The solid, outer layer of Earth that consists of the crust and the rigid
... The process of one tectonic plate sinking beneath another into the mantle at a convergent plate boundary ...
... The process of one tectonic plate sinking beneath another into the mantle at a convergent plate boundary ...
INSIDE THE EARTH
... EQ7: What is the theory of plate tectonics? Theory that pieces of Earth’s lithosphere are in constant slow motion driven by convection currents in the mantle. EQ8: How do the 3 types of plate boundaries move and what major events do they cause? ...
... EQ7: What is the theory of plate tectonics? Theory that pieces of Earth’s lithosphere are in constant slow motion driven by convection currents in the mantle. EQ8: How do the 3 types of plate boundaries move and what major events do they cause? ...
The Land Beneath Our Feet (Geology) Vocabulary
... The layer of rock that forms Earth's outer surface; made of basalt and granite; both oceanic and continental ...
... The layer of rock that forms Earth's outer surface; made of basalt and granite; both oceanic and continental ...
The Interior of Earth
... o More dense materials sunk below (iron and nickel – became core) o Silicate rocks were buoyed up (floated) o This process when material is separated called differentiation All planets are differentiated Mars has a lot of iron on its surface and it rusted (that’s why Mars is red) Mars HAS differenti ...
... o More dense materials sunk below (iron and nickel – became core) o Silicate rocks were buoyed up (floated) o This process when material is separated called differentiation All planets are differentiated Mars has a lot of iron on its surface and it rusted (that’s why Mars is red) Mars HAS differenti ...
Notes 11 – Earth`s Interior
... • Geologists use many different forms of indirect evidence to hypothesize what Earth’s interior is composed of. • Ex: Earthquakes, seismic waves, plate movement, drilling • Its tough to see first hand b/c as you go deeper underground both temperature and pressure increase. • Cool link: Deep Drilling ...
... • Geologists use many different forms of indirect evidence to hypothesize what Earth’s interior is composed of. • Ex: Earthquakes, seismic waves, plate movement, drilling • Its tough to see first hand b/c as you go deeper underground both temperature and pressure increase. • Cool link: Deep Drilling ...
Structure of the Earth
... The Outer Core is made of liquid iron and nickel The Outer Core goes from 2890-5150 km below ground The Outer Core’s material spins around the solid inner core, this creates the Earth’s magnetic field ...
... The Outer Core is made of liquid iron and nickel The Outer Core goes from 2890-5150 km below ground The Outer Core’s material spins around the solid inner core, this creates the Earth’s magnetic field ...
3rd Rock From the Sun - Scott County School District 1
... • How have humans used technology to modify the physical environment in order to settle areas in Southwest Asia? – GHW.9.3 ...
... • How have humans used technology to modify the physical environment in order to settle areas in Southwest Asia? – GHW.9.3 ...
Goal-directed Instructional Design Plan
... slow movement of materials within Earth results from heat flowing out from the deep interior and the action of gravity on regions of different density. Evidence for plate tectonics includes the spreading of the seafloor, the fossil record, and patterns and distribution of earthquakes and volcanoes. ...
... slow movement of materials within Earth results from heat flowing out from the deep interior and the action of gravity on regions of different density. Evidence for plate tectonics includes the spreading of the seafloor, the fossil record, and patterns and distribution of earthquakes and volcanoes. ...
Chapters 1 and 2 Review
... GIS-Geographic Information System • A system that uses digital map information to create a databank • Can add or remove different layers to highlight certain information ...
... GIS-Geographic Information System • A system that uses digital map information to create a databank • Can add or remove different layers to highlight certain information ...
Lecture #1
... metal, mostly iron. Generates magnetic field enveloping the earth. – Mantle - hot, pliable layer surrounding the core. Less dense than core. – Crust - cool, lightweight, brittle outermost layer. Floats on top of mantle. ...
... metal, mostly iron. Generates magnetic field enveloping the earth. – Mantle - hot, pliable layer surrounding the core. Less dense than core. – Crust - cool, lightweight, brittle outermost layer. Floats on top of mantle. ...
Earthquakes Intro. Paragraph By: Isabelle Jones BANG! BOOM! Did
... (Figure 3) Not only that, but these puzzle pieces keep slowly moving around, sliding past one another and bumping into each other. We call these puzzle pieces tectonic plates, and the edges of the plates are called the plate boundaries. The plate boundaries are made up of many faults, and most of th ...
... (Figure 3) Not only that, but these puzzle pieces keep slowly moving around, sliding past one another and bumping into each other. We call these puzzle pieces tectonic plates, and the edges of the plates are called the plate boundaries. The plate boundaries are made up of many faults, and most of th ...
A View of Earth - Cloudfront.net
... Geosphere – layer of Earth under both the atmosphere and the oceans Because the geosphere is not uniform, it is divided into three main parts based on differences in composition—the core, the mantle, and the crust Biosphere – all life on Earth; the parts of the solid Earth, hydrosphere, and atmosphe ...
... Geosphere – layer of Earth under both the atmosphere and the oceans Because the geosphere is not uniform, it is divided into three main parts based on differences in composition—the core, the mantle, and the crust Biosphere – all life on Earth; the parts of the solid Earth, hydrosphere, and atmosphe ...
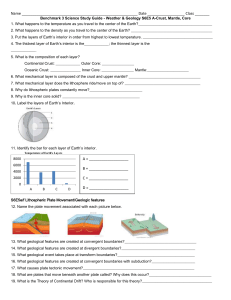
Benchmark 3 Study Guide
... Benchmark 3 Science Study Guide - Weather & Geology S6E5 A-Crust, Mantle, Core 1. What happens to the temperature as you travel to the center of the Earth?_______________________________________ 2. What happens to the density as you travel to the center of the Earth? ________________________________ ...
... Benchmark 3 Science Study Guide - Weather & Geology S6E5 A-Crust, Mantle, Core 1. What happens to the temperature as you travel to the center of the Earth?_______________________________________ 2. What happens to the density as you travel to the center of the Earth? ________________________________ ...
Dangerous Earth: a plate tectonic story
... the Earth is made of a thin, rigid sheet called the lithosphere, which is broken into pieces called plates. The lithosphere is made up of the crust and the upper part of the mantle. Underneath the lithosphere is a thin zone within the mantle called the asthenosphere. Because of radioactive decay dee ...
... the Earth is made of a thin, rigid sheet called the lithosphere, which is broken into pieces called plates. The lithosphere is made up of the crust and the upper part of the mantle. Underneath the lithosphere is a thin zone within the mantle called the asthenosphere. Because of radioactive decay dee ...
Dangerous Earth: a plate tectonic story
... the Earth is made of a thin, rigid sheet called the lithosphere, which is broken into pieces called plates. The lithosphere is made up of the crust and the upper part of the mantle. Underneath the lithosphere is a thin zone within the mantle called the asthenosphere. Because of radioactive decay dee ...
... the Earth is made of a thin, rigid sheet called the lithosphere, which is broken into pieces called plates. The lithosphere is made up of the crust and the upper part of the mantle. Underneath the lithosphere is a thin zone within the mantle called the asthenosphere. Because of radioactive decay dee ...
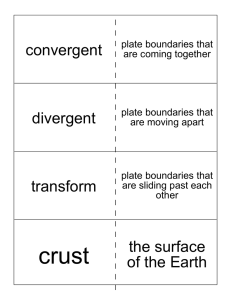
convergent divergent transform the surface of the Earth
... plate boundaries that are sliding past each other ...
... plate boundaries that are sliding past each other ...
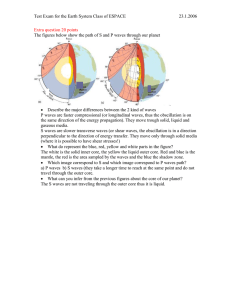
Question 1:
... In order to have magnetic field we need to have fluid and conductive material inside the planet. So since we have magnetic field we have another proof that the core must be fluid (and low viscosity!) ...
... In order to have magnetic field we need to have fluid and conductive material inside the planet. So since we have magnetic field we have another proof that the core must be fluid (and low viscosity!) ...
Chapter 1 Study Guide
... The earth’s crust includes ocean floors and _______________ Dangerous rays from the sun on the earth are screened out by the earth’s _______________. Plates float on liquid rock in the _____________. What is the center of the solar system? Magma comes from what landform? About ____ percent of the ea ...
... The earth’s crust includes ocean floors and _______________ Dangerous rays from the sun on the earth are screened out by the earth’s _______________. Plates float on liquid rock in the _____________. What is the center of the solar system? Magma comes from what landform? About ____ percent of the ea ...
Study Guide- Earth Science
... Review interactive website: http://www.learner.org/interactives/dynamicearth/structure.html ...
... Review interactive website: http://www.learner.org/interactives/dynamicearth/structure.html ...
Colorado State Science Content Standards
... 1. inter-relationships exist between minerals, rocks, and soils 2. humans use renewable and nonrenewable resources (for example: forests and fossil fuels) 3. natural processes shape the Earth’s surface (for example: landslides, weathering, erosion, mountain building, volcanic activity) 4. major geol ...
... 1. inter-relationships exist between minerals, rocks, and soils 2. humans use renewable and nonrenewable resources (for example: forests and fossil fuels) 3. natural processes shape the Earth’s surface (for example: landslides, weathering, erosion, mountain building, volcanic activity) 4. major geol ...
Chapter 1 Introduction
... Winter (2001) An Introduction to Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology. Prentice Hall. ...
... Winter (2001) An Introduction to Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology. Prentice Hall. ...
Geophysics

Geophysics /dʒiːoʊfɪzɪks/ is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and physical properties of the Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. The term geophysics sometimes refers only to the geological applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational and magnetic fields; its internal structure and composition; its dynamics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation. However, modern geophysics organizations use a broader definition that includes the water cycle including snow and ice; fluid dynamics of the oceans and the atmosphere; electricity and magnetism in the ionosphere and magnetosphere and solar-terrestrial relations; and analogous problems associated with the Moon and other planets.Although geophysics was only recognized as a separate discipline in the 19th century, its origins go back to ancient times. The first magnetic compasses were made from lodestones, while more modern magnetic compasses played an important role in the history of navigation. The first seismic instrument was built in 132 BC. Isaac Newton applied his theory of mechanics to the tides and the precession of the equinox; and instruments were developed to measure the Earth's shape, density and gravity field, as well as the components of the water cycle. In the 20th century, geophysical methods were developed for remote exploration of the solid Earth and the ocean, and geophysics played an essential role in the development of the theory of plate tectonics.Geophysics is applied to societal needs, such as mineral resources, mitigation of natural hazards and environmental protection. Geophysical survey data are used to analyze potential petroleum reservoirs and mineral deposits, locate groundwater, find archaeological relics, determine the thickness of glaciers and soils, and assess sites for environmental remediation.