Energy Resources
... friction in a localized area to cause the rock to melt. This molten rock will burn up to the surface and create a volcano over time. Most volcanoes are located in the Pacific Ring of Fire because of subduction zone around the Pacific Ocean. • Not all volcanoes are created this way. Some are created ...
... friction in a localized area to cause the rock to melt. This molten rock will burn up to the surface and create a volcano over time. Most volcanoes are located in the Pacific Ring of Fire because of subduction zone around the Pacific Ocean. • Not all volcanoes are created this way. Some are created ...
Chapter 16
... • How are buried mineral deposits found? How are they then removed? • What are some environmental impacts of using nonrenewable mineral resources? • What is a typical life cycle of a nonrenewable metal resource? • Do we have enough nonrenewable mineral resources? ...
... • How are buried mineral deposits found? How are they then removed? • What are some environmental impacts of using nonrenewable mineral resources? • What is a typical life cycle of a nonrenewable metal resource? • Do we have enough nonrenewable mineral resources? ...
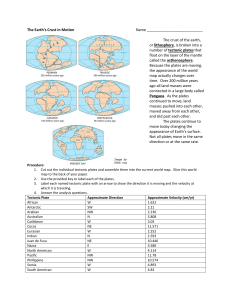
The Earth`s Crust in Motion Name The crust of the earth, or
... The crust of the earth, or lithosphere, is broken into a number of tectonic plates that float on the layer of the mantle called the asthenosphere. Because the plates are moving, the appearance of the world map actually changes over time. Over 200 million years ago all land masses were connected in a ...
... The crust of the earth, or lithosphere, is broken into a number of tectonic plates that float on the layer of the mantle called the asthenosphere. Because the plates are moving, the appearance of the world map actually changes over time. Over 200 million years ago all land masses were connected in a ...
Student Pre/Post Test - College of Arts and Sciences
... a. A flat surface is gradually pushed up into higher and higher mountains until Earth is covered with mountains. b. High mountains gradually wear down until most of Earth is at sea level. c. High mountains and flat plains stay side by side for billions of years with little change. d. High mountains ...
... a. A flat surface is gradually pushed up into higher and higher mountains until Earth is covered with mountains. b. High mountains gradually wear down until most of Earth is at sea level. c. High mountains and flat plains stay side by side for billions of years with little change. d. High mountains ...
Continents change position over time.
... rock rises, cools, and sinks, then is heated and rises again. If this sinking and rising motion continues, it is called a convection current —a motion that transfers heat energy in a material. Chapter 18: Plate Tectonics 621 ...
... rock rises, cools, and sinks, then is heated and rises again. If this sinking and rising motion continues, it is called a convection current —a motion that transfers heat energy in a material. Chapter 18: Plate Tectonics 621 ...
Continental - itslearning
... The presence of identical fossils on widely separated continents belonging to organisms that could not have crossed the ocean or lived in the kind of climate currently found in those locations. ...
... The presence of identical fossils on widely separated continents belonging to organisms that could not have crossed the ocean or lived in the kind of climate currently found in those locations. ...
Earth and Atmoshere Revision
... Scientist once thought that the cause of many of the features was: • A expansion of the crust as it cooled down. • B expansion of the crust as it heated up. • C shrinkage of the crust as it cooled down. • D shrinkage of the crust as it heated up. ...
... Scientist once thought that the cause of many of the features was: • A expansion of the crust as it cooled down. • B expansion of the crust as it heated up. • C shrinkage of the crust as it cooled down. • D shrinkage of the crust as it heated up. ...
print
... (Sun & most planets; Uranus exception) Planets contain 98% of angular momentum Spacing and Composition Spacing increases with distance (roughly logarithmic) Composition varies with distance inner 4: rocky, small, thin atmospheres outer 4: gaseous, large, mostly atmosphere Sun contains 99.9% of mass ...
... (Sun & most planets; Uranus exception) Planets contain 98% of angular momentum Spacing and Composition Spacing increases with distance (roughly logarithmic) Composition varies with distance inner 4: rocky, small, thin atmospheres outer 4: gaseous, large, mostly atmosphere Sun contains 99.9% of mass ...
Objective Analysis –Plate Tectonics test
... 5. Once you have completed this form and know what you need to do to do better on the test retake, sign up to come in and take the re-take with Mrs. Haveman. It must be completed by Tuesday (1/6) or your test grade remains the same. ...
... 5. Once you have completed this form and know what you need to do to do better on the test retake, sign up to come in and take the re-take with Mrs. Haveman. It must be completed by Tuesday (1/6) or your test grade remains the same. ...
Plate tectonics
... • “In plate tectonics, a divergent boundary or divergent plate boundary (also known as a constructive boundary or an extensional boundary) is a linear feature that exists between two tectonic plates that are moving away from each other.” ...
... • “In plate tectonics, a divergent boundary or divergent plate boundary (also known as a constructive boundary or an extensional boundary) is a linear feature that exists between two tectonic plates that are moving away from each other.” ...
study guide questions 3rd nine weeks 2017
... Describe 3 ways in which fossils form. Which one is most common? Describe what limestone is and how does it form Explain what the fall line is and why is it important In relative dating explain how we determine the oldest fossils or rocks List the 5 geologic provinces of VA and give 3 facts about ea ...
... Describe 3 ways in which fossils form. Which one is most common? Describe what limestone is and how does it form Explain what the fall line is and why is it important In relative dating explain how we determine the oldest fossils or rocks List the 5 geologic provinces of VA and give 3 facts about ea ...
Continental Drift
... – Earth has a magnetic field, and new rocks align themselves to this field as they cool and crystallize, serving as a “compass needle” record of the magnetic field at that time – Every few million years or so, a magnetic reversal occurs, where Earth’s magnetic field “flip-flops” (so that our compass ...
... – Earth has a magnetic field, and new rocks align themselves to this field as they cool and crystallize, serving as a “compass needle” record of the magnetic field at that time – Every few million years or so, a magnetic reversal occurs, where Earth’s magnetic field “flip-flops” (so that our compass ...
Earthquakes and Volcanoes
... Types of Seismic Waves During an earthquake, particles in the ground can move back and forth or up and down. Particles can also move in an elliptical motion parallel to the direction the seismic wave travels. Scientists use wave motion, wave speed, and the type of material the wave travels through t ...
... Types of Seismic Waves During an earthquake, particles in the ground can move back and forth or up and down. Particles can also move in an elliptical motion parallel to the direction the seismic wave travels. Scientists use wave motion, wave speed, and the type of material the wave travels through t ...
Course: Geology 12 Big Ideas: Elaborations: Earth Materials
... Questioning and predicting: Sample opportunities to support student inquiry: collect and display rocks and minerals and have students predict what they are and what their environment of formation was classify fossils using student created criteria collect data to establish where most earthquak ...
... Questioning and predicting: Sample opportunities to support student inquiry: collect and display rocks and minerals and have students predict what they are and what their environment of formation was classify fossils using student created criteria collect data to establish where most earthquak ...
Science 3360 - Kennesaw State University | College of Science and
... • The Lithosphere (comprising the first 70 - 125 km of the solid earth) consists of the oceanic and continental crustal material plus the uppermost portion of the mantle. It is rigid and acts as a single unit. • the Asthenosphere ( ~ 100’s km in depth) is characterized by low Pwave velocities. Becau ...
... • The Lithosphere (comprising the first 70 - 125 km of the solid earth) consists of the oceanic and continental crustal material plus the uppermost portion of the mantle. It is rigid and acts as a single unit. • the Asthenosphere ( ~ 100’s km in depth) is characterized by low Pwave velocities. Becau ...
WHAT ARE THE CAUSES OF TECTONIC HAZARDS? 1 Structure of
... WHAT ARE THE CAUSES OF TECTONIC HAZARDS? 1 Structure of the Earth Find/draw a labelled cross section through the earth showing the different layers (asthenosphere, etc) Find/draw a diagram and write a paragraph to show how convection currents work. 2 Theory of plate tectonics Write about Alfre ...
... WHAT ARE THE CAUSES OF TECTONIC HAZARDS? 1 Structure of the Earth Find/draw a labelled cross section through the earth showing the different layers (asthenosphere, etc) Find/draw a diagram and write a paragraph to show how convection currents work. 2 Theory of plate tectonics Write about Alfre ...
File
... • At one time, our solar system could have had as many as 20 planets • When the earth was still molten, it got hit by one of them • The impacting body Took some of earth’s Mantle with it (about 1/3) forming the moon ...
... • At one time, our solar system could have had as many as 20 planets • When the earth was still molten, it got hit by one of them • The impacting body Took some of earth’s Mantle with it (about 1/3) forming the moon ...
Lecture 12
... Observed heat flow through the entire earth surface if 43TW, ~ 50% of heat comes from other sources such as contraction and friction processes. Two kind of heat transport, conduction and convection. Conduction takes place in metals such as Fe-Ni core, convection in molten rock on earth mantle. ...
... Observed heat flow through the entire earth surface if 43TW, ~ 50% of heat comes from other sources such as contraction and friction processes. Two kind of heat transport, conduction and convection. Conduction takes place in metals such as Fe-Ni core, convection in molten rock on earth mantle. ...
Earth Science Project: Three Dimensional Model of
... California Standards: Earth Science 6.1.a: Students know evidence of plate tectonics is derived from the fit of the continents; the location of earthquakes, volcanoes, and midocean ridges; and the distribution of fossils, rock types, and ancient climatic zones. 6.1.b: Students know Earth is composed ...
... California Standards: Earth Science 6.1.a: Students know evidence of plate tectonics is derived from the fit of the continents; the location of earthquakes, volcanoes, and midocean ridges; and the distribution of fossils, rock types, and ancient climatic zones. 6.1.b: Students know Earth is composed ...
from continental drift to plate tectonics
... were somehow compensated by a deficit of mass beneath them—an idea that came to be known as isostasy, or "equal standing." In the early 20th century, isostasy was confirmed by detailed geodetic and gravity measurements across the United States. John Hayford (1868-1925) and William Bowie (1872-1940), ...
... were somehow compensated by a deficit of mass beneath them—an idea that came to be known as isostasy, or "equal standing." In the early 20th century, isostasy was confirmed by detailed geodetic and gravity measurements across the United States. John Hayford (1868-1925) and William Bowie (1872-1940), ...
EarthScience_Topic 9-Properties of Earths Interior
... • Located on Earth’s surface directly above the focus ...
... • Located on Earth’s surface directly above the focus ...
Day 2 Plate Tectonics 11-12
... • The subducting plate is bent downward to form a very deep depression in the ocean floor called a trench. • The deepest parts of the oceans are found along ...
... • The subducting plate is bent downward to form a very deep depression in the ocean floor called a trench. • The deepest parts of the oceans are found along ...
Plate Tectonics PowerPoint
... causing it to sink into the mantle forming a subduction zone. • The subducting plate is bent downward to form a very deep depression in the ocean floor called a deep-sea trench. • The deepest parts of the ocean are found along trenches. – The Mariana Trench is 11 km deep! ...
... causing it to sink into the mantle forming a subduction zone. • The subducting plate is bent downward to form a very deep depression in the ocean floor called a deep-sea trench. • The deepest parts of the ocean are found along trenches. – The Mariana Trench is 11 km deep! ...
Geophysics

Geophysics /dʒiːoʊfɪzɪks/ is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and physical properties of the Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. The term geophysics sometimes refers only to the geological applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational and magnetic fields; its internal structure and composition; its dynamics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation. However, modern geophysics organizations use a broader definition that includes the water cycle including snow and ice; fluid dynamics of the oceans and the atmosphere; electricity and magnetism in the ionosphere and magnetosphere and solar-terrestrial relations; and analogous problems associated with the Moon and other planets.Although geophysics was only recognized as a separate discipline in the 19th century, its origins go back to ancient times. The first magnetic compasses were made from lodestones, while more modern magnetic compasses played an important role in the history of navigation. The first seismic instrument was built in 132 BC. Isaac Newton applied his theory of mechanics to the tides and the precession of the equinox; and instruments were developed to measure the Earth's shape, density and gravity field, as well as the components of the water cycle. In the 20th century, geophysical methods were developed for remote exploration of the solid Earth and the ocean, and geophysics played an essential role in the development of the theory of plate tectonics.Geophysics is applied to societal needs, such as mineral resources, mitigation of natural hazards and environmental protection. Geophysical survey data are used to analyze potential petroleum reservoirs and mineral deposits, locate groundwater, find archaeological relics, determine the thickness of glaciers and soils, and assess sites for environmental remediation.