Binaural Hearing
... – Stationary: accuracy separating two sound sources (Mills, 1958) • Play sound, move left/right play again ...
... – Stationary: accuracy separating two sound sources (Mills, 1958) • Play sound, move left/right play again ...
Narrator: The sense of hearing results from conversion of
... Narrator: The sense of hearing results from conversion of mechanical energy, in the form of a sound wave, into electrical energy by the structures of the outer, middle, and inner ear. Sound waves from the environment impinge upon the ear canal where they are directed to the tympanic membrane, or ear ...
... Narrator: The sense of hearing results from conversion of mechanical energy, in the form of a sound wave, into electrical energy by the structures of the outer, middle, and inner ear. Sound waves from the environment impinge upon the ear canal where they are directed to the tympanic membrane, or ear ...
TSM54 - The Auditory Pathway
... Interference patterns of sounds reflected by different parts of the pinna o Azimuth – in the horizontal plane Interaural onset time or phase difference for low frequency sounds Interaural sound level difference for high frequency sounds Interaural sound level differences are only detected for ...
... Interference patterns of sounds reflected by different parts of the pinna o Azimuth – in the horizontal plane Interaural onset time or phase difference for low frequency sounds Interaural sound level difference for high frequency sounds Interaural sound level differences are only detected for ...
Section 20.4 - CPO Science
... 2. The middle ear is an air-filled cavity that consists of the eardrum and three tiny, interconnected bones: the maleus, incus, and stapes. 3. The eardrum is a tightly stretched membrane that vibrates as the sound wave reaches it. 4. The stapes vibrates against the cochlea. 5. Fluid in the spiral of ...
... 2. The middle ear is an air-filled cavity that consists of the eardrum and three tiny, interconnected bones: the maleus, incus, and stapes. 3. The eardrum is a tightly stretched membrane that vibrates as the sound wave reaches it. 4. The stapes vibrates against the cochlea. 5. Fluid in the spiral of ...
Slide 1
... The asymmetrical design of the Barn Owl's ears is essential for pinpointing its prey in the dark. -The right ear points slightly upward, and the left ear is naturally pointed slightly downward. ...
... The asymmetrical design of the Barn Owl's ears is essential for pinpointing its prey in the dark. -The right ear points slightly upward, and the left ear is naturally pointed slightly downward. ...
Module 10
... Oval window Cochlea Basilar membrane Hair cells Auditory nerve Semicircular canals (3) – motion sensors Otoliths- orientation & acceleration sensors ...
... Oval window Cochlea Basilar membrane Hair cells Auditory nerve Semicircular canals (3) – motion sensors Otoliths- orientation & acceleration sensors ...
Sound - Educator Pages
... Reflected waves are used to determine distances and to create images. Reflected waves from an ultrasound are put into a computer image called a sonogram. Sonar uses reflected waves to determine distance under water (calculates using the velocity equation). Bats use ultrasound to fly and locate food. ...
... Reflected waves are used to determine distances and to create images. Reflected waves from an ultrasound are put into a computer image called a sonogram. Sonar uses reflected waves to determine distance under water (calculates using the velocity equation). Bats use ultrasound to fly and locate food. ...
Hearing - AP Psychology
... the crest of the wave is the louder the sound is. It is measured in decibels. ...
... the crest of the wave is the louder the sound is. It is measured in decibels. ...
here - Macmillan Learning
... The Auditory System This module explains how we hear and how the physical nature of the sound wave determines the quality of the sound experience. 1. What must the ear detect in order for hearing to take place? ...
... The Auditory System This module explains how we hear and how the physical nature of the sound wave determines the quality of the sound experience. 1. What must the ear detect in order for hearing to take place? ...
Slide ()
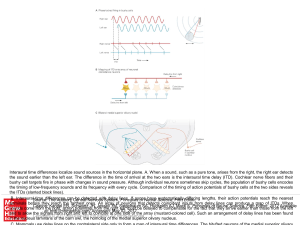
... Interaural time differences localize sound sources in the horizontal plane. A. When a sound, such as a pure tone, arises from the right, the right ear detects the sound earlier than the left ear. The difference in the time of arrival at the two ears is the interaural time delay (ITD). Cochlear nerve ...
... Interaural time differences localize sound sources in the horizontal plane. A. When a sound, such as a pure tone, arises from the right, the right ear detects the sound earlier than the left ear. The difference in the time of arrival at the two ears is the interaural time delay (ITD). Cochlear nerve ...