receptors that sense molecules outside the cell and activate inside signal transduction pathways and, ultimately, cellular responses. Coupling with G proteins, they are called seven-transmembrane receptors because they pass through the cell membrane seven times.G protein–coupled receptors are found only in eukaryotes, including yeast, choanoflagellates, and animals. The ligands that bind and activate these receptors include light-sensitive compounds, odors, pheromones, hormones, and neurotransmitters, and vary in size from small molecules to peptides to large proteins. G protein–coupled receptors are involved in many diseases, and are also the target of approximately 40% of all modern medicinal drugs. Two of the United States's top five selling drugs (Hydrocodone and Lisinopril) act by targeting a G protein–coupled receptor. The 2012 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Brian Kobilka and Robert Lefkowitz for their work that was ""crucial for understanding how G protein–coupled receptors function."". There have been at least seven other Nobel Prizes awarded for some aspect of G protein–mediated signaling.There are two principal signal transduction pathways involving the G protein–coupled receptors: the cAMP signal pathway and the phosphatidylinositol signal pathway. When a ligand binds to the GPCR it causes a conformational change in the GPCR, which allows it to act as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF). The GPCR can then activate an associated G protein by exchanging its bound GDP for a GTP. The G protein's α subunit, together with the bound GTP, can then dissociate from the β and γ subunits to further affect intracellular signaling proteins or target functional proteins directly depending on the α subunit type (Gαs, Gαi/o, Gαq/11, Gα12/13).