Membrane and Action Potentials
... gated channel and K+ voltage gated channel are closed a. Na+ outside cell b. K+ inside cell 2. Depolarization (membrane potential positive): The membrane gets depolarized which causes only the activation gate of the Na+ voltage gated channel to open a. So, Na+ goes INTO the cell b. K+ stays inside c ...
... gated channel and K+ voltage gated channel are closed a. Na+ outside cell b. K+ inside cell 2. Depolarization (membrane potential positive): The membrane gets depolarized which causes only the activation gate of the Na+ voltage gated channel to open a. So, Na+ goes INTO the cell b. K+ stays inside c ...
MEMBRANE PERMEABILITY ! membranes are highly impermeable
... ! when open, forms doughnut-like pore through which solutes flow rapidly by diffusion ! always move from high c to low c (down gradient) ! transport rate # substrate concentration, not saturable ! ΔG !ve, spontaneous, no energy required ! animal cells have many ion channels; highly selective, only l ...
... ! when open, forms doughnut-like pore through which solutes flow rapidly by diffusion ! always move from high c to low c (down gradient) ! transport rate # substrate concentration, not saturable ! ΔG !ve, spontaneous, no energy required ! animal cells have many ion channels; highly selective, only l ...
Plasma Membrane
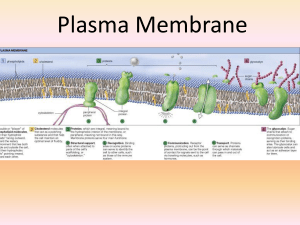
... 4. Cell-to-cell communication – many include carbohydrates attached to protein molecules on outside of cell; they provide an ID tag letting other cells know what type of cell they are 5. Channels for passive transport – integral proteins that have a channel in them to allow substances to ...
... 4. Cell-to-cell communication – many include carbohydrates attached to protein molecules on outside of cell; they provide an ID tag letting other cells know what type of cell they are 5. Channels for passive transport – integral proteins that have a channel in them to allow substances to ...
2_DNA_structure
... Create: ion channels, proton pumps, etc. Extremely important to cell: e.g. a third of the genes in yeast code specifically for them Again: chicken and egg Need DNA to code for membrane proteins but Need membrane proteins to create selective membrane to allow cell to exist. ...
... Create: ion channels, proton pumps, etc. Extremely important to cell: e.g. a third of the genes in yeast code specifically for them Again: chicken and egg Need DNA to code for membrane proteins but Need membrane proteins to create selective membrane to allow cell to exist. ...
Across the Membrane
... Diffusion & the cell membrane The ability of substances to diffuse across a cell membrane depends upon the size and type of the molecules, as well as the chemical nature of the cell membrane. ...
... Diffusion & the cell membrane The ability of substances to diffuse across a cell membrane depends upon the size and type of the molecules, as well as the chemical nature of the cell membrane. ...
Cells: The Living Units: Part A
... • “Rivets” or “spot-welds” that anchor cells together • Where might these be useful in the body? Membrane Junctions: Gap Junctions • Transmembrane proteins form pores that allow small molecules to pass from cell to cell • For spread of ions between cardiac or smooth muscle cells ...
... • “Rivets” or “spot-welds” that anchor cells together • Where might these be useful in the body? Membrane Junctions: Gap Junctions • Transmembrane proteins form pores that allow small molecules to pass from cell to cell • For spread of ions between cardiac or smooth muscle cells ...
SOLVING REAL WORLD PROBLEMS-
... Endocytosis – taking material into cells by means of infoldings or pockets of cell membrane e.g. proteins, polysaccharides Phagocytosis – Pinocytosis – ...
... Endocytosis – taking material into cells by means of infoldings or pockets of cell membrane e.g. proteins, polysaccharides Phagocytosis – Pinocytosis – ...
Transcription Translation Molecular Structure of Ion Channels
... Transcription Translation Molecular Structure of Ion Channels ...
... Transcription Translation Molecular Structure of Ion Channels ...
Nervous System - AP Bio Take 5
... a “wave” action travels along neuron have to re-set channels so neuron can react again ...
... a “wave” action travels along neuron have to re-set channels so neuron can react again ...
Action Potentials
... • After the action potential, it is impossible to stimulate the cell membrane to reach another action potential. • Potassium channels are slow to close so too many K+ ions diffuse out of the neurone. • This makes the cell more negative than -70mV, which is the resting potential. • This is called the ...
... • After the action potential, it is impossible to stimulate the cell membrane to reach another action potential. • Potassium channels are slow to close so too many K+ ions diffuse out of the neurone. • This makes the cell more negative than -70mV, which is the resting potential. • This is called the ...
like a previous Lecture
... 1c. Each millisecond that the cGMP-dependent cation channel in the rod outer segment plasma membrane is open,10,000 ions flow through it. ...
... 1c. Each millisecond that the cGMP-dependent cation channel in the rod outer segment plasma membrane is open,10,000 ions flow through it. ...
Recitation 16 - MIT OpenCourseWare
... This movement of ions does not dissipate the concentration gradient because the number of ions that move to generate a membrane potential is very small compared to the number of ions that need to be pumped to create a concentration gradient. Most cell membranes only contain open K+ channels and thus ...
... This movement of ions does not dissipate the concentration gradient because the number of ions that move to generate a membrane potential is very small compared to the number of ions that need to be pumped to create a concentration gradient. Most cell membranes only contain open K+ channels and thus ...
Cobra® Professional Full Feature CB Radio with 4
... Selectable 4-Color illuminated LCD display allows programming of blue, red, amber or green display Easily programs 10 CB channels into memory with the touch of a button Channel scanning of all 40 CB channels Weather Receiver w/Scan automatically advances to the next clear weather channel when drivin ...
... Selectable 4-Color illuminated LCD display allows programming of blue, red, amber or green display Easily programs 10 CB channels into memory with the touch of a button Channel scanning of all 40 CB channels Weather Receiver w/Scan automatically advances to the next clear weather channel when drivin ...
Slide 1
... The position of kinesin stepping along a microtubule is detected by constant force feedback, where the laser focus follows the bead. Steps of 8 nm can be seen. * Optical tweezers use the attraction of an electric dipole to the high electric field produced at the focus of a laser. Here the electric d ...
... The position of kinesin stepping along a microtubule is detected by constant force feedback, where the laser focus follows the bead. Steps of 8 nm can be seen. * Optical tweezers use the attraction of an electric dipole to the high electric field produced at the focus of a laser. Here the electric d ...
Cell Membrane and Regulation
... The phospholipid bilayer is fluid like a soap bubble. Lipids move around in their side of the bilayer Lipid molecules do NOT move from one layer to the other. (**rare**) ...
... The phospholipid bilayer is fluid like a soap bubble. Lipids move around in their side of the bilayer Lipid molecules do NOT move from one layer to the other. (**rare**) ...
Interactions of KCNE Auxiliary Subunits with K and other Channels
... activity of several ion channels. The different KCNE isoforms are widely and differentially expressed in muscular and neuronal tissues as well as in epithelial cells. Mutations in KCNE genes were shown to lead to disruptions of diverse physiological systems and diseases such as cardiac arrhythmias, ...
... activity of several ion channels. The different KCNE isoforms are widely and differentially expressed in muscular and neuronal tissues as well as in epithelial cells. Mutations in KCNE genes were shown to lead to disruptions of diverse physiological systems and diseases such as cardiac arrhythmias, ...
Ch 48: Nervous System – part 1
... neurons have special ion channels (GATED ION CHANNELS) that allow the cell to change its membrane potential (a.k.a. “excitable” cells) ...
... neurons have special ion channels (GATED ION CHANNELS) that allow the cell to change its membrane potential (a.k.a. “excitable” cells) ...
The Cell Membrane
... • Various Functions – Cytoskeleton: internal support – Protein channels: allow objects to pass – Enzymes: speed up chemical reactions – Markers (carb chains): cell recognition; fight disease ...
... • Various Functions – Cytoskeleton: internal support – Protein channels: allow objects to pass – Enzymes: speed up chemical reactions – Markers (carb chains): cell recognition; fight disease ...
Shape matters in protein mobility within membranes - ICAM
... Lateral Brownian diffusion of proteins in lipid membranes has been predicted by Saffman and Delbrück to depend only on protein size and on the viscosity of the membrane and of the surrounding medium. Using a single-molecule tracking technique on two transmembrane proteins that bend the membrane diff ...
... Lateral Brownian diffusion of proteins in lipid membranes has been predicted by Saffman and Delbrück to depend only on protein size and on the viscosity of the membrane and of the surrounding medium. Using a single-molecule tracking technique on two transmembrane proteins that bend the membrane diff ...
Mechanosensitive channels

Mechanosensitive channels or mechanosensitive ion channels are membrane proteins capable of responding to mechanical stress over a wide dynamic range of external mechanical stimuli. They are found in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. The channels vary in selectivity for the permeating ions from nonselective between anions and cations in bacteria, to cation selective allowing passage Ca2+, K+ and Na+ in eukaryotes, and highly selective K+ channels in bacteria and eukaryotes.All organisms, and apparently all cell types, sense and respond to mechanical stimuli. MSCs function as mechanotransducers capable of generating both electrical and ion flux signals as a response to external or internal stimuli. Under extreme turgor in bacteria, non selective MSCs such as MSCL and MSCS serve as safety valves to prevent lysis. In specialized cells of the higher organisms, other types of MSCs are probably the basis of the senses of hearing and touch and sense the stress needed for muscular coordination. However, none of these channels have been cloned. MSCs also allow plants to distinguish up from down by sensing the force of gravity. MSCs are not pressure-sensitive, but sensitive to local stress, most likely tension in the surrounding lipid bilayer.