The Cell Membrane - Roderick Biology
... • Function: Allow molecules that cannot pass through the phospholipid bilayer to pass only if certain conditions are met ...
... • Function: Allow molecules that cannot pass through the phospholipid bilayer to pass only if certain conditions are met ...
Exam 3B key
... difference (shown at point 'D' in the diagram). List two of these three that are occurring around point 'D' on the figure (2 pts). - the voltage-gated Na+ channel inactivation gate closes - the voltage-gated K+ channel opens - the concentration gradient for Na+ from outside to in is being lost as Na ...
... difference (shown at point 'D' in the diagram). List two of these three that are occurring around point 'D' on the figure (2 pts). - the voltage-gated Na+ channel inactivation gate closes - the voltage-gated K+ channel opens - the concentration gradient for Na+ from outside to in is being lost as Na ...
The Cell Membrane 2015
... membranes, but some are too large or too strongly charged to cross the lipid bilayer. If a substance is able to diffuse across a membrane, the membrane is said to be permeable to it. A membrane is impermeable to substances that cannot pass across it. Most biological membranes are selectively permeab ...
... membranes, but some are too large or too strongly charged to cross the lipid bilayer. If a substance is able to diffuse across a membrane, the membrane is said to be permeable to it. A membrane is impermeable to substances that cannot pass across it. Most biological membranes are selectively permeab ...
Ligand-Gated Ion Channels
... • Functions -Transport of ions and H2O -Regulation of electrical potential across the membrane -Signaling ...
... • Functions -Transport of ions and H2O -Regulation of electrical potential across the membrane -Signaling ...
Ligand Gated Ion ch8
... • Functions -Transport of ions and H2O -Regulation of electrical potential across the membrane -Signaling ...
... • Functions -Transport of ions and H2O -Regulation of electrical potential across the membrane -Signaling ...
Membrane Structure and Function
... peripheral proteins not imbedded in bilayer at all loosely bound to surface ...
... peripheral proteins not imbedded in bilayer at all loosely bound to surface ...
Cell Structures and Functions
... • In plants, made of the polysaccharide cellulose as well as the proteins pectin and lignin. Actually 2 layers, depending on the cell function, the thicknesses of each vary. – Contain openings lined with membrane called Plasmodesmata, that allow things to enter the cell. • In fungi, made of nitrogen ...
... • In plants, made of the polysaccharide cellulose as well as the proteins pectin and lignin. Actually 2 layers, depending on the cell function, the thicknesses of each vary. – Contain openings lined with membrane called Plasmodesmata, that allow things to enter the cell. • In fungi, made of nitrogen ...
Passive Transport
... Diffusion through Ion Channels Sodium Calcium Potassium Chloride All are involved in many important cell functions ...
... Diffusion through Ion Channels Sodium Calcium Potassium Chloride All are involved in many important cell functions ...
Presentation
... The reaction rate is chosen to be the maximum over the range of concentrations used ...
... The reaction rate is chosen to be the maximum over the range of concentrations used ...
Document
... Ion channels and receptors - voltage-gated ion channels are membrane-bound proteins activated by change in transmembrane voltage - they are multi-subunit complexes with circular arrangement of identical or different proteins forming a pore region - it conducts specific species of ions such as Na+, ...
... Ion channels and receptors - voltage-gated ion channels are membrane-bound proteins activated by change in transmembrane voltage - they are multi-subunit complexes with circular arrangement of identical or different proteins forming a pore region - it conducts specific species of ions such as Na+, ...
NMSI - 3 What happens at a synapse
... • The neurotransmitter will then be released from the postsynaptic membrane and degraded. ...
... • The neurotransmitter will then be released from the postsynaptic membrane and degraded. ...
ACTION POTENTIAL Action potential
... electrical stimulation – rheobase, chronaxy graded potential synapse, neurotransmitter, mechanisms of ...
... electrical stimulation – rheobase, chronaxy graded potential synapse, neurotransmitter, mechanisms of ...
AP Biology - gwbiology
... Facilitated diffusion occurs when materials other than water are transported down a concentration gradient, spontaneously. Ion channels are a series of proteins that form channels for the materials/ions to flow through, down concentration gradients, for diffusion to occur. Gated channels are ion cha ...
... Facilitated diffusion occurs when materials other than water are transported down a concentration gradient, spontaneously. Ion channels are a series of proteins that form channels for the materials/ions to flow through, down concentration gradients, for diffusion to occur. Gated channels are ion cha ...
What is “membrane potential”
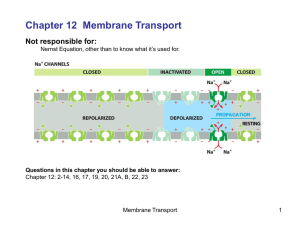
... Not responsible for: Nernst Equation, other than to know what it’s used for. ...
... Not responsible for: Nernst Equation, other than to know what it’s used for. ...
Nervous System
... Form insulating lipid sheath around neuron axon Increase speed of nerve impulse Deterioration of: MS ...
... Form insulating lipid sheath around neuron axon Increase speed of nerve impulse Deterioration of: MS ...
(SREBP 1c) is strongly expressed in MIN6 beta cells
... Protein Kinase B (PKB, also known as Akt) is an important signalling molecule which has been shown to become activated in response to many stimuli, including insulin, growth factors and a variety of survival promoting agents. The signalling pathway by which insulin activates PKB has been well charac ...
... Protein Kinase B (PKB, also known as Akt) is an important signalling molecule which has been shown to become activated in response to many stimuli, including insulin, growth factors and a variety of survival promoting agents. The signalling pathway by which insulin activates PKB has been well charac ...
- Flintbox
... Cystic fibrosis (CF) is the most fatal genetic disease that each year affects one in 2500 infants born. The cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) protein supports the body by regulating anion absorption between epithelial membranes. The CF disease is caused by a mutation of the ...
... Cystic fibrosis (CF) is the most fatal genetic disease that each year affects one in 2500 infants born. The cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) protein supports the body by regulating anion absorption between epithelial membranes. The CF disease is caused by a mutation of the ...
Chapter 3 - Humble ISD
... – Function as enzymes; motor proteins for shape change during cell division and muscle contraction; cell-to-cell connections Six Functions of Membrane Proteins ...
... – Function as enzymes; motor proteins for shape change during cell division and muscle contraction; cell-to-cell connections Six Functions of Membrane Proteins ...
Print
... postulated membrane potential-regulated proton flux, and Hastings (4) illustrated this mechanism explicitly as a cartoon proton channel in 1978. Bioluminescent marine creatures like Noctiluca emit light when stimulated, producing nocturnal luminescence (5). This light is emitted from numerous small ...
... postulated membrane potential-regulated proton flux, and Hastings (4) illustrated this mechanism explicitly as a cartoon proton channel in 1978. Bioluminescent marine creatures like Noctiluca emit light when stimulated, producing nocturnal luminescence (5). This light is emitted from numerous small ...
Mapping the Body.indd
... you open a bottle of something very smelly in a closed room. At first, people standing at the far end of the room can’t smell anything. Then, as time goes on, the smell spreads and fills the room. Soon all areas of the room are equally smelly. Diffusion is the movement of molecules from where th ...
... you open a bottle of something very smelly in a closed room. At first, people standing at the far end of the room can’t smell anything. Then, as time goes on, the smell spreads and fills the room. Soon all areas of the room are equally smelly. Diffusion is the movement of molecules from where th ...
Chem331 Lect 14 Membranes
... Usually have their pores lined with amino acids of the opposite charge of the ion they are transporting Some are gated—open/close upon a signal. ...
... Usually have their pores lined with amino acids of the opposite charge of the ion they are transporting Some are gated—open/close upon a signal. ...
Characterization and Functional Analysis of Rice Outward Rectifier
... promoter regions of the two genes and fused those to GUS reporter gene. The transgenic rice expressing the GUS induced by two potassium channel promoter was stained by histochemical method using X-Gluc. The expression patterns of those genes were quite similar with Arabidopsis. One is expressed in g ...
... promoter regions of the two genes and fused those to GUS reporter gene. The transgenic rice expressing the GUS induced by two potassium channel promoter was stained by histochemical method using X-Gluc. The expression patterns of those genes were quite similar with Arabidopsis. One is expressed in g ...
Mechanosensitive channels

Mechanosensitive channels or mechanosensitive ion channels are membrane proteins capable of responding to mechanical stress over a wide dynamic range of external mechanical stimuli. They are found in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. The channels vary in selectivity for the permeating ions from nonselective between anions and cations in bacteria, to cation selective allowing passage Ca2+, K+ and Na+ in eukaryotes, and highly selective K+ channels in bacteria and eukaryotes.All organisms, and apparently all cell types, sense and respond to mechanical stimuli. MSCs function as mechanotransducers capable of generating both electrical and ion flux signals as a response to external or internal stimuli. Under extreme turgor in bacteria, non selective MSCs such as MSCL and MSCS serve as safety valves to prevent lysis. In specialized cells of the higher organisms, other types of MSCs are probably the basis of the senses of hearing and touch and sense the stress needed for muscular coordination. However, none of these channels have been cloned. MSCs also allow plants to distinguish up from down by sensing the force of gravity. MSCs are not pressure-sensitive, but sensitive to local stress, most likely tension in the surrounding lipid bilayer.