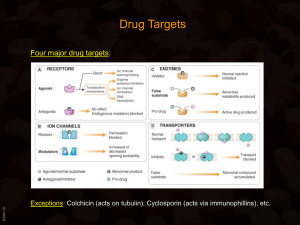
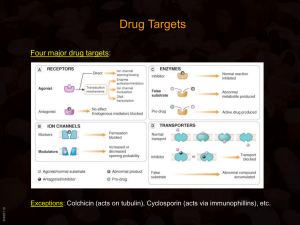
Outline - Membranes Membranes Membrane Phospholipids
... PROTEINS have a key role in transport across membranes I. Passive Transport 1. Always “down” a concentration gradient ...
... PROTEINS have a key role in transport across membranes I. Passive Transport 1. Always “down” a concentration gradient ...
Facilitated diffusion is a process by which molecules are
... Channel proteins are either open at all times or they are "gated," which controls the opening of the channel. The attachment of a particular ion to the channel protein may control the opening or other mechanisms or substances may be involved. In some tissues, sodium and chloride ions pass freely thr ...
... Channel proteins are either open at all times or they are "gated," which controls the opening of the channel. The attachment of a particular ion to the channel protein may control the opening or other mechanisms or substances may be involved. In some tissues, sodium and chloride ions pass freely thr ...
Lecture 4
... • membrane-integrated (unlimited capacity --> transporter systems: Ca-channels, calcium pumps) • non-membranous (limited capacity --> not only buffering, but processing of signal through conformational changes that enable interaction with target proteins: Calmodulin, Troponin C ...) ...
... • membrane-integrated (unlimited capacity --> transporter systems: Ca-channels, calcium pumps) • non-membranous (limited capacity --> not only buffering, but processing of signal through conformational changes that enable interaction with target proteins: Calmodulin, Troponin C ...) ...
No Slide Title
... • membrane-integrated (unlimited capacity --> transporter systems: Ca-channels, calcium pumps) • non-membranous (limited capacity --> not only buffering, but processing of signal through conformational changes that enable interaction with target proteins: Calmodulin, Troponin C ...) ...
... • membrane-integrated (unlimited capacity --> transporter systems: Ca-channels, calcium pumps) • non-membranous (limited capacity --> not only buffering, but processing of signal through conformational changes that enable interaction with target proteins: Calmodulin, Troponin C ...) ...
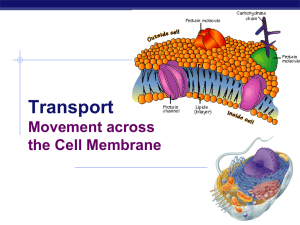
The Cell Membrane
... The polar heads of the phospholipids face outwards to be near polar water molecules (they are hydrophilic). The nonpolar tails of the phospholipids, which do not like to be near water molecules, face within the bilayer (they are hydrophobic). ...
... The polar heads of the phospholipids face outwards to be near polar water molecules (they are hydrophilic). The nonpolar tails of the phospholipids, which do not like to be near water molecules, face within the bilayer (they are hydrophobic). ...
Intro Neurology
... again, K+ channels start to close, but some K+ still sneak through and voltage will peak around -90mV. At this point the cell is hyperpolarized. A hyperpolarized cell is less sensitive to stimuli, because a larger change in voltage is required to hit threshold. d. Sodium-Potassium exchange pumps wil ...
... again, K+ channels start to close, but some K+ still sneak through and voltage will peak around -90mV. At this point the cell is hyperpolarized. A hyperpolarized cell is less sensitive to stimuli, because a larger change in voltage is required to hit threshold. d. Sodium-Potassium exchange pumps wil ...
Mechanosensitive Channels:
... Escherichia Coli (1,2). These two channels were given the names Mechanosensitive channel of small conductance (MscS) and Mechanosensitive channel of large conductance (MscL) because they had conductance of 1nS and 3nS respectively. Both of these channels opened as a result of stress on the strength ...
... Escherichia Coli (1,2). These two channels were given the names Mechanosensitive channel of small conductance (MscS) and Mechanosensitive channel of large conductance (MscL) because they had conductance of 1nS and 3nS respectively. Both of these channels opened as a result of stress on the strength ...
Document
... electric gradient across membrane. Resting squid axons have electric potential ~ -60 mV: inside of cell is negative with respect to outside • Potential arises from ion pumps (Na+/K+ pump) & open membrane channels • Resting membrane has open K+ channels, so flow of K+ (out) makes ...
... electric gradient across membrane. Resting squid axons have electric potential ~ -60 mV: inside of cell is negative with respect to outside • Potential arises from ion pumps (Na+/K+ pump) & open membrane channels • Resting membrane has open K+ channels, so flow of K+ (out) makes ...
Diffusion - U of L Class Index
... •among organisms •among tissues within an organism •between inner and outer membrane leaflet ...
... •among organisms •among tissues within an organism •between inner and outer membrane leaflet ...
Investigating the organization, assembly and physical properties of
... Biological cells and some internal structures are surrounded by membranes comprised of lipid bilayers and membrane proteins. Certain specialized biomembranes are stacked into multi-layers, allowing a high content of protein-lipid bilayers in a small volume. Chloroplasts (the photosynthetic organelle ...
... Biological cells and some internal structures are surrounded by membranes comprised of lipid bilayers and membrane proteins. Certain specialized biomembranes are stacked into multi-layers, allowing a high content of protein-lipid bilayers in a small volume. Chloroplasts (the photosynthetic organelle ...
Action Potential
... Saltatory Conduction: myelinated portions of the axon that lack voltage gated channels can cause loss of current! This problem is solved because some neurons are not myelinated all the way down. There are areas between myelinated parts that are called Nodes of Ranvier- rich in voltage channels whe ...
... Saltatory Conduction: myelinated portions of the axon that lack voltage gated channels can cause loss of current! This problem is solved because some neurons are not myelinated all the way down. There are areas between myelinated parts that are called Nodes of Ranvier- rich in voltage channels whe ...
Human Physiology
... Multi-subunit channels (~300 kDa) Skeletal Na+ Channel: a1 (260 kDa) and b1 (36kDa) Nerve Na+ Channel: a1, b1, b2 (33 kDa) gating/permeation machinery in a1 subunits ...
... Multi-subunit channels (~300 kDa) Skeletal Na+ Channel: a1 (260 kDa) and b1 (36kDa) Nerve Na+ Channel: a1, b1, b2 (33 kDa) gating/permeation machinery in a1 subunits ...
Temperature sensitivity of dopaminergic neurons in the Substantia
... In addition, this cation channel is relatively selective for calcium ions (Xu et al., 2002), which suggests it plays a role not only in the control of neuronal excitability but also of intracellular Ca2+ homeostasis The Substantia Nigra pars compacta (SNc) is a component of the basal ganglia importa ...
... In addition, this cation channel is relatively selective for calcium ions (Xu et al., 2002), which suggests it plays a role not only in the control of neuronal excitability but also of intracellular Ca2+ homeostasis The Substantia Nigra pars compacta (SNc) is a component of the basal ganglia importa ...
Long term memory
... In excitatory and inhibitory synapses, the action of a neurotransmitter tends to promote or inhibit the generation of an action potential in the postsynaptic cell, by binding of the neurotransmitter to an excitatory or inhibitory receptor, respectively. ...
... In excitatory and inhibitory synapses, the action of a neurotransmitter tends to promote or inhibit the generation of an action potential in the postsynaptic cell, by binding of the neurotransmitter to an excitatory or inhibitory receptor, respectively. ...
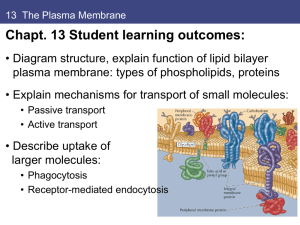
Facilitated diffusion is a process by which molecules are
... The integral proteins involved in facilitated transport are collectively referred to as transport proteins; they function as either channels for the material or carriers. In both cases, they are transmembrane proteins. Channels are specific for the substance that is being transported. Channel protei ...
... The integral proteins involved in facilitated transport are collectively referred to as transport proteins; they function as either channels for the material or carriers. In both cases, they are transmembrane proteins. Channels are specific for the substance that is being transported. Channel protei ...
Facilitated diffusion is a process by which molecules are
... The integral proteins involved in facilitated transport are collectively referred to as transport proteins; they function as either channels for the material or carriers. In both cases, they are transmembrane proteins. Channels are specific for the substance that is being transported. Channel protei ...
... The integral proteins involved in facilitated transport are collectively referred to as transport proteins; they function as either channels for the material or carriers. In both cases, they are transmembrane proteins. Channels are specific for the substance that is being transported. Channel protei ...
Q18 Describe the processes of excitation and
... released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, although the SR is poorly developed and is only a minor source of Ca) in response to nerve stimulation, hormonal stimulation, stretch of the fibre or change in ...
... released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, although the SR is poorly developed and is only a minor source of Ca) in response to nerve stimulation, hormonal stimulation, stretch of the fibre or change in ...
bio12_sm_02_2
... 5. (a) “Membrane fluidity” is the dynamic nature of the membrane, which allows for it to be flexible. That is, membrane lipids undergo free movement on their side of the bilayer. (b) Membranes are composed of a bilayer of phospholipids, which interact with each other by nonpolar fatty acid chains an ...
... 5. (a) “Membrane fluidity” is the dynamic nature of the membrane, which allows for it to be flexible. That is, membrane lipids undergo free movement on their side of the bilayer. (b) Membranes are composed of a bilayer of phospholipids, which interact with each other by nonpolar fatty acid chains an ...
Chapter 4
... 1. All Organisms are made from one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of structure and function in organisms. 3. All cells are produced from other cells. ...
... 1. All Organisms are made from one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of structure and function in organisms. 3. All cells are produced from other cells. ...
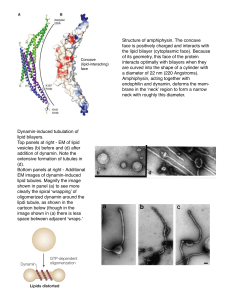
Structure of amphiphysin. The concave face is positively charged
... shown in panel (a) to see more clearly the spiral ʻwrappingʼ of oligomerized dynamin around the lipdi tubule, as shown in the cartoon below (though in the image shown in (a) there is less space between adjacent ʻwraps.ʼ ...
... shown in panel (a) to see more clearly the spiral ʻwrappingʼ of oligomerized dynamin around the lipdi tubule, as shown in the cartoon below (though in the image shown in (a) there is less space between adjacent ʻwraps.ʼ ...
Mechanosensitive channels

Mechanosensitive channels or mechanosensitive ion channels are membrane proteins capable of responding to mechanical stress over a wide dynamic range of external mechanical stimuli. They are found in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. The channels vary in selectivity for the permeating ions from nonselective between anions and cations in bacteria, to cation selective allowing passage Ca2+, K+ and Na+ in eukaryotes, and highly selective K+ channels in bacteria and eukaryotes.All organisms, and apparently all cell types, sense and respond to mechanical stimuli. MSCs function as mechanotransducers capable of generating both electrical and ion flux signals as a response to external or internal stimuli. Under extreme turgor in bacteria, non selective MSCs such as MSCL and MSCS serve as safety valves to prevent lysis. In specialized cells of the higher organisms, other types of MSCs are probably the basis of the senses of hearing and touch and sense the stress needed for muscular coordination. However, none of these channels have been cloned. MSCs also allow plants to distinguish up from down by sensing the force of gravity. MSCs are not pressure-sensitive, but sensitive to local stress, most likely tension in the surrounding lipid bilayer.