ysics P2 Graded Task Bungee Jumping with equations
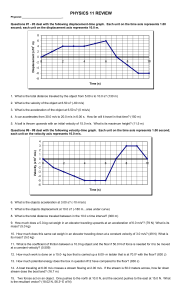
... the box above. Calculate the momentum of the jumper when they are at 20m/s. Calculate the kinetic energy of the jumper at this velocity. The bungee cord stretches as he falls. Name the energy stored in the cord. ...
... the box above. Calculate the momentum of the jumper when they are at 20m/s. Calculate the kinetic energy of the jumper at this velocity. The bungee cord stretches as he falls. Name the energy stored in the cord. ...
Momentum
... at the point of impact with zero momentum. If the green truck was moving at 10 m/s, how fast was the ...
... at the point of impact with zero momentum. If the green truck was moving at 10 m/s, how fast was the ...
Physics: The very basics
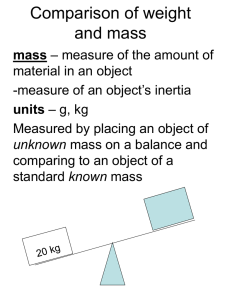
... • For non moving objects only • Can be seen as threshold of force needed to accelerate a mass ...
... • For non moving objects only • Can be seen as threshold of force needed to accelerate a mass ...
8.012 Physics I: Classical Mechanics
... (b) [5 pts] Determine the minimum amount of mechanical energy that must be added to the planet to cause it to escape from the star (i.e., r→∞). By what factor must the speed of the planet be increased to cause it to escape? (c) [5 pts] Now assume that the planet in subject to a viscous force of the ...
... (b) [5 pts] Determine the minimum amount of mechanical energy that must be added to the planet to cause it to escape from the star (i.e., r→∞). By what factor must the speed of the planet be increased to cause it to escape? (c) [5 pts] Now assume that the planet in subject to a viscous force of the ...
Ch - Hays High Indians
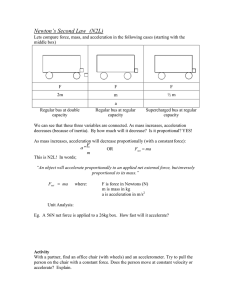
... 7. Calculate the acceleration of a 20-kg dodo bird just before takeoff when the total thrust of its wings is 50N. 8. Calculate the acceleration of a 5-kg box when you push with a 12-N horizontal force along a horizontal floor having a frictional force of 2-N. 9. Explain why the accelerations caused ...
... 7. Calculate the acceleration of a 20-kg dodo bird just before takeoff when the total thrust of its wings is 50N. 8. Calculate the acceleration of a 5-kg box when you push with a 12-N horizontal force along a horizontal floor having a frictional force of 2-N. 9. Explain why the accelerations caused ...
7-2 Conservation of Momentum During a collision, measurements
... This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permit ...
... This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permit ...
Q = Ne
... b. fall faster through the air because they have similar charges c. induce an opposite charge on the leaves so they are attracted to them d. repel each other and spread out, thus the effect of the wind is minimized Electrostatics Two particles, I and II, of equal mass have opposite charges. The nega ...
... b. fall faster through the air because they have similar charges c. induce an opposite charge on the leaves so they are attracted to them d. repel each other and spread out, thus the effect of the wind is minimized Electrostatics Two particles, I and II, of equal mass have opposite charges. The nega ...