Chapter 5 PowerPoint
... from packing tightly • Most membranes also contain sterols such as cholesterol, which can either increase or decrease membrane fluidity, depending on the temperature ...
... from packing tightly • Most membranes also contain sterols such as cholesterol, which can either increase or decrease membrane fluidity, depending on the temperature ...
02 Cell. Cell metabolism
... may be either integral or peripheral proteins. Intercellular communication and recognition are important because cells are not isolated entities and they must work together to ensure normal body functions. ...
... may be either integral or peripheral proteins. Intercellular communication and recognition are important because cells are not isolated entities and they must work together to ensure normal body functions. ...
figures from Lin et al.
... 18. The main ion channels responsible for changes in the membrane potential of hair cells are a. ligand-gated b. mechanically gated-YES c. voltage-gated d. bill-gated e. not gated 19. How do G proteins contribute to the function of photoreceptors? a. G proteins are stimulated by rhodopsin to activat ...
... 18. The main ion channels responsible for changes in the membrane potential of hair cells are a. ligand-gated b. mechanically gated-YES c. voltage-gated d. bill-gated e. not gated 19. How do G proteins contribute to the function of photoreceptors? a. G proteins are stimulated by rhodopsin to activat ...
Lecture 3 - ISpatula
... Revision of last lecture : - All systems work for general aim which is homeostasis & keep the internal environment almost constant - Internal environment is the interstitial space - Fluids are around 60 % of our body weight - There are two kinds of fluids : 1. Intracellular fluids (ICF) 2. Extrace ...
... Revision of last lecture : - All systems work for general aim which is homeostasis & keep the internal environment almost constant - Internal environment is the interstitial space - Fluids are around 60 % of our body weight - There are two kinds of fluids : 1. Intracellular fluids (ICF) 2. Extrace ...
chapt05_lecture_anim
... from packing tightly • Most membranes also contain sterols such as cholesterol, which can either increase or decrease membrane fluidity, depending on the temperature ...
... from packing tightly • Most membranes also contain sterols such as cholesterol, which can either increase or decrease membrane fluidity, depending on the temperature ...
Neuronal Function
... Neurotransmitter activity is stopped by: diffusion away from the synapse, transport into cells (glial or back into presynaptic neuron), or degradation by specific enzymes. ...
... Neurotransmitter activity is stopped by: diffusion away from the synapse, transport into cells (glial or back into presynaptic neuron), or degradation by specific enzymes. ...
Membrane Transport
... • Inhibit growth of other bacteria (even other strains of E. coli) • Single colicin molecule can kill a host! ...
... • Inhibit growth of other bacteria (even other strains of E. coli) • Single colicin molecule can kill a host! ...
Online Activity: Types of Transport
... 6) In each case, the molecules moved from _____________________ concentration to ____________________ concentration. 7) Dialysis is a technique used to purify blood in cases of kidney failure. During dialysis, what substances would you want to remove from the bloodstream? What substances would you w ...
... 6) In each case, the molecules moved from _____________________ concentration to ____________________ concentration. 7) Dialysis is a technique used to purify blood in cases of kidney failure. During dialysis, what substances would you want to remove from the bloodstream? What substances would you w ...
WLC4 91-92
... o In same cell scenario, if another user is much closer to the base than the desired user, its adjacent channel signal can cause significant interference. o Assume the ratio of distance from the two sources to the base (D1/D2), is equal to 20, then SIR =20-n which for n=4 is equal to -52dB. o If Rx ...
... o In same cell scenario, if another user is much closer to the base than the desired user, its adjacent channel signal can cause significant interference. o Assume the ratio of distance from the two sources to the base (D1/D2), is equal to 20, then SIR =20-n which for n=4 is equal to -52dB. o If Rx ...
Lidocaine: a Common Local Anaesthetic How does it work and how
... of administration to the brain. They are designed not to distribute widely in the body. They are easily broken down (chemically) by the body's defence mechanisms that exist to allow excretion of xenobiotics (foreign molecules). This means that the duration of action is limited and so feeling returns ...
... of administration to the brain. They are designed not to distribute widely in the body. They are easily broken down (chemically) by the body's defence mechanisms that exist to allow excretion of xenobiotics (foreign molecules). This means that the duration of action is limited and so feeling returns ...
Structural and functional differences between two homologous
... Fig. 4. Activity of the recombinant MscMJLR. (A, left) SDS±PAGE of the Ni-NTA puri®ed His6 MscMJLR protein expressed in E.coli. Lane 1, total E.coli proteins before induction with IPTG; lane 2, total E.coli proteins after induction with IPTG; lane 3, puri®ed and concentrated MscMJLR protein. (A, rig ...
... Fig. 4. Activity of the recombinant MscMJLR. (A, left) SDS±PAGE of the Ni-NTA puri®ed His6 MscMJLR protein expressed in E.coli. Lane 1, total E.coli proteins before induction with IPTG; lane 2, total E.coli proteins after induction with IPTG; lane 3, puri®ed and concentrated MscMJLR protein. (A, rig ...
Sound perception
... Adaptation is blocked by ADP, analogous to muscle rigor. Evidence for myosin in hair bundle. ...
... Adaptation is blocked by ADP, analogous to muscle rigor. Evidence for myosin in hair bundle. ...
Action Potential
... Cell body - location of nucleus. Axon - single long protrusion that sends signal away from the cell body. ...
... Cell body - location of nucleus. Axon - single long protrusion that sends signal away from the cell body. ...
Chapt 5 - Workforce Solutions
... “This workforce solution was funded by a grant awarded under the President’s Community-Based Job Training Grants as implemented by the U.S. Department of Labor’s Employment and Training Administration. The solution was created by the grantee and does not necessarily reflect the official position of ...
... “This workforce solution was funded by a grant awarded under the President’s Community-Based Job Training Grants as implemented by the U.S. Department of Labor’s Employment and Training Administration. The solution was created by the grantee and does not necessarily reflect the official position of ...
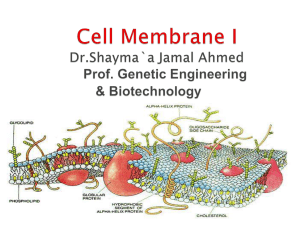
Cell Membrane Structure & Function
... Passive transport is a function of molecular size, lipid solubility, and size of the concentration gradient ...
... Passive transport is a function of molecular size, lipid solubility, and size of the concentration gradient ...
Neural Phys
... Action potentials occur at the nodes and jump from one node to the next because that is only place current can flow through the axonal membrane ...
... Action potentials occur at the nodes and jump from one node to the next because that is only place current can flow through the axonal membrane ...
PowerPoint
... Changes in membrane potential are the basis for electrical signaling Only nerve and muscle cells are excitable (= able to propagate electrical signals) Review “resting membrane potential” (Ch 5) Factors influencing membrane potential ...
... Changes in membrane potential are the basis for electrical signaling Only nerve and muscle cells are excitable (= able to propagate electrical signals) Review “resting membrane potential” (Ch 5) Factors influencing membrane potential ...
Na+/K+ (Sodium/Potassium) Pump
... • A class of ion channel's that open and close in response to change in the electrical potential across the plasma membrane of the cell; voltage-gated Na_ c.'s are important for conducting action potential along nerve cell processes. • 2. Ligand gated ion channel • a transmembrane ion channel whose ...
... • A class of ion channel's that open and close in response to change in the electrical potential across the plasma membrane of the cell; voltage-gated Na_ c.'s are important for conducting action potential along nerve cell processes. • 2. Ligand gated ion channel • a transmembrane ion channel whose ...
Mechanosensitive channels

Mechanosensitive channels or mechanosensitive ion channels are membrane proteins capable of responding to mechanical stress over a wide dynamic range of external mechanical stimuli. They are found in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. The channels vary in selectivity for the permeating ions from nonselective between anions and cations in bacteria, to cation selective allowing passage Ca2+, K+ and Na+ in eukaryotes, and highly selective K+ channels in bacteria and eukaryotes.All organisms, and apparently all cell types, sense and respond to mechanical stimuli. MSCs function as mechanotransducers capable of generating both electrical and ion flux signals as a response to external or internal stimuli. Under extreme turgor in bacteria, non selective MSCs such as MSCL and MSCS serve as safety valves to prevent lysis. In specialized cells of the higher organisms, other types of MSCs are probably the basis of the senses of hearing and touch and sense the stress needed for muscular coordination. However, none of these channels have been cloned. MSCs also allow plants to distinguish up from down by sensing the force of gravity. MSCs are not pressure-sensitive, but sensitive to local stress, most likely tension in the surrounding lipid bilayer.