Membranes Reading Guide
... compose it. If the hydrocarbon tails are unsaturated, they have kinks which prevent tight packing, making the membrane more fluid, even at relatively low temperatures. Cholesterol has an effect on fluidity, acting as a buffer against change. It decreases fluidity when the temperature is high, and in ...
... compose it. If the hydrocarbon tails are unsaturated, they have kinks which prevent tight packing, making the membrane more fluid, even at relatively low temperatures. Cholesterol has an effect on fluidity, acting as a buffer against change. It decreases fluidity when the temperature is high, and in ...
Fluorescently-Labeled Toxins
... can bind to the protein at unknown locations and with unknown stochiometry. Even more importantly, it may bind to crucial residues which participate in the toxin-receptor binding interface. Numerous papers have described the structure/ function of toxins, based on mutagenesis experiments, molecular ...
... can bind to the protein at unknown locations and with unknown stochiometry. Even more importantly, it may bind to crucial residues which participate in the toxin-receptor binding interface. Numerous papers have described the structure/ function of toxins, based on mutagenesis experiments, molecular ...
... wind back and forth through the membrane and carriers a. Create a in the membrane like that in a donut b. pass through these channels c. Example: photosynthetic transmembrane protein 3. Attach to the cytoplasm a. link cells to the 4. Enzymes – cause interior 5. Cell surface identity markers – identi ...
Homeostasis and Transport
... 1. What are the two parts of a solution? 2. In cells, what is normally the solvent? 3. When would water need to move across ...
... 1. What are the two parts of a solution? 2. In cells, what is normally the solvent? 3. When would water need to move across ...
Document
... depolarization, repolarization, or hyperpolarization? The ion in or out of the cell? K+; hyperpolarizaion; out e. Is an EPSP produced by depolarization or hyperpolarization of the synaptic cell (indicate which)? Depolarization f. What is the substance that speeds up conduction of a nervous impulses ...
... depolarization, repolarization, or hyperpolarization? The ion in or out of the cell? K+; hyperpolarizaion; out e. Is an EPSP produced by depolarization or hyperpolarization of the synaptic cell (indicate which)? Depolarization f. What is the substance that speeds up conduction of a nervous impulses ...
AP Chap 48 Nervous System AP
... (-50 mv), more Na gates open and an action potential is triggered that results in complete depolarization. • This stimulates neighboring Na gates, further down the neuron, to open. The action potential is an all or none event, always creating the same voltage spike once the threshold is reached. ...
... (-50 mv), more Na gates open and an action potential is triggered that results in complete depolarization. • This stimulates neighboring Na gates, further down the neuron, to open. The action potential is an all or none event, always creating the same voltage spike once the threshold is reached. ...
Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue
... • Cells produce electrical signals called action potentials • Transfer of information from one part of body to another • Electrical properties result from ionic concentration differences across plasma membrane and permeability of membrane ...
... • Cells produce electrical signals called action potentials • Transfer of information from one part of body to another • Electrical properties result from ionic concentration differences across plasma membrane and permeability of membrane ...
Lab 11-Muscles and nerves, pt 1
... their original sides of the membrane. The action potential begins at one spot on the membrane, but spreads to adjacent areas of the membrane, propagating the message along the length of the cell membrane. After passage of the action potential, there is a brief period, the refractory period, during w ...
... their original sides of the membrane. The action potential begins at one spot on the membrane, but spreads to adjacent areas of the membrane, propagating the message along the length of the cell membrane. After passage of the action potential, there is a brief period, the refractory period, during w ...
Lecture 4: Cellular Building Blocks
... • Transmembrane proteins span the bilayer • Peripheral membrane proteins associate with one side ...
... • Transmembrane proteins span the bilayer • Peripheral membrane proteins associate with one side ...
Lanosterol Biosynthesis in the Membrane Environment
... substrates are part of the membrane. These enzymes must actively influence the structure of the lipid bilayer in order to access, steer, and release their reactants. Among the enzymes specialized in lipidic substrates, is the family of monotopic enzymes. Members of this family permanently reside in ...
... substrates are part of the membrane. These enzymes must actively influence the structure of the lipid bilayer in order to access, steer, and release their reactants. Among the enzymes specialized in lipidic substrates, is the family of monotopic enzymes. Members of this family permanently reside in ...
11 Signal Transduction
... • Each TK adds a phosphate from an ATP to a tyrosine on the tail of the other polypeptide • The receptor is fully activated as a result ...
... • Each TK adds a phosphate from an ATP to a tyrosine on the tail of the other polypeptide • The receptor is fully activated as a result ...
chapt05_lecture
... from packing tightly • Most membranes also contain sterols such as cholesterol, which can either increase or decrease membrane fluidity, depending on the temperature ...
... from packing tightly • Most membranes also contain sterols such as cholesterol, which can either increase or decrease membrane fluidity, depending on the temperature ...
Nervous System I
... –In CNS regeneration is unlikely because oligodendrocytes don’t proliferate like Schwann cells to form sheaths for guidance ...
... –In CNS regeneration is unlikely because oligodendrocytes don’t proliferate like Schwann cells to form sheaths for guidance ...
Plasma Membrane: Structure and Function
... phospholipid. Phospholipids are amphipathic. Write down what that means. ...
... phospholipid. Phospholipids are amphipathic. Write down what that means. ...
Molecular Structure and Physiological Function of Chloride
... binding site. The Fast phase is attributed to site 2, which has a lower affinity for ATP. The slow phase is attributed to site one, which has a higher affinity for ATP ...
... binding site. The Fast phase is attributed to site 2, which has a lower affinity for ATP. The slow phase is attributed to site one, which has a higher affinity for ATP ...
Nervous System: General Principles
... • Electrical signal (action potential (AP)) descends axon to synaptic knob (nerve end) • Depolarization opens Ca++ channels to open in presynaptic membrane • Triggers a number of synaptic vesicles to fuse with outer membrane • Dumps neurotransmitter (NT) into synaptic cleft • NT diffuses across clef ...
... • Electrical signal (action potential (AP)) descends axon to synaptic knob (nerve end) • Depolarization opens Ca++ channels to open in presynaptic membrane • Triggers a number of synaptic vesicles to fuse with outer membrane • Dumps neurotransmitter (NT) into synaptic cleft • NT diffuses across clef ...
Resting potential - Neurons in Action
... Answer all underlined questions. You can answer them directly on this worksheet. Plots should be drawn on separate sheets of paper. In the Panel and Graph Manager window, press the button that says “K conductance only”. This will set the conductance to zero for all ions but potassium. In this simula ...
... Answer all underlined questions. You can answer them directly on this worksheet. Plots should be drawn on separate sheets of paper. In the Panel and Graph Manager window, press the button that says “K conductance only”. This will set the conductance to zero for all ions but potassium. In this simula ...
Mechanisms of Ischemic Brain Damage
... •When glutamate activates the AMPA receptor, a channel is opened that allows the passage of Na+, K+ and H+. When Na+ enters down its electrochemical gradient, it depolarizes the membrane. This allows the influx of Ca+2 by way of any voltage-sensitive calcium channels that may be localized to the p ...
... •When glutamate activates the AMPA receptor, a channel is opened that allows the passage of Na+, K+ and H+. When Na+ enters down its electrochemical gradient, it depolarizes the membrane. This allows the influx of Ca+2 by way of any voltage-sensitive calcium channels that may be localized to the p ...
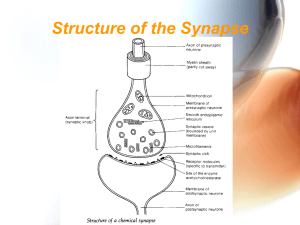
Structure of the Synapse
... threshold is reached then action potential is initated • Inhibitory ion channels - neuroreceptors are Cl- channels. When Cl- channels open, hyperpolarisation occurs, making action potential less likely • Non channel synapses - neuroreceptors are membrane-bound enzymes. When activated, they catalyse ...
... threshold is reached then action potential is initated • Inhibitory ion channels - neuroreceptors are Cl- channels. When Cl- channels open, hyperpolarisation occurs, making action potential less likely • Non channel synapses - neuroreceptors are membrane-bound enzymes. When activated, they catalyse ...
Major components of cells
... • Portions of these integral membrane proteins are inserted into the lipid bilayer. • They are dissociated by reagents of small amphipathic molecules. – The hydrophobic portions of detergents disrupt hydrophobic interactions. – The hydrophilic part makes the detergent-protein complexes soluble in aq ...
... • Portions of these integral membrane proteins are inserted into the lipid bilayer. • They are dissociated by reagents of small amphipathic molecules. – The hydrophobic portions of detergents disrupt hydrophobic interactions. – The hydrophilic part makes the detergent-protein complexes soluble in aq ...
Contribution of calcium-conducting channels to the transport of
... Zinc (Zn) is a vital nutrient participating in a myriad of biological processes. The mechanisms controlling its transport through the plasma membrane are far from being completely understood. Two families of eukaryotic zinc transporters are known to date: the Zip (SLC39) and ZnT (SLC30) proteins. In ...
... Zinc (Zn) is a vital nutrient participating in a myriad of biological processes. The mechanisms controlling its transport through the plasma membrane are far from being completely understood. Two families of eukaryotic zinc transporters are known to date: the Zip (SLC39) and ZnT (SLC30) proteins. In ...
Lecture 7 - Université d`Ottawa
... • Ion channels are highly selective; specific channel proteins allow passage of Na+, K+, Ca2+, and Cl– • Voltage-gated channels open in response to changes in electric potential across the plasma membrane • Voltage-gated Na+ and K+ channels are selective • Na+ (0.95 Å) is smaller than K+ (1.33 Å), a ...
... • Ion channels are highly selective; specific channel proteins allow passage of Na+, K+, Ca2+, and Cl– • Voltage-gated channels open in response to changes in electric potential across the plasma membrane • Voltage-gated Na+ and K+ channels are selective • Na+ (0.95 Å) is smaller than K+ (1.33 Å), a ...
cell-transport-questions-2012
... Diagram and label a section of a cell membrane (include what parts are hydrophobic and hydrophilic) ...
... Diagram and label a section of a cell membrane (include what parts are hydrophobic and hydrophilic) ...
Chapter 5
... from packing tightly • Most membranes also contain sterols such as cholesterol, which can either increase or decrease membrane fluidity, depending on the temperature ...
... from packing tightly • Most membranes also contain sterols such as cholesterol, which can either increase or decrease membrane fluidity, depending on the temperature ...
Mechanosensitive channels

Mechanosensitive channels or mechanosensitive ion channels are membrane proteins capable of responding to mechanical stress over a wide dynamic range of external mechanical stimuli. They are found in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. The channels vary in selectivity for the permeating ions from nonselective between anions and cations in bacteria, to cation selective allowing passage Ca2+, K+ and Na+ in eukaryotes, and highly selective K+ channels in bacteria and eukaryotes.All organisms, and apparently all cell types, sense and respond to mechanical stimuli. MSCs function as mechanotransducers capable of generating both electrical and ion flux signals as a response to external or internal stimuli. Under extreme turgor in bacteria, non selective MSCs such as MSCL and MSCS serve as safety valves to prevent lysis. In specialized cells of the higher organisms, other types of MSCs are probably the basis of the senses of hearing and touch and sense the stress needed for muscular coordination. However, none of these channels have been cloned. MSCs also allow plants to distinguish up from down by sensing the force of gravity. MSCs are not pressure-sensitive, but sensitive to local stress, most likely tension in the surrounding lipid bilayer.