PHYSICS 231 Review problems for midterm 1 1 PHY 231
... Initially, the velocity is pointing up, but is decreasing in magnitude (speed is decreasing) since the gravitational force is slowing it down. This goes on until it reaches the highest point, where the velocity/speed equals zero. The ball than moves down: the velocity becomes negative, but the spee ...
... Initially, the velocity is pointing up, but is decreasing in magnitude (speed is decreasing) since the gravitational force is slowing it down. This goes on until it reaches the highest point, where the velocity/speed equals zero. The ball than moves down: the velocity becomes negative, but the spee ...
PHYS 1443 – Section 501 Lecture #1
... energy in time by a retarding force such as friction or air resistance. How do you think the motion would look? ...
... energy in time by a retarding force such as friction or air resistance. How do you think the motion would look? ...
Mechanical Vibrations
... Damped Free Vibrations • All vibrations are damped to some degree by forces due to dry friction, fluid friction, or internal ...
... Damped Free Vibrations • All vibrations are damped to some degree by forces due to dry friction, fluid friction, or internal ...
ForcedVibrations-freestudy-co-uk.pdf
... In order for the damping ratio δ to be less than zero, that is, to be negative, we would have to have the opposite of damping, something that puts energy into the system instead of taking it out. As the energy is added to the system the amplitude grows and grows. The energy is added by an outside so ...
... In order for the damping ratio δ to be less than zero, that is, to be negative, we would have to have the opposite of damping, something that puts energy into the system instead of taking it out. As the energy is added to the system the amplitude grows and grows. The energy is added by an outside so ...
CIRCULAR MOTION, ORBITS, AND GRAVITY
... (b) The riders in the Gravitron carnival ride (Section 6.4) have a centripetal acceleration caused by the normal force of the walls on them. Another example would be the biological sample in a centrifuge. The test tube walls exert a normal force on the sample toward the center of the circle. Assess: ...
... (b) The riders in the Gravitron carnival ride (Section 6.4) have a centripetal acceleration caused by the normal force of the walls on them. Another example would be the biological sample in a centrifuge. The test tube walls exert a normal force on the sample toward the center of the circle. Assess: ...
No Slide Title
... Two persons try to go through a rotating door at the same time, one on the l.h.s. of the rotator and one the r.h.s. of the rotator. If the forces are applied as shown in the drawing, what will happen? ...
... Two persons try to go through a rotating door at the same time, one on the l.h.s. of the rotator and one the r.h.s. of the rotator. If the forces are applied as shown in the drawing, what will happen? ...
Document
... After the torque is applied to the rigid bar the angular velocity increases to 5.27 r/s. If the rigid bar has a moment of inertia of 0.8 kg∙m2 what was the final angular momentum? If the torque was applied for t = 0.9 s, what was the angular impulse? ...
... After the torque is applied to the rigid bar the angular velocity increases to 5.27 r/s. If the rigid bar has a moment of inertia of 0.8 kg∙m2 what was the final angular momentum? If the torque was applied for t = 0.9 s, what was the angular impulse? ...
MECHANICS Lecture notes for Phys 111 Abstract
... beats per min. How many gallons of blood does the heart pump in 1 year? ( 1 gallon= 3800 cm3 ). ...
... beats per min. How many gallons of blood does the heart pump in 1 year? ( 1 gallon= 3800 cm3 ). ...
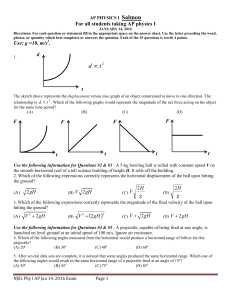
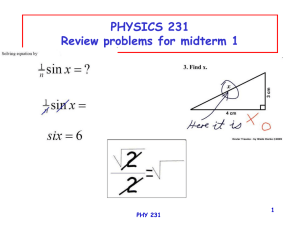
Find
... objects. Rank each situation according to mass. That is, order the situation from largest to smallest mass, using Newton’s Second Law. ...
... objects. Rank each situation according to mass. That is, order the situation from largest to smallest mass, using Newton’s Second Law. ...